
EBK PHYSICS
5th Edition
ISBN: 8220103026918
Author: Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 12PCE
Driving home from school one day, you spot a ball rolling out into the street (Figure 5-27). You brake for 1 20 s, slowing your 950-kg car from 16 0 m/s to 9 50 m/s. (a) What was the average force exerted on your car during braking? (b) How far did you travel while braking?
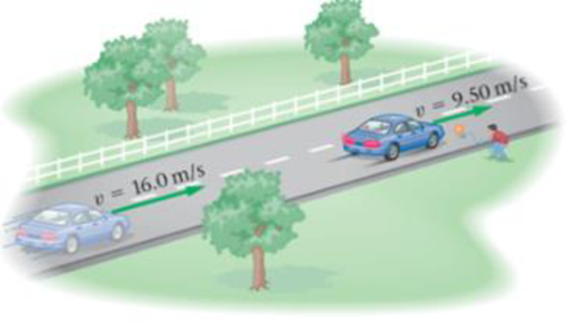
Figure 5-27 Problem 12
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
If the 50-kg crate starts from rest and attains a speed of
6 m/s when it has traveled a distance of 15 m, determine the
force P acting on the crate. The coefficient of kinetic friction
between the crate and the ground is μ = 0.3.
12.)John and Peter were pushing a 2000 kg car and it reached a speed of 3.0 m/s after starting from rest. It covered a distance of 10 meter; What is the amount of force (Newton) exerted by John and Peter if the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.100?
A person steps horizontally off the roof of a single-story house that is 3.1 m high. When his feet hit theground below, he bends his knees such that his torso decelerates over a distance of 0.65 m before coming to astop. If the mass of his torso is 50 kg, what is the average net force exerted on his torso over this distance?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS
Ch. 5.1 - Two forces have magnitudes F1 and F2. If these...Ch. 5.2 - Which of the following statements is correct? A: A...Ch. 5.3 - The acceleration of an object has a magnitude a....Ch. 5.4 - A force F pushes on three boxes that slide without...Ch. 5.5 - An object is acted on by a single force that is at...Ch. 5.6 - When a certain person steps onto a scale on solid...Ch. 5.7 - Figure 5-23 shows four identical bricks that are...Ch. 5 - Driving down the road, you hit the brakes...Ch. 5 - Youve probably seen pictures of someone pulling a...Ch. 5 - As you read this, you are most likely sitting...
Ch. 5 - When a dog gets wet, it shakes its body from head...Ch. 5 - A young girl slides down a rope. As she slides...Ch. 5 - A block of mass m hangs from a string attached to...Ch. 5 - An astronaut on a space walk discovers that his...Ch. 5 - Two untethered astronauts on a space walk decide...Ch. 5 - In Figure 5-25 Wilbur asks Mr. Ed, the talking...Ch. 5 - A whole brick has more mass than half a brick,...Ch. 5 - The force exerted by gravity on a whole brick is...Ch. 5 - Is it possible for an object at rest to have only...Ch. 5 - Is it possible for an object to be in motion and...Ch. 5 - A bird cage, with a parrot inside, hangs from a...Ch. 5 - Suppose you jump from the cliffs of Acapulco and...Ch. 5 - A friend tells you that since his car is at rest,...Ch. 5 - Since all objects are weightless in orbit, how is...Ch. 5 - To clean a rug, you can hang it from a clothesline...Ch. 5 - If you step off a high board and drop to the water...Ch. 5 - Is it possible for an object to be moving in one...Ch. 5 - Since a bucket of water is weightless in space,...Ch. 5 - In the movie The Rocketeer, a teenager discovers a...Ch. 5 - List three common objects that have a weight of...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m is initially at rest. After a...Ch. 5 - On a planet far, far away, an astronaut picks up a...Ch. 5 - In a grocery store, you push a 15.4-kg shopping...Ch. 5 - You are pulling your little sister on her sled...Ch. 5 - A 0.53-kg billiard ball initially at rest is given...Ch. 5 - A 92-kg water skier floating in a lake is pulled...Ch. 5 - A 0.5-kg object is acted on by a force whose x...Ch. 5 - Predict/Explain You drop two balls of equal...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate A 42.0-kg parachutist is moving...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate In baseball, a pitcher can...Ch. 5 - A major-league catcher gloves a 92 mi/h pitch and...Ch. 5 - Driving home from school one day, you spot a ball...Ch. 5 - Stopping a 747 A 747 jetliner lands and begins to...Ch. 5 - The Ux-versus-time graph for a 1.8-kg object is...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate A drag racer crosses the finish...Ch. 5 - Predict/Explain A small car collides with a large...Ch. 5 - Predict/Explain A small car collides with a large...Ch. 5 - As you catch a 0.14-kg ball it accelerates at...Ch. 5 - BIO Woodpecker Concussion Prevention A woodpecker...Ch. 5 - On vacation, your 1400-kg car pulls a 560-kg...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate An 85-kg parent and a ?4-kg...Ch. 5 - A force of magnitude 7.50 N pushes three boxes...Ch. 5 - A force of magnitude 7.50 N pushes three boxes...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate Two boxes sit side-by-side on a...Ch. 5 - A skateboarder on a ramp is accelerated by a...Ch. 5 - Three objects, A, B, and C, have x and y...Ch. 5 - A farm tractor tows a 3300-kg trailer up a 14...Ch. 5 - A shopper pushes a 7 5-kg shopping cart up a 13...Ch. 5 - Two crewmen pull a rail through a lock, as shown...Ch. 5 - A hockey puck is acted on by one or more forces as...Ch. 5 - To give a 19-kg child a ride, two teenagers pull...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate A 65-kg skier speeds down a...Ch. 5 - An object acted on by three forces moves with...Ch. 5 - A train is traveling up a 2 88 incline at a speed...Ch. 5 - The Force Exerted on the Moon In Figure 5-37 we...Ch. 5 - You pull upward on a stuffed suitcase with a force...Ch. 5 - BIO Brain Growth A newborn babys brain grows...Ch. 5 - Suppose a rocket launches with an acceleration of...Ch. 5 - During an episode of turbulence in an airplane you...Ch. 5 - At the bow of a ship on a stormy sea, a crewman...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate As part of a physics experiment...Ch. 5 - When you weigh yourself on good old terra firma...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate BIO Flight of the Samara A...Ch. 5 - When you lift a bowling ball with a force of 82 N,...Ch. 5 - A 23-kg suitcase is pulled with constant speed by...Ch. 5 - (a) Draw a free-body diagram for the skier in...Ch. 5 - A 9.3-kg child sits in a 3.7-kg high chair. (a)...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-39 shows the normal force N experienced...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-40 shows the normal force N as a function...Ch. 5 - A 5.0-kg bag of potatoes sits on the bottom of a...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate (a) Find the normal force...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate A gardener mows a lawn with an...Ch. 5 - Figure 5-41 Problems 53 53 An ant walks slowly...Ch. 5 - CE Predict/Explain Riding in an elevator moving...Ch. 5 - CE Predict/Explain Riding in an elevator moving...Ch. 5 - CE Give the direction of the net force acting on...Ch. 5 - CE Predict/Explain You jump out of an airplane and...Ch. 5 - In a tennis serve, a 0.070-kg ball can be...Ch. 5 - BIO Human Heart Force The left ventricle of the...Ch. 5 - A 51 5-kg swimmer with an initial speed of 1.25...Ch. 5 - The ax-versus-time graph for a 2.0-kg object is...Ch. 5 - A skateboarder starts from rest and rolls down a...Ch. 5 - The rotors of a 15,200-kg heavy-lift helicopter...Ch. 5 - As it pulls itself up to a branch, a chimpanzee...Ch. 5 - CE Each of the three identical hockey pucks shown...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate The VASIMR Rocket NASA plans to...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m = 5.95 kg has an acceleration...Ch. 5 - At the local grocery store, you push a 14.5-kg...Ch. 5 - BIO Predict/Calculate The Force of Running...Ch. 5 - BIO Predict/Calculate Grasshopper Liftoff To...Ch. 5 - Takeoff from an Aircraft Carrier On an aircraft...Ch. 5 - The Ux-versus-time graph for a 1.8-kg object is...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate An archer shoots a 0.024-kg...Ch. 5 - An apple of mass m = 0.13 kg falls out of a tree...Ch. 5 - BIO The Fall of T. rex Paleontologists estimate...Ch. 5 - Deep Space 1 The NASA spacecraft Deep Space 1 was...Ch. 5 - Your groceries are in a bag with paper handles....Ch. 5 - BIO A Leafhopper's Leap The motion of jumping...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate At the airport, you observe some...Ch. 5 - Prob. 80GPCh. 5 - Two boxes are at rest on a smooth, horizontal...Ch. 5 - You have been hired to help improve the material...Ch. 5 - Prob. 83GPCh. 5 - A baseball of mass m and initial speed U strikes a...Ch. 5 - When two people push in the same direction on an...Ch. 5 - An air-track cart of mass m1 = 0.14 kg is moving...Ch. 5 - BIO Increasing Safety in a Collision Safety...Ch. 5 - BIO Increasing Safety in a Collision Safety...Ch. 5 - BIO Increasing Safety in a Collision Safety...Ch. 5 - BIO Increasing Safety in a Collision Safety...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 5-8 Suppose...Ch. 5 - Referring to Example 5-8 Suppose the force of 30.0...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Figure 5-13 Suppose...Ch. 5 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Figure 5-13 Suppose...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1.1 Write a one-sentence definition for each of the following:
a. chemistry
b. chemical
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
1. Why is the quantum-mechanical model of the atom important for understanding chemistry?
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Fibrous connective tissue consists of ground substance and fibers that provide strength, support, and flexibili...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Match the following examples of mutagens. Column A Column B ___a. A mutagen that is incorporated into DNA in pl...
Microbiology: An Introduction
4. Three groups of nonvascular plants are _______, ______, and _______. Three groups of seedless vascular plant...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
2. Whether an allele is dominant or recessive depends on
a. how common the allele is, relative to other alleles...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A cart is set rolling across a level table, at the same speed on every trial. If it runs into a patch of sand, the cart exerts on the sand an average horizontal force of 6 N and travels a distance of 6 cm through the sand as it comes to a stop. It instead the cart runs into a patch of gravel on which the can exerts an average horizontal force of 9 N, how far into the gravel will the cart roll before stopping? (a) 9 cm (b) 6 cm (c) 4 cm (d) 3 cm (e) none of those answersarrow_forwardProblems 67. 70. 71. and 72 are grouped. A A block of mass M is placed on a frictionless plane. The plane is inclined at an angle , and the block is a distance d from its end. Of course, we would expect the block to slip down the plane. Suppose we revolve the incline around the vertical axis shown in Figure P6.67 instead. At what period of revolution will the block remain in place on the plane? FIGURE P6.67 Problems 67. 71. and 72.arrow_forwardA warehouse worker is pushing a 90.0 kg crate with a horizontal force of 291 N at a speed of v = 0.875 m/s across the warehouse floor. He encounters a rough horizontal section of the floor that is 0.75 m long and where the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and floor is 0.351. T↑ m Determine the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on the crate while it is pushed over the rough section of the floor. magnitude -18.60 xarrow_forward
- In a laboratory model of cars skidding to a stop, data is collected on blocks sliding across a table as each comes to rest. The stopping distance for each block is measured after it has been launched with some initial speed. Experiments are performed on four blocks, each with mass m = 7 kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction and the initial speed of each block was as follows: a) Block 1: Hx = 0.2 , vị = 2 m/s b) Block 2: µk = 0.2 , Vị = 4 m/s c) Block 3: µz = 0.4 , v; = 2 m/s d) Block 4: Hx = 0.4 , vị = 4 m/s Calculate the stopping distance for each block. Note that you can use either energetics (conservation of energy) or kinematics (forces) to answer this question. Try both!arrow_forwardDancers experience large forces associated with the jumps they make. For example, when a dancer lands after a vertical jump, the force exerted on the head by the neck must exceed the head's weight by enough to cause the head to slow down and come to rest. The head is about 9.4%% of a typical person's mass. Video analysis of a 70 kgkg dancer landing after a vertical jump shows that her head slows down from 4.2 m/sm/s to rest in a time of 0.19 s.What is the magnitude of the average force that her neck exerts on her head during the landing?arrow_forwardF(x) A 8kg block initially at rest is acted on by the force shown at an angle of 0 = 20'. The magnitude of this force changes as the block 4. moves: F(x) = (7.5 N/m)x. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the floor and the box is µ = 0.2. Determine the speed of the block after the block has moved 5.0m.arrow_forward
- The coefficient of friction between the tires of Shirley's 1985 Ford Coupe and the dry pavement is 0.74. She doesn't drive the car often because it's becoming an antique, but she took it out for a gentle drive yesterday. While driving, she has to suddenly and forcefully brake when the light turned red. She probably shouldn't have been texting and driving! Her car (mass = 1.31x10³ kg) skids to a stop with an acceleration of m/s². Use the approximation g = 10 m/s².arrow_forwardBeginning at time t = 0, a student exerts a horizontal force on a box of mass 30 kg, causing it to move at 1.2 m/s toward an elevator door located 16 m away, as shown above. The coefficient of kinetic friction uk between the box and the floor is 0.20. At t = 4.0 s, the elevator door opens and remains open for 5.0 s. The student immediately exerts a larger constant force on the box and the front of the box reaches the elevator door just as it starts to close. (c) Calculate the magnitude of the new force that the student exerts.arrow_forwardA swimmer has just jumped off a diving board. The swimmer has a mass of m = 56.4 kg and jumps off a board that is h = 7.15 m above the water. Exactly T = 4.1 seconds after entering the water, her downward motion is stopped. a) Write an expression for the magnitude of the average upward force Fw exerted on her by the water in terms of the variables given in the problem statement and g (9.80 m/s2). b) What is the magnitude of the average upward force Fw (in N) exerted on her by the water?arrow_forward
- An object with a mass 10 kg moves at a constant velocity of 10 m/s. A constant force then acts for 4 seconds on the object giving it a speed of 2m/s in opposite direction. The acceleration produced is:- A 3m/s² B -3m/s² C 0.3m/s² D -0.3m/s²arrow_forwardBeginning at time t = 0, a student exerts a horizontal force on a box of mass 30 kg, causing it to move at 1.2 m/s toward an elevator door located 16 m away, as shown above. The coefficient of kinetic friction uk between the box and the floor is 0.20. At t = 4.0 s, the elevator door opens and remains open for 5.0 s. The student immediately exerts a larger constant force on the box and the front of the box reaches the elevator door just as it starts to close. (d) On the axes below, sketch graphs of the acceleration a, velocity v, and position x of the box versus time t between t = 0 and the time the front of the box reaches the elevator.arrow_forwardThe motorcycle has a mass of 0.5-Mg and a negligible size. Itpasses point ‘A’ traveling with a speed of 15m/s, which isincreasing at a constant rate of 1.5m/s2. Determine the resultant frictional force exerted by the road on the tires at this instant.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F = ma; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzA6IBWUEDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY