
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780137514724
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 1FP
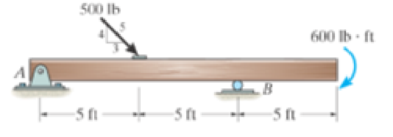
Determine the horizontal and vertical components of reaction at the supports. Neglect the thickness of the beam.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The uniform rods have a mass per unit length of 10kg/m
. (Figure 1)If the dashpot has a damping coefficient of c=50N⋅s/m
, and the spring has a stiffness of k=600N/m
, show that the system is underdamped, and then find the pendulum's period of oscillation.
10-50.
The principal plane stresses and associated strains in a plane
at a point are σ₁ = 30 ksi, σ₂ = -10 ksi, e₁ = 1.14(10-3),
€2=-0.655(103). Determine the modulus of elasticity and
Poisson's ratio.
emps to plum...
Wednesday
FI
a
וח
2
Q Search
48 F5
- F6
4+
F7
FB
F9
FIO
FII
F12
&
*
S
6
7
8
9
ㅁ
F2
#
*F3
3
$
4
F4
%
W
E
R
T
Y
ப
S
ALT
D
F
G
H
X
C
V
B
N
J
Σ
H
L
ว
{
P
[
]
ALT
"
DELETE
BACKSPACE
NUM
LOCK
T
7
HOME
ENTER
4
PAUSE
SHIFT
CTRL
E
10−9. The state of strain at the point has components of ϵx = −100(10−6), ϵy = −200(10−6), and γxy=100(10−6). Use the strain transformation equations to determine (a) the in-plane principal strains and (b) the maximum in-plane shear strain and average normal strain. In each case specify the orientation of the element and show how the strains deform the element within the x−y plane.
Chapter 5 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Ch. 5 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5 - The truss is supported by a pin at A and a roller...Ch. 5 - Prob. 4FPCh. 5 - The 25 kg bar has a center of mass at G. If it is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 6FPCh. 5 - Determine the reactions at the supports. Prob....Ch. 5 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5 - Determine the reactions at the supports. Prob....Ch. 5 - A uniform glass rod having a length L is placed in...
Ch. 5 - If the intensity of the distributed load acting on...Ch. 5 - Prob. 23PCh. 5 - Prob. 24PCh. 5 - Prob. 25PCh. 5 - Prob. 27PCh. 5 - Prob. 30PCh. 5 - Prob. 35PCh. 5 - The cantilevered jib crane is used to support the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 38PCh. 5 - Prob. 39PCh. 5 - Determine the stiffness k of each spring so that...Ch. 5 - The boom supports the two vertical loads. Neglect...Ch. 5 - Prob. 43PCh. 5 - The 10-kg uniform rod is pinned at end A. If It is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 46PCh. 5 - Prob. 47PCh. 5 - Prob. 48PCh. 5 - Prob. 53PCh. 5 - The uniform rod has a length I and weight W. It is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 7FPCh. 5 - Prob. 8FPCh. 5 - Prob. 9FPCh. 5 - Determine the support reactions at the smooth...Ch. 5 - Prob. 11FPCh. 5 - Determine the components of reaction that the...Ch. 5 - The uniform loads has a mass of 600 kg and is...Ch. 5 - The 100-lb door has its center of gravity at G....Ch. 5 - Determine me tension in each cable and the...Ch. 5 - The bent rod is supported at A, B, and C by smooth...Ch. 5 - The bent rod is supported at A, B, and C by smooth...Ch. 5 - Prob. 77PCh. 5 - Prob. 78PCh. 5 - Prob. 80PCh. 5 - Prob. 82PCh. 5 - The bar AB is supported by two smooth collars. At...Ch. 5 - Prob. 84PCh. 5 - Prob. 85PCh. 5 - Prob. 86PCh. 5 - Both pulleys are fixed to the shaft and as the...Ch. 5 - Member AB is supported by a cable BC and at A by a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 2RPCh. 5 - Prob. 4RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The strain gage is placed on the surface of the steel boiler as shown. If it is 0.5 in. long, determine the pressure in the boiler when the gage elongates 0.2(10−3) in. The boiler has a thickness of 0.5 in. and inner diameter of 60 in. Also, determine the maximum x, y in-plane shear strain in the material. Take Est=29(103)ksi, vst=0.3.arrow_forward(read image, answer given)arrow_forward6/86 The connecting rod AB of a certain internal-combustion engine weighs 1.2 lb with mass center at G and has a radius of gyration about G of 1.12 in. The piston and piston pin A together weigh 1.80 lb. The engine is running at a constant speed of 3000 rev/min, so that the angular velocity of the crank is 3000(2)/60 = 100л rad/sec. Neglect the weights of the components and the force exerted by the gas in the cylinder compared with the dynamic forces generated and calculate the magnitude of the force on the piston pin A for the crank angle 0 = 90°. (Suggestion: Use the alternative moment relation, Eq. 6/3, with B as the moment center.) Answer A = 347 lb 3" 1.3" B 1.7" PROBLEM 6/86arrow_forward
