1. Write a Java application in a project called Alphabet. It should print the uppercase alphabet, three letters per line. The first, third, fifth, etc. lines should be indented one space. The final line contains only Y and Z. The output should look exactly as follows. ABC DEF GHI JKL MNO PQR STU VWX YZ Place a header comment in each program that includes your name, the assignment the number and a description of what the program does. 2. Write a Java application in a project called Falling. It inputs a distance in meters from the user and computes the amount of time for the object falling from that distance to hit the ground and the velocity of the object just before impact. Air resistance is discounted (assumed to fall in a vacuum). To compute the time, use the formula: t = Square Root (2d / g) where d is the distance in meters and g is the acceleration due to gravity on earth (use 9.807 meters/sec2 ). The time is measured in seconds. To compute the velocity, use the formula: v = Square Root (2dg) The velocity is measured in meters per second. A sample run is shown on the next page. Computed values should be printed with two digits after the decimal. The spacing and text should follow the example exactly. Place a header comment in this program that includes your name, the assignment number and a description of what the program does. Comment each variable indicating what it is used for in the program.
1. Write a Java application in a project called Alphabet. It should print the uppercase
alphabet, three letters per line. The first, third, fifth, etc. lines should be indented one
space. The final line contains only Y and Z. The output should look exactly as follows.
ABC
DEF
GHI
JKL
MNO
PQR
STU
VWX
YZ
Place a header comment in each program that includes your name, the assignment
the number and a description of what the program does.
2. Write a Java application in a project called Falling. It inputs a distance in meters from
the user and computes the amount of time for the object falling from that distance to hit
the ground and the velocity of the object just before impact. Air resistance is discounted
(assumed to fall in a vacuum).
To compute the time, use the formula:
t = Square Root (2d / g)
where d is the distance in meters and g is the acceleration due to gravity on earth (use
9.807 meters/sec2
). The time is measured in seconds.
To compute the velocity, use the formula:
v = Square Root (2dg)
The velocity is measured in meters per second.
A sample run is shown on the next page. Computed values should be printed with two
digits after the decimal. The spacing and text should follow the example exactly.
Place a header comment in this program that includes your name, the assignment number
and a description of what the program does. Comment each variable indicating what it is
used for in the program.
Problem 2 Sample Run (input shown in bold):
Enter the distance: 100
Distance: 100.0
Time: 4.52 seconds
Velocity: 44.29 meters/second
/*******************************************************************************/
///beginning
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
char ch;
int i=1,j=1;
///First blank space
System.out.print(" ");
for( ch = 'A' ; ch <= 'Z' ; ch++ ){
////This will print each character
System.out.print(ch);
if(i==3){
///condition to switch to new line
System.out.println(" ");
if(j%2==0){
//condition to take space in new line
System.out.print(" ");
}
i=0;
j=j+1;
}
i=i+1;
}
}
}
///////////end
Output: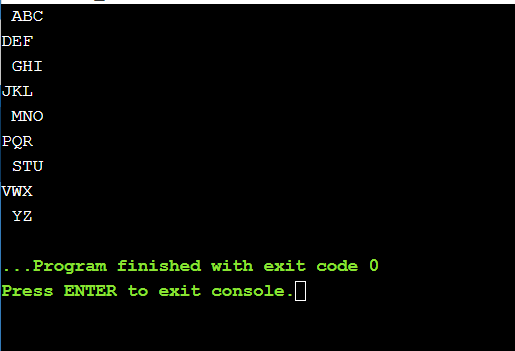
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









