
INTEGRATION EXERCISE I Different Costs for Different Purposes, Cost-Volume-Profit-Relationships
Hixson Company manufactures and sells one product for $34 per unit. The company maintains no beginning or ending inventories and its relevant range of production is 20,000 units to 30,000 units. When Hixson produces and sells 25,000 units, its unit costs are as follows:
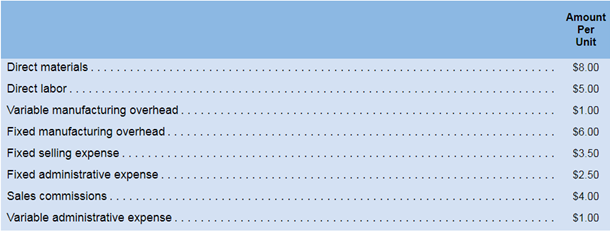
Required:
- For financial accounting purposes. what is the total amount of product costs incurred to make 25.000 units? What is the total amount of period costs incurred to sell 25.000 units?
1
Product cost Product cost include all the costs or expenses that are directly related to product. These costs are incurred only during the production process. For example- cost incurred for direct material, direct labor, etc.
Period cost Period costs are the expenses that are incurred even when there is no production. These costs are not related to products but to passage of time. For example, depreciation expense, advertising expense, etc.
To calculate: Total amount of product cost and period cost incurred to produce 25,000 units.
Answer to Problem 1IE
Total product cost for manufacturing 25,000 units is $500,000 and total period cost is $275,000.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of product cost for 25,000 units will be as follows:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) | |
| Direct materials | (25,000 * $8) | 200,000 |
| Direct labors | (25,000 * $5) | 125,000 |
| Manufacturing overheads (variable) | (25,000 * $1) | 25,000 |
| Manufacturing overheads (fixed) | (25,000 * $6) | 150,000 |
| Total product cost | 500,000 |
Calculation of period cost for 25,000 units will be as follows:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) | |
| Selling expense (fixed) | (25,000 * $3.5) | 87,500 |
| Administration expense (fixed) | (25,000 * $2.5) | 62,500 |
| Sales commission | (25,000 * $4) | 100,000 |
| Administrative expense | (25,000 * $1) | 25,000 |
| Total product cost | 275,000 |
For 25,000 units, total product cost is $500,000 and total period cost is $275,000.
2
Variable cost per unit This is the total variable cost that a company incurs to produce one unit. This is calculated by the division of total variable cost and the number of manufactured units. Variable cost per unit remains the same.
Average fixed manufacturing cost per unit This shows fixed manufacturing cost incurred for one unit. This is calculated by the division of total fixed manufacturing expenses and total units.
To calculate: Per unit variable manufacturing cost and average fixed manufacturing cost for 24,000 units.
Answer to Problem 1IE
Variable manufacturing cost is calculated as $14 per unit and fixed manufacturing overhead is $6.25 per unit.
Explanation of Solution
For 24,000 units, Variable manufacturing cost per unit will be calculated as:
| Particulars | Amount (in S) |
| Direct material (per unit) | 8 |
| Direct labor (per unit) | 5 |
| Manufacturing overhead (variable) (per unit) | 1 |
| Variable manufacturing cost (per unit) | 14 |
Fixed manufacturing cost per unit will be calculated as:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) |
| Total fixed manufacturing overheads (shown in sub part 1) | 150,000 |
| Total units | 24,000 units |
| Per unit fixed manufacturing cost (total cost / units) | 6.25 |
Variable manufacturing cost per unit is $14.00 and per unit fixed manufacturing overhead is $6.25.
3
Variable manufacturing cost per unit This is the total variable cost that a company incurs to manufacture one unit. This is calculated by the division of total variable cost and the number of manufactured units. Variable cost per unit remains the same.
Fixed manufacturing cost per unit This shows fixed manufacturing cost incurred for one unit. This is calculated by the division of total fixed manufacturing expenses and total units.
To calculate: For 26,000 units per unit variable and fixed manufacturing costs.
Answer to Problem 1IE
Variable manufacturing cost is calculated as $14 per unit and fixed manufacturing overhead is $5.77 per unit.
Explanation of Solution
For 26,000 units, Variable manufacturing cost per unit will be calculated as:
| Particulars | Amount (in S) |
| Direct material (per unit) | 8.00 |
| Direct labor (per unit) | 5.00 |
| Manufacturing overhead (variable) (per unit) | 1.00 |
| Total variable manufacturing cost (per unit) | 14.00 |
Note: Variable cost per unit remains the same, irrespective of the number of units produced.
Fixed manufacturing cost per unit for 26,000 units will be calculated as:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) |
| Total fixed manufacturing overheads (shown in sub part 1) | 150,000 |
| Total units | 26,000 units |
| Per unit fixed manufacturing cost (total cost / units) | 5.77 |
Note: Total fixed cost incurred by the company does not change.
Variable manufacturing cost per unit is $14.00 and fixed manufacturing overhead per unit is $5.77.
4
Direct manufacturing cost Direct cost covers all the costs that are directly associated with a product. For example, costs related to direct material, labor, etc.
Indirect manufacturing cost Indirect cost covers all the costs that are not directly associated with a product but help in operating in a more efficient way. For example, supervision cost, advertising cost, etc.
To calculate: Total direct and indirect manufacturing costs for 27,000 units.
Answer to Problem 1IE
Total direct manufacturing cost for 27,000 units is $351,000 and total indirect manufacturing cost is $177,000.
Explanation of Solution
For 27,000 units, total direct manufacturing cost will be calculated as:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) |
| Direct material (27,000 * $8) | 216,000 |
| Direct labor (27,000 * $5) | 135,000 |
| Total direct manufacturing cost | 351,000 |
For 27,000 units, total indirect manufacturing cost will be calculated as:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) |
| Manufacturing overhead (variable) (27,000 * $1) | 27,000 |
| Manufacturing overhead (fixed) | 150,000 |
| Total indirect manufacturing cost | 177,000 |
For 27,000 units, total direct manufacturing expense is $351,000 and total indirect manufacturing expense is $177,000.
5
Incremental manufacturing cost Incremental cost refers to the additional cost that a company incurs by producing one addiyional unit.
To calculate: Total incremental manufacturing cost that the company would incur if number of units change from 25,000 to 25,001.
Answer to Problem 1IE
Incremental cost that the company will incur by increasing one unit is $14.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation for incremental cost will be done as follows:
| Particulars | For 25,000 units | For 25,001 units |
| Direct material ($8) | 200,000 | 200,008 |
| Direct labor ($5) | 125,000 | 125,005 |
| Manufacturing overhead (variable) (1) | 25,000 | 25,001 |
| Manufacturing overhead (fixed) (fixed cost does not change in total) | 150,000 | 150,000 |
| Total | 500,000 | 500,014 |
So, incremental cost when company changes the number of units from 25,000 to 25,001 is $14 (500,014 − 500,000).
6
Contribution margin Contribution margin represents the portion of sales, which does not include any amount of variable costs. This portion of sale includes only fixed costs and profit. It is calculated by deducting total variable cost from sale price or by adding amount of fixed costs and profit.
To calculate: Per unit contribution margin and contribution margin ratio of the company.
Answer to Problem 1IE
Contribution margin is $15 per unit and Contribution margin ratio is 44.1%.
Explanation of Solution
Contribution margin per unit is calculated by the following formula:
Selling price is given as $34 per unit and total variable cost per unit will be calculated as:
| Particulars | Amount (in S) |
| Direct material (per unit) | 8.00 |
| Direct labor (per unit) | 5.00 |
| Manufacturing overhead (variable) (per unit) | 1.00 |
| Sales commission | 4.00 |
| Variable administration expense | 1.00 |
| Total variable manufacturing cost (per unit) | 19.00 |
So, contribution margin per unit will be:
Formula to calculate contribution margin ratio is:
Contribution margin ratio will be:
So, contribution is $15 per unit and contribution margin ratio is 44.1%.
7
Break even point It is that level of sales at which, cost incurred by a company is exactly equal to the revenue earned. It is known as the level of no profit or no loss as, at this level company does not earn any profit and covers all of its costs.
To calculate:Break-even point in units and in sales.
Answer to Problem 1IE
Break-even point in units is calculated as 20,000 units and in sales, it is calculated as $680,000.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation for total fixed cost:
| Particulars | Amount (in S) |
| Fixed manufacturing cost | 150,000 |
| Fixed selling expense | 87,500 |
| Fixed administrative expense | 62,500 |
| Total fixed costs | 300,000 |
Now, break even point (in units) will be calculated as:
Break even point (in sales) will be:
Break even point in units is 20,000 units and break even point in sales $680,000.
8
Net operating income It is the net income generated by a company and it is obtained after deducting both types of costs, variable and fixed, from the sale value.
To calculate:Increase in net operating income when units increase from 25,000 units to 26,500 units.
Answer to Problem 1IE
Net operating income will increase by $22,500.
Explanation of Solution
Net operating income is calculated by deducting amount of total fixed cost from contribution (in rupees).
Calculation for increase in net operating income will be done as follows:
| Particulars | For 25,000 units | For 26,500 units |
| Contribution margin per unit | $15 | $15 |
| Total units | 25,000 | 26,500 |
| Total contribution in rupees | $375,000 | $397,500 |
| Total fixed cost (computed in sub part 7) | $300,000 | $300,000 |
| Net operating income | $75,000 | $97,500 |
So, increase in net operating income of the company number of units increase from 25,000 to 26,500 is $22,500 ($97,500 − 75,000).
9
Margin of safety Margin of safety represents the sales made by a company in addition to its break-even level. It is calculated by deducting break even sales from the actual sales made.
To calculate:Margin of safety at 25,000 units.
Answer to Problem 1IE
Margin of safety at 25,000 unit is $170,000.
Explanation of Solution
Margin of safety is calculated by deducting break even sales from the total actual sales. So, it will be calculated as:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) |
| Total sales (25,000 * 34) | 850,000 |
| Less: Break-even point (in sales) (computed in sub part 7) | 680,000 |
| Margin of safety | 170,000 |
So, margin of safety is $170,000.
10
Operating leverage Operating leverage measures the degree by which operating income for a company will increase with an increase in its revenue.
To calculate:Degree of operating leverage at 25,000 units.
Answer to Problem 1IE
Operating leverage at 25,000 units is 5.0.
Explanation of Solution
Degree of operating leverage is obtained by dividing contribution margin and net operating income. So, Calculation for degree of operating leverage will be done as follows:
So, degree of operating leverage, at 25,000 units, is 5.0.
Note: contribution margin and net operating income both are calculated in sub part 8.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter IE Solutions
Introduction To Managerial Accounting
- Please provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using appropriate methods.arrow_forwardI need help solving this general accounting question with the proper methodology.arrow_forwardI need guidance with this general accounting problem using the right accounting principles.arrow_forward
- Please help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct financial process.arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub


