0 1.73 2.16
Q: Step 1: Enter the number of degrees of freedom. Step 2: Select one-tailed or two-tailed. O…
A: The mean amount of gamma radiation needed to sterilize a colony of tardigrades is not equal to 1150…
Q: Find z given that P(.24 <Z <z) = .12
A:
Q: p(z < 1.29)
A: standard normal distribution Z~N(0,1) P(z<1.29) = ?
Q: Find P(-1.40 < Z < 0) .4192 .1259 .4357 .8907
A: Solution: Let Z be the standard normal random variable with mean μ=0 and standard deviation σ=1…
Q: To find P(x<2.35) where do you shade?
A: Left side
Q: Find the interval values for Z such that P(-z<Z<z)= 0.9886.
A: P(-z<Z<z) =0.9886.·. x=1-0.9886 =0.0114
Q: P(z>1.2)
A: Given problem Given that P(z>1.2) Ans) P( z>1.2 ) is, = 1 - P( z ≤ 1.2 )
Q: P(Z<1.89) (less than or equal to)
A: Given that. X~N( 0 , 1 ) μ=0 , ?=1 (for standard normal distribution) Z-score =( x - μ )/?
Q: Calculate P(Z < 1.5)
A:
Q: If m rst = 164, what is m<RVT?
A:
Q: P(x < 17.872)
A: Let's take the given Sample size n=33 from a population, with mean=16 and standard deviation=8.4…
Q: P(1.15 < Z < 2.77) =
A: X~N( 0 , 1 ) μ=0 , ?=1 (for standard normal distribution) Z-score =( x - μ )/?
Q: P (Z<1.8572)
A: Answer - Find P (Z<1.8572)
Q: P(x) = . Let and let = 10. Find P(9) x!
A: We have to find p(9)
Q: P(0.51 ≤ Z ≤ 1.4) =
A: Draw the normal curve and shade the area between z=0.51 and z=1.4.
Q: (h) P(1.26 ≤ Z ≤ 2.50) (1) P(1.90 ≤ Z) (1) P(|Z| ≤ 2.50)
A: It is given that the standard normal random variable Z with mean 0 and variance 1. Note: The…
Q: p(0 < z < 1.30)= p(0 < z < 1.83)= p(1.30 < z < 1.83)=
A: Given that:Z is standard normal Distributed with i.e. mean µ =0 and standard deviation σ =1 By…
Q: P(X ≤ 1). n = 5, p = 0.6
A:
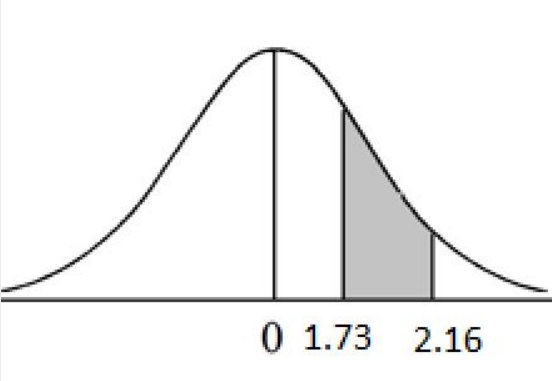
Find P(1.73< Z < 2.16)

Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

- A die is rolled 1200 times. Let X be the number of sixes rolled. Estimate P (190P(- c ≤ Z ≤ c)=0.9399Let X-N(3,02). Suppose that P(3what is p(z<?)=0.88P(z<1.53 U z>2.57)Owners of Major League Baseball teams have been concerned with attendance in recent years as declines have been noticed across the board. There are a variety of factors that are causing this decline, but it is believed that a team's win-loss record, payroll, stadium age, and home run ability help to drive attendance. space What was the average attendance per team in 2018? Round your answer to 3 decimal places. SPACE What team had the highest and lowest total attendance in 2018? Enter the team names along with their attendance figures as they appear in the data file. Round your attendance numbers to 3 decimal places. SPACE Team Attendance Highest attendance mil Lowest attendance mil space What was the range of attendance in 2018? Round your answer to 3 decimal places.SEE MORE QUESTIONSRecommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman