1. Let X and Y have joint probability density function (pdf) given by [1,0
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:Sheldon Ross
Chapter1: Combinatorial Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P: a. How many different 7-place license plates are possible if the first 2 places are for letters and...
Related questions
Question
![1. Let \( X \) and \( Y \) have joint probability density function (pdf) given by
\[
f(x_1, x_2) =
\begin{cases}
1, & 0 < x_1, x_2 < 1 \\
0, & \text{elsewhere}
\end{cases}
\]
Find the joint probability density function of \( Y_1 = X_1 + X_2 \) and \( Y_2 = X_1 - X_2 \).
Also find the marginal density functions of \( Y_1 \) and \( Y_2 \).](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F7cfacfab-59af-4282-af0d-4cc91507460a%2F97a4b9f4-16c0-408b-9fa4-5f4aece952cc%2Fk471h4b_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:1. Let \( X \) and \( Y \) have joint probability density function (pdf) given by
\[
f(x_1, x_2) =
\begin{cases}
1, & 0 < x_1, x_2 < 1 \\
0, & \text{elsewhere}
\end{cases}
\]
Find the joint probability density function of \( Y_1 = X_1 + X_2 \) and \( Y_2 = X_1 - X_2 \).
Also find the marginal density functions of \( Y_1 \) and \( Y_2 \).
Expert Solution
Step 1:-
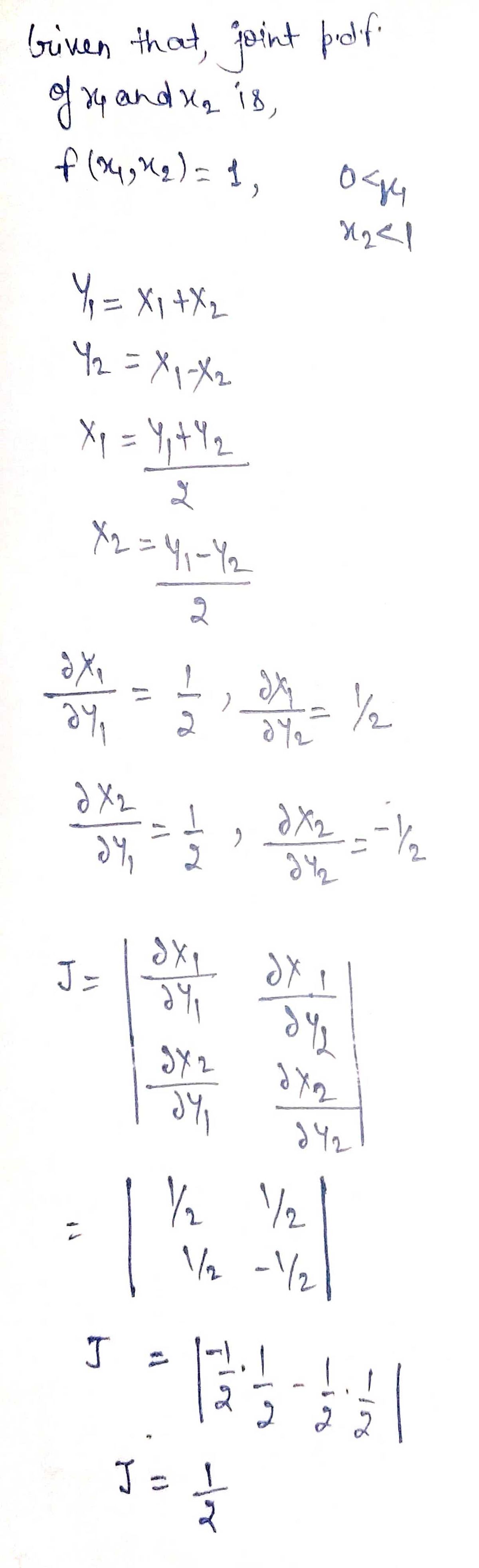
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON


A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON
