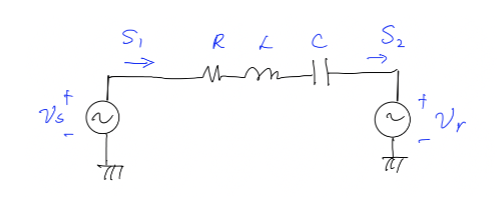
1. Circuit analysis using phasor/impedance, complex power calculation: An RLC circuit is shown below. The reactance of the capacitor is 40 Ohm. The reactance of the inductor is 80 Ohm, and the resistor is 8 Ohm. The sending end voltage is v₁(t) = 345 cos(wt + 7) kV, where w = 2 · 60 rad/s. The receiving end voltage is v₂(t) = 345 cos(wt) kV. Ask: • What is the total impedance of the RLC circuit at 60 Hz? What are the sending end and receiving end voltage phasors in kV? • Please find the current through the line in phasor and in time-domain and in unit kA. • What is the complex power S₁? What is the complex power S₂? Please use a unit of MVA. • What is the power loss due to the resistor? What is the reactive power consumption by the inductor? How much reactive power is generated by the capacitor? . For the same sending end voltage and receiving end voltage, if the series capacitor is not installed, what is the real power delivered to the receiving end? Please compare this number with the one from the series compensated case, compare the current magnitude and the net reactance of the RL circuit and the RLC circuit, and state the advantage of series compensation. S, →>>> 777 RL с mm F S₂ টা
1. Circuit analysis using phasor/impedance, complex power calculation: An RLC circuit is shown below. The reactance of the capacitor is 40 Ohm. The reactance of the inductor is 80 Ohm, and the resistor is 8 Ohm. The sending end voltage is v₁(t) = 345 cos(wt + 7) kV, where w = 2 · 60 rad/s. The receiving end voltage is v₂(t) = 345 cos(wt) kV. Ask: • What is the total impedance of the RLC circuit at 60 Hz? What are the sending end and receiving end voltage phasors in kV? • Please find the current through the line in phasor and in time-domain and in unit kA. • What is the complex power S₁? What is the complex power S₂? Please use a unit of MVA. • What is the power loss due to the resistor? What is the reactive power consumption by the inductor? How much reactive power is generated by the capacitor? . For the same sending end voltage and receiving end voltage, if the series capacitor is not installed, what is the real power delivered to the receiving end? Please compare this number with the one from the series compensated case, compare the current magnitude and the net reactance of the RL circuit and the RLC circuit, and state the advantage of series compensation. S, →>>> 777 RL с mm F S₂ টা
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:Robert L. Boylestad
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P: Visit your local library (at school or home) and describe the extent to which it provides literature...
Related questions
Question
This is part of a review I'm studying, NOT a graded assignment, please do not reject. Thank you for your help!
I only need the last two out of the five sub-parts, I already got a solution for the first three sub-parts. Thank you again for your help!

Transcribed Image Text:1. Circuit analysis using phasor/impedance, complex power calculation: An RLC circuit is shown
below. The reactance of the capacitor is 40 Ohm. The reactance of the inductor is 80 Ohm, and the resistor
is 8 Ohm. The sending end voltage is v₁ (t) = 343 cos(wt + 7) kV, where w = 2 - 60 rad/s. The receiving end
voltage is v₂ (t) = 3 cos (wt) kV. Ask:
• What is the total impedance of the RLC circuit at 60 Hz? What are the sending end and receiving end
voltage phasors in kV?
• Please find the current through the line in phasor and in time-domain and in unit kA.
• What is the complex power S₁? What is the complex power S₂? Please use a unit of MVA.
• What is the power loss due to the resistor? What is the reactive power consumption by the inductor?
How much reactive power is generated by the capacitor?
• For the same sending end voltage and receiving end voltage, if the series capacitor is not installed, what
is the real power delivered to the receiving end? Please compare this number with the one from the series
compensated case, compare the current magnitude and the net reactance of the RL circuit and the RLC
circuit, and state the advantage of series compensation.
f
Vs
~
S₁
RL C
mm t
S₂
Expert Solution
Step 1: Determine the given variables:-
Solution of all the five parts is as below:
The RLC circuit is shown below,
a
Step by step
Solved in 8 steps with 22 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028229
Author:
Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134746968
Author:
James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028151
Author:
Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,