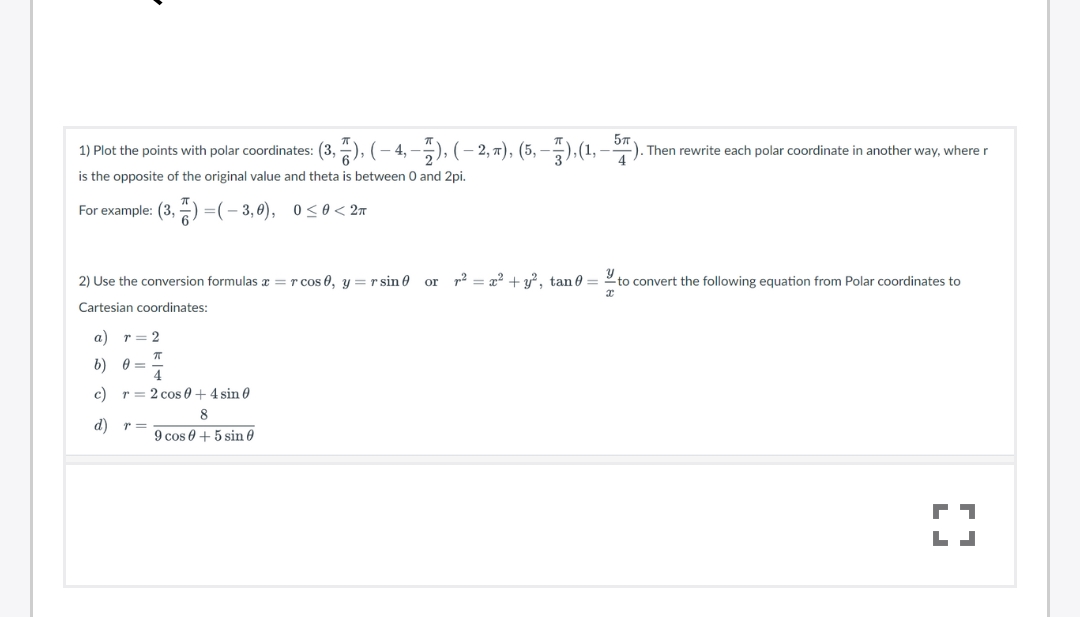
1) Plot the points with polar coordinates: (3, 7), (-4,-7), (– 2, π), (5, –77), (1, – 57). Then rewrite each polar coordinate in another way, where r is the opposite of the original value and theta is between 0 and 2pi. For example: (3, 7) =( − 3,0), 0≤0<2π 2) Use the conversion formulas = r cos 0, y =r sin Cartesian coordinates: a) b) 0= c) d) r = 2 πT 4 r = 2 cos 0 + 4 sin 0 r = 8 9 cos 0+5 sin 0 p² = x² + y², tan 0 = to convert the following equation from Polar coordinates to x
1) Plot the points with polar coordinates: (3, 7), (-4,-7), (– 2, π), (5, –77), (1, – 57). Then rewrite each polar coordinate in another way, where r is the opposite of the original value and theta is between 0 and 2pi. For example: (3, 7) =( − 3,0), 0≤0<2π 2) Use the conversion formulas = r cos 0, y =r sin Cartesian coordinates: a) b) 0= c) d) r = 2 πT 4 r = 2 cos 0 + 4 sin 0 r = 8 9 cos 0+5 sin 0 p² = x² + y², tan 0 = to convert the following equation from Polar coordinates to x
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
ChapterP: Preliminary Concepts
SectionP.CT: Test
Problem 1CT
Related questions
Question
W7Q1
![1) Plot the points with polar coordinates: \( \left( 3, \frac{\pi}{6} \right), \left( -4, -\frac{\pi}{2} \right), \left( -2, \pi \right), \left( 5, -\frac{\pi}{3} \right), \left( 1, -\frac{5\pi}{4} \right) \). Then rewrite each polar coordinate in another way, where \( r \) is the opposite of the original value and \( \theta \) is between 0 and \( 2\pi \).
For example:
\[ \left( 3, \frac{\pi}{6} \right) = \left( -3, \theta \right), \quad 0 \leq \theta < 2\pi \]
2) Use the conversion formulas \( x = r \cos \theta \), \( y = r \sin \theta \) or \( r^2 = x^2 + y^2 \), \( \tan \theta = \frac{y}{x} \) to convert the following equation from Polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates:
a) \( r = 2 \)
b) \( \theta = \frac{\pi}{4} \)
c) \( r = 2 \cos \theta + 4 \sin \theta \)
d) \( r = \frac{8}{9 \cos \theta + 5 \sin \theta} \)](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Ffe2257a7-ec8b-4cb2-8972-c13e17aa7768%2F366fb644-dff5-4495-87b1-a89b11e3e719%2Fxuxnlvm_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:1) Plot the points with polar coordinates: \( \left( 3, \frac{\pi}{6} \right), \left( -4, -\frac{\pi}{2} \right), \left( -2, \pi \right), \left( 5, -\frac{\pi}{3} \right), \left( 1, -\frac{5\pi}{4} \right) \). Then rewrite each polar coordinate in another way, where \( r \) is the opposite of the original value and \( \theta \) is between 0 and \( 2\pi \).
For example:
\[ \left( 3, \frac{\pi}{6} \right) = \left( -3, \theta \right), \quad 0 \leq \theta < 2\pi \]
2) Use the conversion formulas \( x = r \cos \theta \), \( y = r \sin \theta \) or \( r^2 = x^2 + y^2 \), \( \tan \theta = \frac{y}{x} \) to convert the following equation from Polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates:
a) \( r = 2 \)
b) \( \theta = \frac{\pi}{4} \)
c) \( r = 2 \cos \theta + 4 \sin \theta \)
d) \( r = \frac{8}{9 \cos \theta + 5 \sin \theta} \)
Expert Solution
Step 1: Given
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning