1. Atomic Structure Label the parts of the atom below and indicate the placement of the subatomic particles within the atom. Part of atom: Subatomic Particle(s): Part of atom: Subatomic Particle(s):_
1. Atomic Structure Label the parts of the atom below and indicate the placement of the subatomic particles within the atom. Part of atom: Subatomic Particle(s): Part of atom: Subatomic Particle(s):_
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Concept explainers
Atomic Structure
The basic structure of an atom is defined as the component-level of atomic structure of an atom. Precisely speaking an atom consists of three major subatomic particles which are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Many theories have been stated for explaining the structure of an atom.
Shape of the D Orbital
Shapes of orbitals are an approximate representation of boundaries in space for finding electrons occupied in that respective orbital. D orbitals are known to have a clover leaf shape or dumbbell inside where electrons can be found.
Question
100%
First labling part only

Transcribed Image Text:1. Atomic Structure
Label the parts of the atom below and indicate the placement of the subatomic particles within the
atom.
proton
atomic number
electrop
II. Atoms and Isotopes
A. Draw a line to correctly match the word in column 1 with the description in column 2.
mass number
neutron
Part of atom:
atomic mass
Subatomic Particle(s):
Part of atom:
Subatomic Particle(s):
subatomic particle with a mass of ~0 amu and
a charge of -1
represent the number of protons and
neutrons in an atom
subatomic particle with a mass of ~1 amu and
no charge
subatomic particle with a mass of ~1 amu and
a charge of +1
represents the weighted average mass
number of all naturally occurring isotopes
represents the number of protons in an atom
B. Use the information provided for each isotope to complete the chart.
9
Expert Solution
Step 1: Introduction
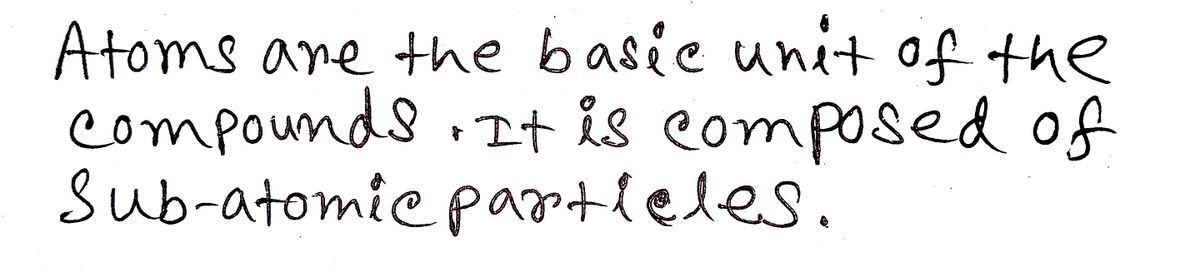
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY