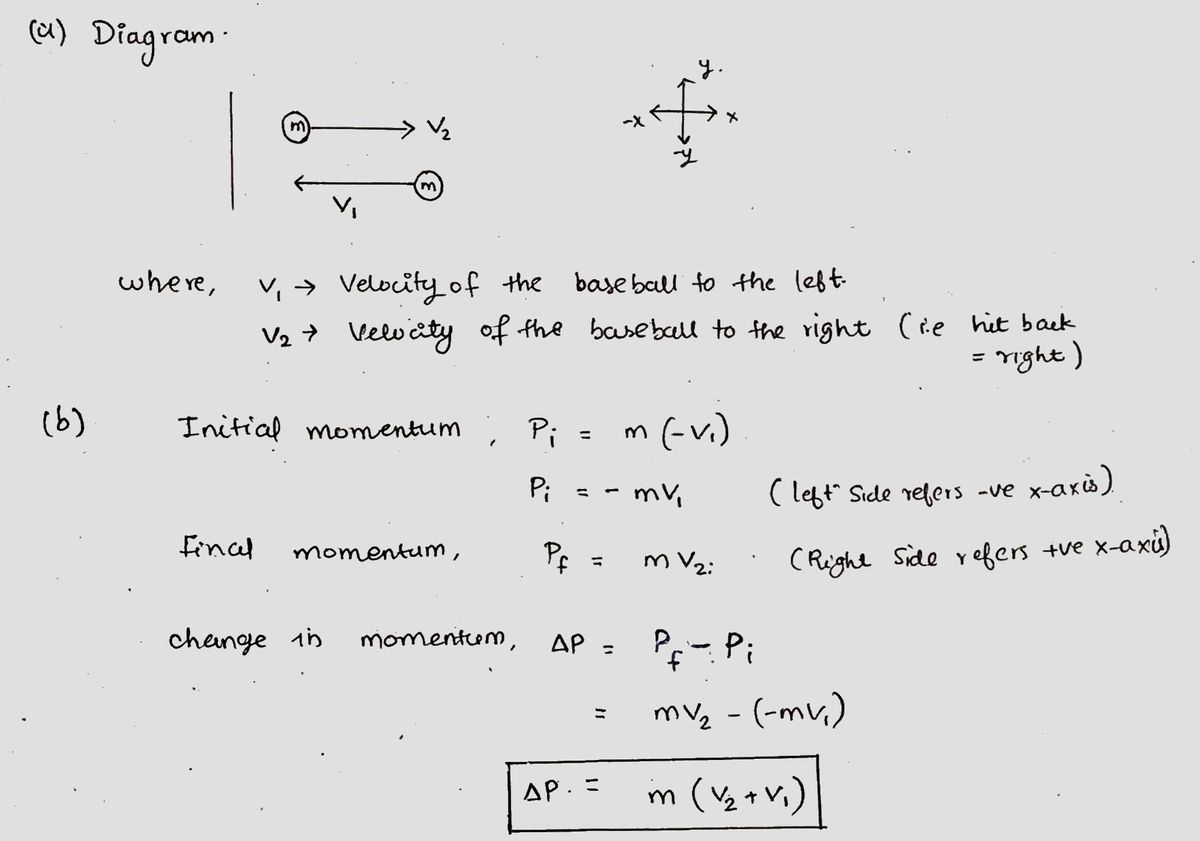
1. A baseball (m = 145 g), pitched horizontally to the left at 30.0 m/s, is hit back in a straight line toward the pitcher at 45.0 m/s. a) Draw a diagram showing the velocities of the baseball before and after hitting the bat. b) Write down the algebraic expression for the change in momentum of the baseball (assume the rightward direction to be positive). c) What is the magnitude and direction of the change in momentum of the baseball? d) Ifthe baseball is in contact with the bat for a time of 2.40 ms, what is the magnitude and direction of the average force exerted on the baseball by the bat?
1. A baseball (m = 145 g), pitched horizontally to the left at 30.0 m/s, is hit back in a straight line toward the pitcher at 45.0 m/s. a) Draw a diagram showing the velocities of the baseball before and after hitting the bat. b) Write down the algebraic expression for the change in momentum of the baseball (assume the rightward direction to be positive). c) What is the magnitude and direction of the change in momentum of the baseball? d) Ifthe baseball is in contact with the bat for a time of 2.40 ms, what is the magnitude and direction of the average force exerted on the baseball by the bat?
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter1: Units, Trigonometry. And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Estimate the order of magnitude of the length, in meters, of each of the following; (a) a mouse, (b)...
Related questions
Question
![### Momentum and Force Analysis of a Baseball
1. **Problem Statement:**
- A baseball (mass = 145 g) is pitched horizontally to the left at a speed of 30.0 m/s. It is hit back in a straight line toward the pitcher at 45.0 m/s.
a) **Diagram Requirement:**
- Draw a diagram representing the velocities of the baseball before and after it contacts the bat.
b) **Algebraic Expression for Change in Momentum:**
- Write the algebraic expression for the change in momentum of the baseball. Assume the rightward direction to be positive.
c) **Magnitude and Direction of Change in Momentum:**
- Determine the magnitude and direction of the change in momentum of the baseball.
d) **Average Force Exerted by the Bat:**
- If the baseball is in contact with the bat for a duration of 2.40 milliseconds, calculate the magnitude and direction of the average force applied to the baseball by the bat.
### Explanation:
- **Velocity Diagram:**
- Illustrate the initial velocity of the baseball (30.0 m/s to the left) and the final velocity after being hit (45.0 m/s to the right).
- **Change in Momentum:**
- The change in momentum (\( \Delta p \)) can be expressed as:
\[
\Delta p = m(v_f - v_i)
\]
where \( m \) is the mass of the baseball, \( v_f \) is the final velocity, and \( v_i \) is the initial velocity.
- **Calculation of Force:**
- Use the impulse-momentum theorem, which relates the change in momentum to the force:
\[
F_{\text{avg}} \times \Delta t = \Delta p
\]
Solve for \( F_{\text{avg}} \) by dividing the change in momentum by the contact time.
These calculations will help understand the concepts of momentum change and force application in a practical scenario involving a baseball.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F9134ba06-2f31-44e0-a0ce-878bcf6ef040%2F172bd9c5-ea5c-48e2-be26-8b6db2ab33ed%2F4rmqmni_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:### Momentum and Force Analysis of a Baseball
1. **Problem Statement:**
- A baseball (mass = 145 g) is pitched horizontally to the left at a speed of 30.0 m/s. It is hit back in a straight line toward the pitcher at 45.0 m/s.
a) **Diagram Requirement:**
- Draw a diagram representing the velocities of the baseball before and after it contacts the bat.
b) **Algebraic Expression for Change in Momentum:**
- Write the algebraic expression for the change in momentum of the baseball. Assume the rightward direction to be positive.
c) **Magnitude and Direction of Change in Momentum:**
- Determine the magnitude and direction of the change in momentum of the baseball.
d) **Average Force Exerted by the Bat:**
- If the baseball is in contact with the bat for a duration of 2.40 milliseconds, calculate the magnitude and direction of the average force applied to the baseball by the bat.
### Explanation:
- **Velocity Diagram:**
- Illustrate the initial velocity of the baseball (30.0 m/s to the left) and the final velocity after being hit (45.0 m/s to the right).
- **Change in Momentum:**
- The change in momentum (\( \Delta p \)) can be expressed as:
\[
\Delta p = m(v_f - v_i)
\]
where \( m \) is the mass of the baseball, \( v_f \) is the final velocity, and \( v_i \) is the initial velocity.
- **Calculation of Force:**
- Use the impulse-momentum theorem, which relates the change in momentum to the force:
\[
F_{\text{avg}} \times \Delta t = \Delta p
\]
Solve for \( F_{\text{avg}} \) by dividing the change in momentum by the contact time.
These calculations will help understand the concepts of momentum change and force application in a practical scenario involving a baseball.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9780321820464
Author:
Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:
Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio…
Physics
ISBN:
9780134609034
Author:
Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:
PEARSON