
Place the lettered features in proper sequence, from oldest to youngest, in the space provided on the figure.
The correct sequence of lettered features.
Introduction:
The scientists have developed many techniques and methods to detect the actual year of Earth. There are two types of data that are used to indicate the geological history of an area. These are relative data and numerical data. The relative data is helpful in determining the correct sequence of the formation of rock layers.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial Representation: Fig 1 represents the correct sequence of lettered features.
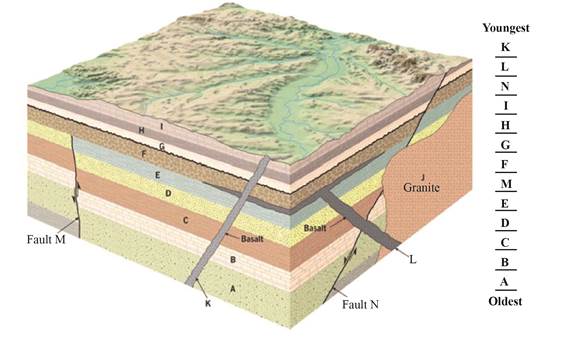
Fig 1: The correct sequence of lettered features (from oldest to youngest).
According to figure 10.24 given in the textbook, the letter featuring K is the youngest while the letter featuring A is the oldest. The letters are representations of rock layers. The layers A, B, C, D, and E are formed first while the layers F, G, H and I are formed latter. M and N are the faults that are responsible for the formation of layers F, G, H and I. The fault N cuts the layer A. K and L are the basalt layers.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (8th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life (5th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
- My question: How does unequal school resources and fundings affect job opportunities for underprivileged groups? Can you go into 2. Gather facts related to your topic by using recommended Dallas College Library databases, like PubMed and Psychology Gale Academic OneFile. select important facts and statistics that will help you to answer your research question. Articles you select must be published within 5 years (2019-2024). Can you find as much articles that you can that answer my question.arrow_forwardhwarrow_forwardhwarrow_forward
- 1. The field of hydrogeology includes: a. soil water movement b. rainfall runoff and flood generation c. placement of water wells to optimize the quantity and quality of water supplies d. all of the above e. a and c 2. Groundwater occurrence and movement has no direct influence on: a. earthquake activity b. land subsidence c. land slide potential d. hydraulic conductivity e. soil formation f. none of the above 3. In terms of Earth's water budget, groundwater ranks a. higher b. lower 4. Ultimately, the hydrological cycle is driven by: a. geothermal energy fluxes toward Earth's surface b. orographic rainfall due to abrupt changes in elevation c. solar energy fluxes toward Earth's surface d. adiabatic cooling in the atmosphere 5. In the equation below, the variable "Var" refers to: a. void ratio b. pressure head c. hydraulic conductivity d. intrinsic permeability than glaciers and ice caps: P Var = p.garrow_forwardDeep water- waves with constant wavelength Wave movement Approaching shore- waves touch bottom (wavelength decreases) Surf zone (breakers form) Waves touch bottom as they encounter water depths that are less than half a wavelength C E B 00000 00000 Depth is >½ wavelength 0000 0000 Velocity decreases (wave height increases)arrow_forwardActivity 12.1: Wave Characteristics Pg 200 1. Refer to Figure 12.1 and select the letter that identifies each of the following.wave crestwave troughwavelengthwave heightwave base 2. Below what depth would a submarine have to submerge so that it would not be swayed by surface waves with a wavelength of 24 meters?____ mActivity 12.2: Deep Versus Shallow Water Waves Pgs 201-202Refer to Figure 12.1 to answer the following questions. 1. Do particles in deep-water waves trace out circular or elliptical paths? 2. Near the shore in shallow water, do water particles trace out circular or elliptical 3. In shallow water, are water particles in the wave crest ahead of or behind those at the bottom of the wave? 4. As waves approach the shore, do their heights increase or decrease? Do wavelengths become longer or shorter? 5. In the surf zone, is the water in the crest of a wave falling forward or standing still? 6. What is the velocity of deep-water waves that have a wavelength of 46 meters and a…arrow_forward
 Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON
Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





