1 n2 + in n=1
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
100%
Does the attached series converge or diverge?
![The image displays a mathematical formula representing an infinite series. The series is expressed as follows:
\[
\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} \frac{1}{n^2 + i^n}
\]
### Explanation:
- **Summation Symbol (\(\sum\))**: This symbol denotes the sum of a sequence of terms.
- **Index of Summation (\(n=1\))**: It indicates that the summation starts from \(n=1\).
- **Upper Limit of Summation (\(\infty\))**: The summation continues indefinitely towards infinity.
- **Expression Within the Sum**: The term \(\frac{1}{n^2 + i^n}\) represents each term in the series. Here:
- \(n^2\) is the square of the index \(n\).
- \(i^n\) is \(i\) raised to the power of \(n\), where \(i\) is the imaginary unit (\(i = \sqrt{-1}\)).
This series is a complex infinite series due to the presence of the imaginary unit \(i\), and it may converge to a specific value or diverge. The behavior of such a series would typically be analyzed in complex analysis or advanced calculus.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F88e1e2e4-888b-4182-8c02-fd46dda7f6b1%2Fea6f6e6a-afe4-4a1d-91a5-92a30667f98f%2Fwnpnxag_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:The image displays a mathematical formula representing an infinite series. The series is expressed as follows:
\[
\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} \frac{1}{n^2 + i^n}
\]
### Explanation:
- **Summation Symbol (\(\sum\))**: This symbol denotes the sum of a sequence of terms.
- **Index of Summation (\(n=1\))**: It indicates that the summation starts from \(n=1\).
- **Upper Limit of Summation (\(\infty\))**: The summation continues indefinitely towards infinity.
- **Expression Within the Sum**: The term \(\frac{1}{n^2 + i^n}\) represents each term in the series. Here:
- \(n^2\) is the square of the index \(n\).
- \(i^n\) is \(i\) raised to the power of \(n\), where \(i\) is the imaginary unit (\(i = \sqrt{-1}\)).
This series is a complex infinite series due to the presence of the imaginary unit \(i\), and it may converge to a specific value or diverge. The behavior of such a series would typically be analyzed in complex analysis or advanced calculus.
Expert Solution
Step 2
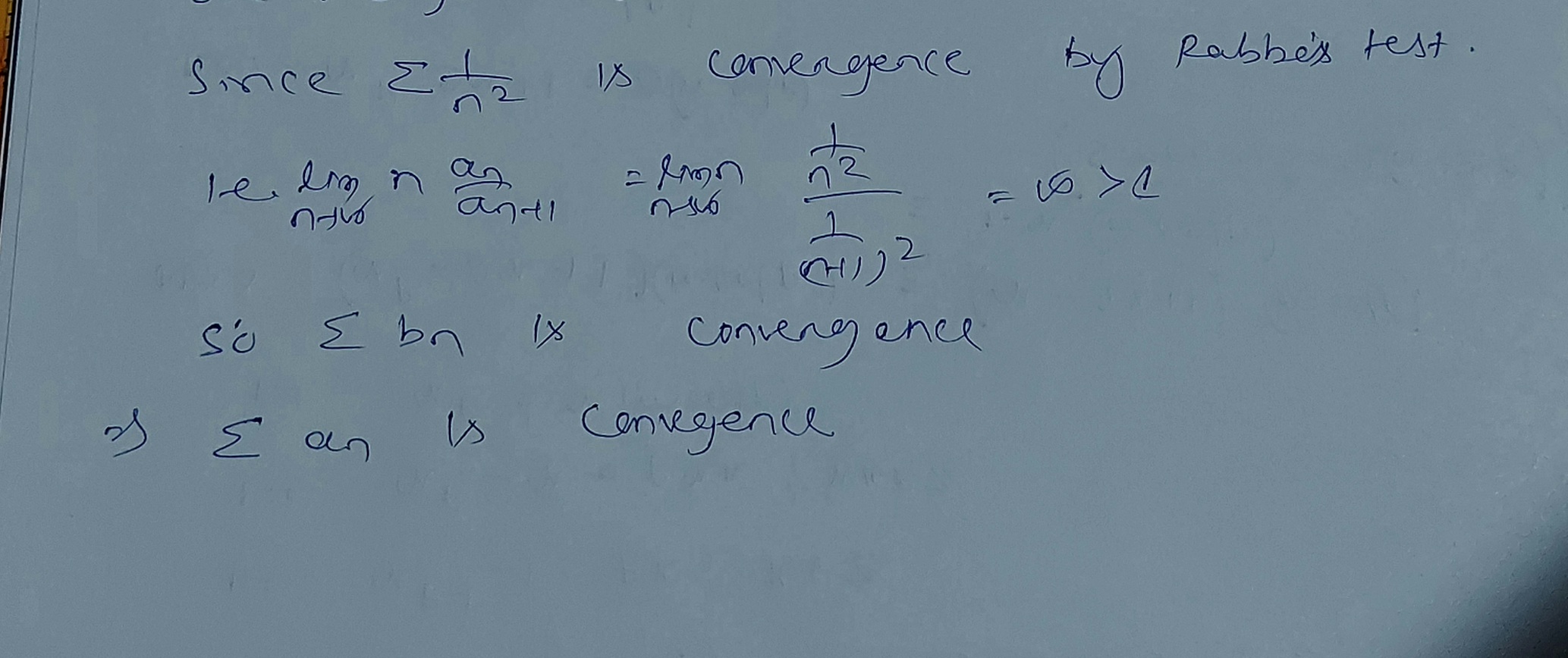
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

