
What is the difference between the upstream velocity and the free-stream velocity? For what types of flow are these two velocities equal to each other?
Difference between"Upstream flow velocity" and "free stream velocity"and for which flow are they equal.
Answer to Problem 1CP
Upstream velocity represents approaching velocity while free stream velocity represents velocity of fluid relative to the immersed body(solid).
They are equal in uniform flow.
The difference between upstream flow velocity and free stream velocity is given in table below:
| Upstream flow velocity | Free stream velocity |
| The velocity(V) at which any fluid flow approaches an immersed body is known as upstream flow velocity. | The sufficiently far away velocity of the fluid which is relative to the immersed body(solid) is the free stream velocity. It is denoted by |
| It is the actual velocity of fluid flowing just before approaching the immersed body | It is the velocity which exists at end of the velocity boundary layer around the immersed body. |
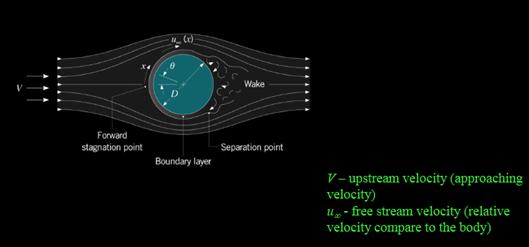
"Upstream flow velocity " and "free stream velocity" are same/equal when:
a. There is uniform fluid flow.
b. When the immersed body in fluid is relatively in comparison to uniform fluid flow rate, where it is immersed.
Explanation of Solution
The difference between upstream flow velocity and free stream velocity is given in table below:
| Upstream flow velocity | Free stream velocity |
| The velocity(V) at which any fluid flow approaches an immersed body is known as upstream flow velocity. | The sufficiently far away velocity of the fluid which is relative to the immersed body(solid) is the free stream velocity. It is denoted by |
| It is the actual velocity of fluid flowing just before approaching the immersed body | It is the velocity which exists at end of the velocity boundary layer around the immersed body. |

"Upstream flow velocity " and "free stream velocity" are same/equal when:
a. There is uniform fluid flow.
b. When the immersed body in fluid is relatively in comparison to uniform fluid flow rate, where it is immersed.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals and Applications
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- Part A: Suppose you wanted to drill a 1.5 in diameter hole through a piece of 1020 cold-rolled steel that is 2 in thick, using an HSS twist drill. What values if feed and cutting speed will you specify, along with an appropriate allowance? Part B: How much time will be required to drill the hole in the previous problem using the HSS drill?arrow_forward1.1 m 1.3 m B 60-mm diameter Brass 40-mm diameter Aluminum PROBLEM 2.52 - A rod consisting of two cylindrical portions AB and BC is restrained at both ends. Portion AB is made of brass (E₁ = 105 GPa, α = 20.9×10°/°C) and portion BC is made of aluminum (Ę₁ =72 GPa, α = 23.9×10/°C). Knowing that the rod is initially unstressed, determine (a) the normal stresses induced in portions AB and BC by a temperature rise of 42°C, (b) the corresponding deflection of point B.arrow_forward30 mm D = 40 MPa -30 mm B C 80 MPa PROBLEM 2.69 A 30-mm square was scribed on the side of a large steel pressure vessel. After pressurization, the biaxial stress condition at the square is as shown. For E = 200 GPa and v=0.30, determine the change in length of (a) side AB, (b) side BC, (c) diagnonal AC.arrow_forward
- Please solve in detail this problem thank youarrow_forward0,5 mm 450 mm 350 mm Bronze A = 1500 mm² E = 105 GPa प 21.6 × 10-PC Aluminum A = 1800 mm² £ = 73 GPa = a 23.2 × 10-PC PROBLEM 2.58 Knowing that a 0.5-mm gap exists when the temperature is 24°C, determine (a) the temperature at which the normal stress in the aluminum bar will be equal to -75 MPa, (b) the corresponding exact length of the aluminum bar.arrow_forward0.5 mm 450 mm -350 mm Bronze Aluminum A 1500 mm² A 1800 mm² E 105 GPa E 73 GPa K = 21.6 X 10 G < = 23.2 × 10-G PROBLEM 2.59 Determine (a) the compressive force in the bars shown after a temperature rise of 82°C, (b) the corresponding change in length of the bronze bar.arrow_forward
- The truss shown below sits on a roller at A and a pin at E. Determine the magnitudes of the forces in truss members GH, GB, BC and GC. State whether they are in tension or compression or are zero force members.arrow_forwardA weight (W) hangs from a pulley at B that is part of a support frame. Calculate the maximum possible mass of the weight if the maximum permissible moment reaction at the fixed support is 100 Nm. Note that a frictionless pin in a slot is located at C.arrow_forwardIt is the middle of a winter snowstorm. Sally and Jin take shelter under an overhang. The loading of the snow on top of the overhang is shown in the figure below. The overhang is attached to the wall at points A and B with pin supports. Another pin is at C. Determine the reactions of the pin supports at A and B. Express them in Cartesian vector form.arrow_forward
- Recall that the CWH equation involves two important assumptions. Let us investigate how these assumptions affect the accuracy of state trajectories under the control inputs optimized in (a) and (b). (c.1): Discuss the assumptions about the chief and deputy orbits that are necessary for deriving CWH.arrow_forwardPROBLEM 2.50 1.8 m The concrete post (E-25 GPa and a = 9.9 x 10°/°C) is reinforced with six steel bars, each of 22-mm diameter (E, = 200 GPa and a, = 11.7 x 10°/°C). Determine the normal stresses induced in the steel and in the concrete by a temperature rise of 35°C. 6c " 0.391 MPa 240 mm 240 mm 6₁ = -9.47 MPaarrow_forwardFor some viscoelastic polymers that are subjected to stress relaxation tests, the stress decays with time according to a(t) = a(0) exp(-4) (15.10) where σ(t) and o(0) represent the time-dependent and initial (i.e., time = 0) stresses, respectively, and t and T denote elapsed time and the relaxation time, respectively; T is a time-independent constant characteristic of the material. A specimen of a viscoelastic polymer whose stress relaxation obeys Equation 15.10 was suddenly pulled in tension to a measured strain of 0.5; the stress necessary to maintain this constant strain was measured as a function of time. Determine E (10) for this material if the initial stress level was 3.5 MPa (500 psi), which dropped to 0.5 MPa (70 psi) after 30 s.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





