Concept explainers
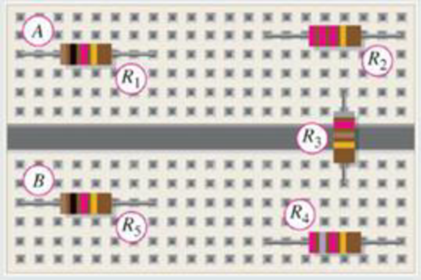
Five resistors are positioned on a protoboard as shown in Figure 6-3. Show the wiring required to connect all of the resistors in parallel between A and B. Draw a schematic and label each of the resistors with its value.
Figure 6-3
Related Problem How could the circuit wiring be simplified if R2 is removed?
Draw the simplified wiring diagram of the circuit when the resistor
Explanation of Solution
Discussion:
Refer to Figure 6-3 in the textbook for the five resistors in a proto board.
Consider the resistor
The schematic of wiring diagram to connect the resistors
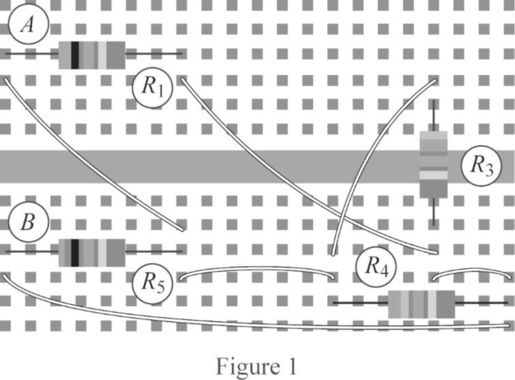
Conclusion:
Thus, the simplified wiring diagram is drawn when
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Principles Of Electric Circuits
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
- Find Va and Vb using Nodal analysisarrow_forward4. A battery operated sensor transmits to a receiver that is plugged in to a power outlet. The device is continuously operated. The battery is a 3.6 V coin-cell battery with a 245mAHr capacity. The application requires a bit rate of 36 Mbps and an error rate of less than 10^-3. The channel has a center frequency of 2.4 GHz, a bandwidth of 10 MHz and a noise power spectral density of 10^-14 W/Hz. The maximum distance is 36 meters and the losses in the channel attenuates the signal by 0.25 dB/meter. Your company has two families of chips that you can use. An M-ary ASK and an M-ary QAM chip. The have very different power requirements as shown in the table below. The total current for the system is the current required to achieve the desired Eb/No PLUS the current identified below: Hokies PSK Chip Set Operating Current NOT Including the required Eb/No for the application Hokies QAM Chip Set Operating Current NOT Including the required Eb/No for the application Chip ID M-ary Voltage (volts)…arrow_forwardUsing the 802.11a specifications given below, in Matlab (or similar tool) create the time domain signal for one OFDM symbol using QPSK modulation. See attached plot for the QPSK constellation. Your results should include the power measure in the time and frequency domain and comment on those results. BW 802.11a OFDM PHY Parameters 20 MHZ OBW Subcarrer Spacing Information Rate Modulation Coding Rate Total Subcarriers Data Subcarriers Pilot Subcarriers DC Subcarrier 16.6 MHZ 312.5 Khz (20MHz/64 Pt FFT) 6/9/12/18/24/36/48/54 Mbits/s BPSK, QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM 1/2, 2/3, 3/4 52 (Freq Index -26 to +26) 48 4 (-21, -7, +7, +21) *Always BPSK Null (0 subcarrier) 52 subarriers -7 (48 Data, 4 Pilot (BPSK), 1 Null) -26 -21 0 7 21 +26 14 One Subcarrier 1 OFDM symbol 1 OFDM Burst -OBW 16.6 MHz BW 20 MHZ 1 constellation point = 52 subcarriers = one or more OFDM symbols 802.11a OFDM Physical Parameters Show signal at this point x bits do Serial Data d₁ S₁ Serial-to- Input Signal Parallel Converter IFFT…arrow_forward
- Find Vb and Va using Mesh analysisarrow_forward1. The communication channel bandwidth is 25 MHz centered at 1GHz and has a noise power spectral density of 10^-9 W/Hz. The channel loss between the transmitter and receiver is 25dB. The application requires a bit rate of 200Mbps and BER of less than 10^-4. Excluding Mary FSK, Determine the minimum transmit power required.arrow_forward2. An existing system uses noncoherent BASK. The application requires a BER of <10^-5. The current transmit power is 25 Watts. If the system changes to a coherent BPSK modulation scheme, what is the new transmit power required to deliver the same BER?arrow_forward
- 3. You are to design a 9-volt battery operated communication system that must last 3 years without replacing batteries. The communication channel bandwidth is 100 KHz centered at 5.8 GHz. The application requires a BER of <10^-5 and a data rate of 1 Mbps. The channel can be modeled as AWGN with a noise power spectral density of 10^-8 W/Hz. ((a) What modulation scheme would you use? B) what is the required capacity of the batteries? and (c) is the battery commercially available?arrow_forwardDesign a traffic light PIC microcontroller program with Green LED has 3 Sec Yellow LED has 0.5 Sec Red LED has 3 Sec RASAN4SSC20UT 8 RBOINT RB1 9 RB2 U1 PIC16F877A-I/PT 18 19 MCLRVPP RAOANO 20 RA1AN1 30 OSCICLKI 21 RAZAN2VREF-CVREF 31 OSC2CLKO RABAN3VREF+ 22 LED1 LED-3MM 〃 R1 330 RA4TOCKIC1OUT 23 7 VDD 28 VDD 6 VSS 29 VSS 24 LED2 LED-3MM R2 10 330 RB3PGM 11 + 14 RB4 38 RDOPSPO RB5 15 LED3 39 RD1PSP1 40 RD2PSP2 RB6PGC- RB7PGD 17 16 LED-3MM R3 330 41 RD3PSP3 2 RD4PSP4 RCOT1OSOTICKK 3 RDSPSPS RC1T10SICCP24 RD6PSP6 RC2CCP1 5 RD7PSP7 RC3SCKSCL RC4SDISDA 25 REORDANS RCSSDO 27 29 REIWRANG RC6TXCK- RE2CSAN7 RC7RXDT DAWWWW 32 35 36 37 42 43 44 1 12 NO 13 NC 33 NO 34 NCarrow_forward: +0 العنوان I need a detailed drawing with explanation しじ ined sove in peaper Anoting Q4// Draw and Evaluate √√√xy-²sin(y²)dydx PU+96er Lake Ge Q3// Find the volume of the region between the cylinder 2 = y² and the xy- plane that is bounded by the planes x = 1, x = 2, y = -2, and y = 2. T Marrow_forward
 Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
