
MORTON SALT
Introduction
Morton Salt is a subsidiary of Morton International, a manufacturer of specialty chemicals, air bags, and salt products. The Morton salt-processing facility in Silver Springs, New York, between Buffalo and Rochester, is one of six similar Morton salt-processing facilities in the United States. The Silver Springs plant employs about 200 people, ranging from unskilled to skilled. It produces salt products for water conditioning, grocery, industrial, and agricultural markets. The grocery business consists of 26-oz. round cans of iodized salt. Although the grocery business represents a relatively small portion of the total output (approximately 15 percent), it is the most profitable.
Salt production
The basic raw material, salt, is obtained by injecting water into salt caverns that are located some 2,400 feet below the surface. There, the salt deposits dissolve in the water. The resulting brine is pumped to the surface where it is converted into salt crystals. The brine is boiled, and much of the liquid evaporates, leaving salt crystals and some residual moisture, which is removed in a drying process. This process is run continuously for about six weeks at a time. Initially, salt is produced at the rate of 45 tons per hour. But the rate of output decreases due to scale buildup, so that by the sixth week, output is only 75 percent of the initial rate. At that point, the process is halted to perform maintenance on the equipment and remove the scale, after which salt production resumes.
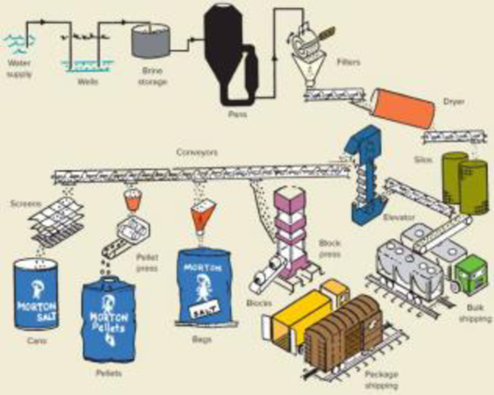
The salt is stored in silos until it is needed for production, or it is needed for production, or it is shipped in bulk to industrial customers. Conveyors move the salt to each of the four dedicated production areas, one of which is round can production (see diagram.). The discussion here focuses exclusively on round can production.
Round Can Production
Annual round can production averages roughly 3.8 million cans. Approximately 70 percent of the output is for the Morton label, and the rest is for private label. There are two parallel, high-speed production lines. The lines share common processes at the beginning of the lines, and then branch out into two identical lines. Each line is capable of producing 9,600 cans per hour (160 cans per minute). The equipment is not flexible, so the production rate is fixed. The operations are completely standardized; the only variable is the brand label that is applied. One line requires 12 production workers, while both lines together can be operated by 18 workers because of the common processes. Workers on the line perform low-skilled, repetitive tasks.
The plant produces both the salt and the cans the salt is packaged in. The cans are essentially a cylinder with a top and a bottom; they are made of cardboard, except for a plastic pour spout in the top. The cylinder portion is formed from two sheets of chip board that are glued together and then rolled into a continuous tube. The glue not only binds the material, it also provides a moisture barrier. The tube is cut in a two-step process. It is first cut into long sections, and those sections are then cut into can-size pieces. The top and bottom pieces for the cans are punched from a continuous strip of cardboard. The separate pieces move along conveyor belts to the lines where the components are assembled into cans and glued. The cans are then filled with salt and the pour spout is added. Finally, the cans are loaded onto pallets and placed into inventory, ready to be shipped to distributors.
Quality
Quality is checked at several points in the production process. Initially, the salt is checked for purity when it is obtained from the wells, Iodine and an anti-caking compound are added to the salt, and their levels are verified using chemical analysis. Crystal size is important. In order to achieve the desired size and to remove lumps, the salt is forced through a scraping screen, which can cause very fine pieces of metal to mix with the salt. However, these pieces are effectively removed by magnets that are placed at appropriate points in the process. If, for any reason, the salt is judged to be contaminated, it is diverted to a nonfood product.
Checking the quality of the cans is done primarily by visual inspection, including verifying the assembly operation is correct, checking filed cans for correct weight, inspecting cans to see that labels are labels are properly aligned, and checking to see that plastic pour spouts are correctly attached.
The equipment on the production line is sensitive to misshapen or damaged cans, and frequently jams, cussing production delays. This greatly reduces the chance of a defective can getting through the process, but it reduces productivity, and the salt in the defective cans must be scrapped. The cost of quality is fairly high, owing to the amount of product that is scrapped, the large number of inspectors, and the extensive laboratory testing that is needed.
Production Planning and Inventory
The plant can sell all of the salt it produces. The job of the production
Equipment Maintenance and Repair
The equipment is 1950s vintage, and it requires a fair amount of maintenance to keep it in good working order. Even so, breakdowns occur as parts wear out. The plant has its own tool shop where skilled workers repair parts or make new parts because replacement parts are no longer available for the old equipment.
1. Briefly describe salt production, from brine production to finished round cans.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Accounting Information Systems (14th Edition)
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Advanced Financial Accounting
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
- Prepare a graph of the monthly forecasts and average forecast demand for Chicago Paint Corp., a manufacturer of specialized paint for artists. Compute the demand per day for each month (round your responses to one decimal place). Month B Production Days Demand Forecast Demand per Day January 21 950 February 19 1,150 March 21 1,150 April 20 1,250 May 23 1,200 June 22 1,000' July 20 1,350 August 21 1,250 September 21 1,050 October 21 1,050 November 21 December 225 950 19 850arrow_forwardThe president of Hill Enterprises, Terri Hill, projects the firm's aggregate demand requirements over the next 8 months as follows: 2,300 January 1,500 May February 1,700 June 2,100 March April 1,700 1,700 July August 1,900 1,500 Her operations manager is considering a new plan, which begins in January with 200 units of inventory on hand. Stockout cost of lost sales is $125 per unit. Inventory holding cost is $25 per unit per month. Ignore any idle-time costs. The plan is called plan C. Plan C: Keep a stable workforce by maintaining a constant production rate equal to the average gross requirements excluding initial inventory and allow varying inventory levels. Conduct your analysis for January through August. The average monthly demand requirement = units. (Enter your response as a whole number.) In order to arrive at the costs, first compute the ending inventory and stockout units for each month by filling in the table below (enter your responses as whole numbers). Ending E Period…arrow_forwardMention four early warning indicators that a business may be at risk.arrow_forward
- 1. Define risk management and explain its importance in a small business. 2. Describe three types of risks commonly faced by entrepreneurs. 3. Explain the purpose of a risk register. 4. List and briefly describe four risk response strategies. (5 marks) (6 marks) (4 marks) (8 marks) 5. Explain how social media can pose a risk to small businesses. (5 marks) 6. Identify and describe any four hazard-based risks. (8 marks) 7. Mention four early warning indicators that a business may be at risk. (4 marks)arrow_forwardState whether each of the following statements is TRUE or FALSE. 1. Risk management involves identifying, analysing, and mitigating risks. 2. Hazard risks include interest rate fluctuations. 3. Entrepreneurs should avoid all forms of risks. 4. SWOT analysis is a tool for risk identification. 5. Scenario building helps visualise risk responses. 6. Risk appetite defines how much risk an organisation is willing to accept. 7. Diversification is a risk reduction strategy. 8. A risk management framework must align with business goals. 9. Political risk is only relevant in unstable countries. 10. All risks can be eliminated through insurance.arrow_forward9. A hazard-based risk includes A. Political instability B. Ergonomic issues C. Market demand D. Taxation changesarrow_forward
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,