- 6/85 In a study of head injury against the instrument panel of a car during sudden or crash stops where lap belts without shoulder straps or airbags are used, the segmented human model shown in the figure is analyzed. The hip joint O is assumed to remain fixed relative to the car, and the torso above the hip is treated as a rigid body of mass m freely pivoted at O. The center of mass of the torso is at G with the initial position of OG taken as vertical. The radius of gyration of the torso about O is ko. If the car is brought to a sudden stop with a constant deceleration a, determine the speed v relative to the car with which the model's head strikes the instrument panel. Substitute the values m = 50 kg, 7 = 450 mm, r = 800 mm, ko = 550 mm, 0 = 45°, and a = 10g and compute v. Answer v = 11.73 m/s PROBLEM 6/85arrow_forwardUsing AutoCADarrow_forward340 lb 340 lb Δarrow_forward
- 4. In a table of vector differential operators, look up the expressions for V x V in a cylindrical coordinate system. (a) Compute the vorticity for the flow in a round tube where the velocity profile is = vo [1-(³] V₂ = Vo (b) Compute the vorticity for an ideal vortex where the velocity is Ve= r where constant. 2πг (c) Compute the vorticity in the vortex flow given by Ve= r 2лг 1- exp ( r² 4vt (d) Sketch all the velocity and vorticity profiles.arrow_forwardIn the figure, Neglects the heat loss and kinetic and potential energy changes, calculate the work produced by the turbine in kJ T = ??? Steam at P=3 MPa, T = 280°C Turbine Rigid tank V = 1000 m³ Turbine Rigid tank V = 100 m³ V = 1000 m³ V = 100 m³ The valve is opened. Initially: evacuated (empty) tank O a. 802.8 Initially: Closed valve O b. 572 O c. 159.93 Od. 415 e. 627.76 equilibriumarrow_forwardPlease find the torsional yield strength, the yield strength, the spring index, and the mean diameter. Use: E = 28.6 Mpsi, G = 11.5 Mpsi, A = 140 kpsi·in, m = 0.190, and relative cost= 1.arrow_forward
- A viscoelastic column is made of a material with a creep compliance of D(t)= 0.75+0.5log10t+0.18(log10t)^2 GPA^-1 for t in s. If a constant compressive stress of σ0 = –100 MPa is applied at t = 0, how long will it take (= t1/2) for the height of the column to decrease to ½ its original value? Note: You will obtain multiple answers for this problem! One makes sense physically and one does not.arrow_forwardA group of 23 power transistors, dissipating 2 W each, are to be cooled by attaching them to a black-anodized square aluminum plate and mounting the plate on the wall of a room at 30°C. The emissivity of the transistor and the plate surfaces is 0.9. Assuming the heat transfer from the back side of the plate to be negligible and the temperature of the surrounding surfaces to be the same as the air temperature of the room, determine the length of the square plate if the average surface temperature of the plate is not to exceed 50°C. Start the iteration process with an initial guess of the size of the plate as 43 cm. The properties of air at 1 atm and the film temperature of (Ts + T)/2 = (50 + 30)/2 = 40°C are k = 0.02662 W/m·°C, ν = 1.702 × 10–5 m2 /s, Pr = 0.7255, and β = 0.003195 K–1. Multiple Choice 0.473 m 0.284 m 0.513 m 0.671 marrow_forwardA 40-cm-diameter, 127-cm-high cylindrical hot water tank is located in the bathroom of a house maintained at 20°C. The surface temperature of the tank is measured to be 44°C and its emissivity is 0.4. Taking the surrounding surface temperature to be also 20°C, determine the rate of heat loss from all surfaces of the tank by natural convection and radiation. The properties of air at 32°C are k=0.02603 W/m-K, v=1.627 x 10-5 m²/s, Pr = 0.7276, and ẞ = 0.003279 K-1 The rate of heat loss from all surfaces of the tank by natural convection is The rate of heat loss from all surfaces of the tank by radiation is W. W.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY