
| Classify angles. | (a) 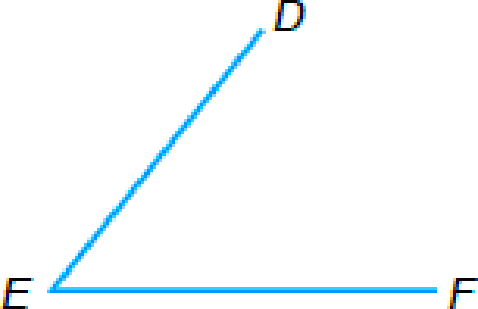 |
(a) ∡DEF is _____ |
(b) 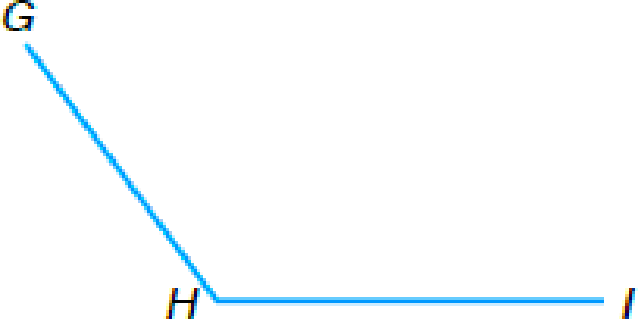 |
(b) ∡GHI is _____ | |
(c) 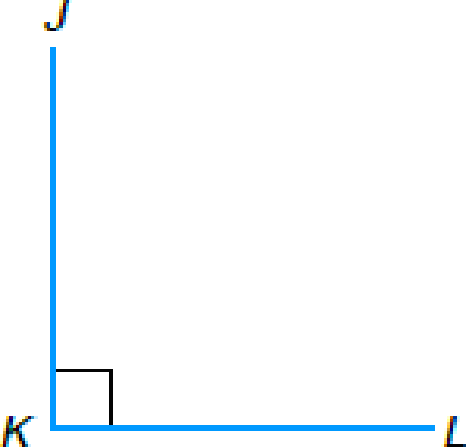 |
(c) ∡JKL is _____ |
a.
To classify: The angle DEF as acute, obtuse, or right.
Answer to Problem 2P
The angle DEF is
Explanation of Solution
Definition used:
An angle is acute when the measure of the angle is in between
An angle is right when the measure of the angle is exactly
An angle is obtuse when the measure of the angle is in between
Calculation:
Note that the measure of the given angle is less than
Thus by the above definition, the angle DEF is
b.
To classify: The angle GHI as acute, obtuse, or right.
Answer to Problem 2P
The angle GHI is
Explanation of Solution
Definition used:
An angle is said to be acute when the measure of the angle is in between
An angle is said to be right when the measure of the angle is exactly
An angle is said to be obtuse when the measure of the angle is in between
Calculation:
Note that the measure of the given angle is less than
Thus by the above definition, the angle GHI is
c.
To classify: The angle JKL as acute, obtuse, or right.
Answer to Problem 2P
The angle JKL is
Explanation of Solution
Definition used:
An angle is said to be acute when the measure of the angle is in between
An angle is said to be right when the measure of the angle is exactly
An angle is said to be obtuse when the measure of the angle is in between
Calculation:
Note that the measure of the angle JKL is exactly
Thus by the above definition, the angle JKL is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Mathematics for the Trades: A Guided Approach (11th Edition) (What's New in Trade Math)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
Elementary and Intermediate Algebra: Concepts and Applications (7th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
College Algebra (7th Edition)
- Can you help me solved this problem using generalized combination:How many combinations are there to pick r objects from 2n objects numbered from 1to 2n when repetitions are allowed and at least one object of odd type does not appear?arrow_forwardNarrow_forward1. Given that h(t) = -5t + 3 t². A tangent line H to the function h(t) passes through the point (-7, B). a. Determine the value of ẞ. b. Derive an expression to represent the gradient of the tangent line H that is passing through the point (-7. B). c. Hence, derive the straight-line equation of the tangent line H 2. The function p(q) has factors of (q − 3) (2q + 5) (q) for the interval -3≤ q≤ 4. a. Derive an expression for the function p(q). b. Determine the stationary point(s) of the function p(q) c. Classify the stationary point(s) from part b. above. d. Identify the local maximum of the function p(q). e. Identify the global minimum for the function p(q). 3. Given that m(q) = -3e-24-169 +9 (-39-7)(-In (30-755 a. State all the possible rules that should be used to differentiate the function m(q). Next to the rule that has been stated, write the expression(s) of the function m(q) for which that rule will be applied. b. Determine the derivative of m(q)arrow_forward
- Please help me organize the proof of the following theorem:arrow_forwardThe population mean and standard deviation are given below. Find the required probability and determine whether the given sample mean would be considered unusual. For a sample of n = 65, find the probability of a sample mean being greater than 225 if μ = 224 and σ = 3.5. For a sample of n = 65, the probability of a sample mean being greater than 225 if μ=224 and σ = 3.5 is 0.0102 (Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwarduestion 10 of 12 A Your answer is incorrect. L 0/1 E This problem concerns hybrid cars such as the Toyota Prius that are powered by a gas-engine, electric-motor combination, but can also function in Electric-Vehicle (EV) only mode. The figure below shows the velocity, v, of a 2010 Prius Plug-in Hybrid Prototype operating in normal hybrid mode and EV-only mode, respectively, while accelerating from a stoplight. 1 80 (mph) Normal hybrid- 40 EV-only t (sec) 5 15 25 Assume two identical cars, one running in normal hybrid mode and one running in EV-only mode, accelerate together in a straight path from a stoplight. Approximately how far apart are the cars after 15 seconds? Round your answer to the nearest integer. The cars are 1 feet apart after 15 seconds. Q Search M 34 mlp CHarrow_forward
- Find the volume of the region under the surface z = xy² and above the area bounded by x = y² and x-2y= 8. Round your answer to four decimal places.arrow_forwardУ Suppose that f(x, y) = · at which {(x, y) | 0≤ x ≤ 2,-x≤ y ≤√x}. 1+x D Q Then the double integral of f(x, y) over D is || | f(x, y)dxdy = | Round your answer to four decimal places.arrow_forwardD The region D above can be describe in two ways. 1. If we visualize the region having "top" and "bottom" boundaries, express each as functions of and provide the interval of x-values that covers the entire region. "top" boundary 92(x) = | "bottom" boundary 91(x) = interval of values that covers the region = 2. If we visualize the region having "right" and "left" boundaries, express each as functions of y and provide the interval of y-values that covers the entire region. "right" boundary f2(y) = | "left" boundary fi(y) =| interval of y values that covers the region =arrow_forward
- Find the volume of the region under the surface z = corners (0,0,0), (2,0,0) and (0,5, 0). Round your answer to one decimal place. 5x5 and above the triangle in the xy-plane witharrow_forwardGiven y = 4x and y = x² +3, describe the region for Type I and Type II. Type I 8. y + 2 -24 -1 1 2 2.5 X Type II N 1.5- x 1- 0.5 -0.5 -1 1 m y -2> 3 10arrow_forwardGiven D = {(x, y) | O≤x≤2, ½ ≤y≤1 } and f(x, y) = xy then evaluate f(x, y)d using the Type II technique. 1.2 1.0 0.8 y 0.6 0.4 0.2 0- -0.2 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 X X This plot is an example of the function over region D. The region identified in your problem will be slightly different. y upper integration limit Integral Valuearrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
