Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
Thanks

Transcribed Image Text:**Exercise 1: Evaluating Limits from a Graph**
For the function \( f \) whose graph is provided, determine the value of each limit. If a limit does not exist, write "DNE."
### Graph Description:
- The graph is plotted on a standard Cartesian coordinate system.
- The vertical axis represents the values of \( f(x) \).
- The horizontal axis represents the \( x \)-values.
### Key Features:
- The function appears to approach different values from the left and right of \( x = 1 \).
- There is a discontinuity at \( x = 1 \).
### Limits to Determine:
1. **\(\lim_{{x \to 1^-}} f(x) =\ ? \)**
- This represents the limit of \( f(x) \) as \( x \) approaches 1 from the left.
2. **\(\lim_{{x \to 1^+}} f(x) =\ ? \)**
- This represents the limit of \( f(x) \) as \( x \) approaches 1 from the right.
3. **\(\lim_{{x \to 1}} f(x) =\ ? \)**
- This represents the overall limit of \( f(x) \) as \( x \) approaches 1 from both sides.
**Exercise 2: (Section for future content or additional problems)**
Expert Solution
Step 1
From the given graph :
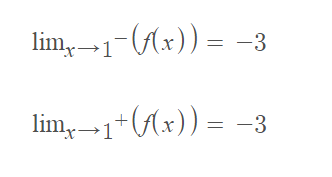
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 5 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning