
Applying the Concepts 4–2
Which Pain Reliever Is Best?
Assume that following an injury you received from playing your favorite sport, you obtain and read information on new pain medications. In that information you read of a study that was conducted to test the side effects of two new pain medications. Use the following table to answer the questions and decide which, if any, of the two new pain medications you will use.
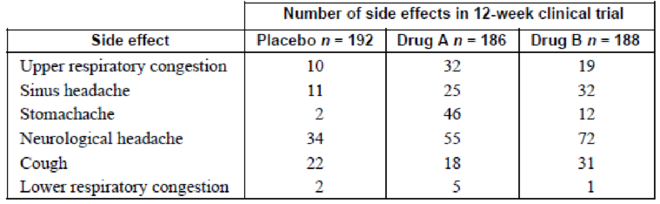
1. How many subjects were in the study?
2. How long was the study?
3. What were the variables under study?
4. What type of variables are they, and what level of measurement are they on?
5. Are the numbers in the table exact figures?
6. What is the
7. What is the probability that a person was receiving a placebo or drug A? Are these mutually exclusive events? What is the complement to this
8. What is the probability that a randomly selected person was receiving a placebo or experienced a neurological headache?
9. What is the probability that a randomly selected person was not receiving a placebo or experienced a sinus headache?
1.
To obtain: The number of objects in the study.
Answer to Problem 1AC
The number of objects in the study is 566.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The data set represents the three groups. Those are placebo, Drug A and drug B.
Calculation:
The placebo group contains 192 subjects, group A contains 186 subjects and Group B contains 188 subjects.
The total number of subjects in the given study is
Thus, the total number of subjects in the given study is 566.
2.
To identify: The time duration for the study.
Answer to Problem 1AC
The time duration for the study is 12 weeks.
Explanation of Solution
Justification:
In a clinical trial, the number of side effects for three groups was observed for 12 weeks.
Thus, the time duration for the study is 12 weeks.
3.
To identify: The variables in the study.
Answer to Problem 1AC
The variables in the study are type of pain reliever and the side effects.
Explanation of Solution
Justification:
In the study, the side effects for three groups are observed. That is, the study represents the number of side effects for each group.
Thus, the variables in the study are side effects and pain relievers.
4.
To identify: The type of variables and the level of measurement.
Answer to Problem 1AC
The type of variable is qualitative and the level of measurement is nominal.
Explanation of Solution
Justification:
The variable ‘side effect’ represents 6 categories and ‘pain reliever’ represents 3 groups like placebo, group A and group B. Therefore, the variables in the study represent the qualitative variables. Moreover, the qualitative variables measured on nominal scale.
Thus, the type of variables is qualitative and the level of measurement is nominal.
5.
To observe: Whether the figures in the table or exact or not.
Answer to Problem 1AC
The numbers in the study are exact figures.
Explanation of Solution
Justification:
The numbers in the table represents the number of side effects. Hence, the numbers are exact.
Thus, the numbers in the study are exact figures.
6.
To obtain: The probability of randomly selected person was receiving a placebo.
Answer to Problem 1AC
The probability of randomly selected person was receiving a placebo is 0.339.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The table shows the number of side effects in placebo group is 192 and the total number of side effects is 566.
Calculation:
The formula for probability of randomly selected person with placebo is,
Substitute 192 for ‘Number of side effects in placebo’ and 566 for ‘Total number of side effects’,
Thus, the probability of randomly selected person was receiving a placebo is 0.339.
7.
To obtain: The probability of randomly selected person was receiving a placebo or drug A.
To observe: Whether the events are mutually exclusive or not.
To identify: The complement to the event.
Answer to Problem 1AC
The probability of randomly selected person was receiving a placebo or drug A is 0.668.
The events placebo and drug A are mutually exclusive.
The complement for the event is the randomly selected person was receiving drug B.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The table shows the number of side effects in placebo group is 192, the number side effects in drug A is 186 and the total number of side effects is 566.
Calculation:
The formula for probability of randomly selected person with drug A is,
Substitute 186 for ‘Number of side effects in drug A’ and 566 for ‘Total number of side effects’,
Addition Rule:
The formula for probability of getting placebo group or drug A is,
Substitute 0.339 for ‘
Thus, the probability of randomly selected person was receiving a placebo or drug A is 0.668.
Justification:
There is intersection part between place and drug A. Hence, the placebo and drug A are mutually exclusive events. The complement event for ‘person receiving the placebo or drug A’ is the randomly selected person was receiving drug B.
Thus, the events placebo and drug A are mutually exclusive and the complement for the event is the randomly selected person was receiving drug B.
8.
To obtain: The probability of randomly selected person was receiving a placebo or experienced a neurological headache.
Answer to Problem 1AC
The probability of randomly selected person was receiving a placebo or experienced a neurological headache is 0.564.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The table shows the number of side effects in placebo group is 192, the number side effects in placebo and neurological headache is 34.
Calculation:
The formula for probability of randomly selected person with neurological headache is,
The formula for probability of randomly selected person with placebo and neurological headache is,
Addition Rule for non-mutually exclusive events:
The formula for probability of getting placebo group or neurological headache is,
Substitute 0.339 for ‘
Thus, the probability of randomly selected person was receiving a placebo or experienced a neurological headache is 0.564.
9.
To obtain: The probability of randomly selected person was not receiving a placebo or experienced a sinus headache.
Answer to Problem 1AC
The probability of randomly selected person was not receiving a placebo or experienced a sinus headache is 0.68.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The table shows the number of side effects in placebo group is 192, the number side effects in placebo and sinus headache is 11.
Calculation:
The probability of randomly selected person with no placebo is
The formula for probability of randomly selected person with placebo and sinus headache is,
Addition Rule for non-mutually exclusive events:
The formula for probability of getting placebo group or sinus headache is,
Substitute 0.339 for ‘
Thus, the probability of randomly selected person was not receiving a placebo or experienced a sinus headache is0.68.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Elementary Statistics: A Step By Step Approach
- The following ordered data list shows the data speeds for cell phones used by a telephone company at an airport: A. Calculate the Measures of Central Tendency from the ungrouped data list. B. Group the data in an appropriate frequency table. C. Calculate the Measures of Central Tendency using the table in point B. 0.8 1.4 1.8 1.9 3.2 3.6 4.5 4.5 4.6 6.2 6.5 7.7 7.9 9.9 10.2 10.3 10.9 11.1 11.1 11.6 11.8 12.0 13.1 13.5 13.7 14.1 14.2 14.7 15.0 15.1 15.5 15.8 16.0 17.5 18.2 20.2 21.1 21.5 22.2 22.4 23.1 24.5 25.7 28.5 34.6 38.5 43.0 55.6 71.3 77.8arrow_forwardII Consider the following data matrix X: X1 X2 0.5 0.4 0.2 0.5 0.5 0.5 10.3 10 10.1 10.4 10.1 10.5 What will the resulting clusters be when using the k-Means method with k = 2. In your own words, explain why this result is indeed expected, i.e. why this clustering minimises the ESS map.arrow_forwardwhy the answer is 3 and 10?arrow_forward
- PS 9 Two films are shown on screen A and screen B at a cinema each evening. The numbers of people viewing the films on 12 consecutive evenings are shown in the back-to-back stem-and-leaf diagram. Screen A (12) Screen B (12) 8 037 34 7 6 4 0 534 74 1645678 92 71689 Key: 116|4 represents 61 viewers for A and 64 viewers for B A second stem-and-leaf diagram (with rows of the same width as the previous diagram) is drawn showing the total number of people viewing films at the cinema on each of these 12 evenings. Find the least and greatest possible number of rows that this second diagram could have. TIP On the evening when 30 people viewed films on screen A, there could have been as few as 37 or as many as 79 people viewing films on screen B.arrow_forwardQ.2.4 There are twelve (12) teams participating in a pub quiz. What is the probability of correctly predicting the top three teams at the end of the competition, in the correct order? Give your final answer as a fraction in its simplest form.arrow_forwardThe table below indicates the number of years of experience of a sample of employees who work on a particular production line and the corresponding number of units of a good that each employee produced last month. Years of Experience (x) Number of Goods (y) 11 63 5 57 1 48 4 54 5 45 3 51 Q.1.1 By completing the table below and then applying the relevant formulae, determine the line of best fit for this bivariate data set. Do NOT change the units for the variables. X y X2 xy Ex= Ey= EX2 EXY= Q.1.2 Estimate the number of units of the good that would have been produced last month by an employee with 8 years of experience. Q.1.3 Using your calculator, determine the coefficient of correlation for the data set. Interpret your answer. Q.1.4 Compute the coefficient of determination for the data set. Interpret your answer.arrow_forward
- Can you answer this question for mearrow_forwardTechniques QUAT6221 2025 PT B... TM Tabudi Maphoru Activities Assessments Class Progress lIE Library • Help v The table below shows the prices (R) and quantities (kg) of rice, meat and potatoes items bought during 2013 and 2014: 2013 2014 P1Qo PoQo Q1Po P1Q1 Price Ро Quantity Qo Price P1 Quantity Q1 Rice 7 80 6 70 480 560 490 420 Meat 30 50 35 60 1 750 1 500 1 800 2 100 Potatoes 3 100 3 100 300 300 300 300 TOTAL 40 230 44 230 2 530 2 360 2 590 2 820 Instructions: 1 Corall dawn to tha bottom of thir ceraan urina se se tha haca nariad in archerca antarand cubmit Q Search ENG US 口X 2025/05arrow_forwardThe table below indicates the number of years of experience of a sample of employees who work on a particular production line and the corresponding number of units of a good that each employee produced last month. Years of Experience (x) Number of Goods (y) 11 63 5 57 1 48 4 54 45 3 51 Q.1.1 By completing the table below and then applying the relevant formulae, determine the line of best fit for this bivariate data set. Do NOT change the units for the variables. X y X2 xy Ex= Ey= EX2 EXY= Q.1.2 Estimate the number of units of the good that would have been produced last month by an employee with 8 years of experience. Q.1.3 Using your calculator, determine the coefficient of correlation for the data set. Interpret your answer. Q.1.4 Compute the coefficient of determination for the data set. Interpret your answer.arrow_forward
- Q.3.2 A sample of consumers was asked to name their favourite fruit. The results regarding the popularity of the different fruits are given in the following table. Type of Fruit Number of Consumers Banana 25 Apple 20 Orange 5 TOTAL 50 Draw a bar chart to graphically illustrate the results given in the table.arrow_forwardQ.2.3 The probability that a randomly selected employee of Company Z is female is 0.75. The probability that an employee of the same company works in the Production department, given that the employee is female, is 0.25. What is the probability that a randomly selected employee of the company will be female and will work in the Production department? Q.2.4 There are twelve (12) teams participating in a pub quiz. What is the probability of correctly predicting the top three teams at the end of the competition, in the correct order? Give your final answer as a fraction in its simplest form.arrow_forwardQ.2.1 A bag contains 13 red and 9 green marbles. You are asked to select two (2) marbles from the bag. The first marble selected will not be placed back into the bag. Q.2.1.1 Construct a probability tree to indicate the various possible outcomes and their probabilities (as fractions). Q.2.1.2 What is the probability that the two selected marbles will be the same colour? Q.2.2 The following contingency table gives the results of a sample survey of South African male and female respondents with regard to their preferred brand of sports watch: PREFERRED BRAND OF SPORTS WATCH Samsung Apple Garmin TOTAL No. of Females 30 100 40 170 No. of Males 75 125 80 280 TOTAL 105 225 120 450 Q.2.2.1 What is the probability of randomly selecting a respondent from the sample who prefers Garmin? Q.2.2.2 What is the probability of randomly selecting a respondent from the sample who is not female? Q.2.2.3 What is the probability of randomly…arrow_forward
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning





