
Physics for Science and Engineering With Modern Physics, VI - Student Study Guide
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780132273244
Author: Doug Giancoli
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 34, Problem 56GP
Consider two antennas
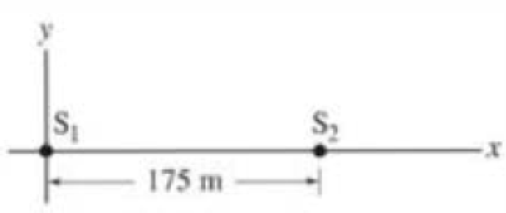
FIGURE 34–30
Problem 56.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Solve and answer the problem correctly please. Thank you!!
Solve and answer the problem correctly please. Thank you!!
Chapter 34 Solutions
Physics for Science and Engineering With Modern Physics, VI - Student Study Guide
Ch. 34.2 - A light beam in air with wavelength = 500 nm,...Ch. 34.4 - What are the values for the intensity I when (a) y...Ch. 34 - Prob. 1QCh. 34 - What is the evidence that light is energy?Ch. 34 - Why is light sometimes described as rays and...Ch. 34 - We can hear sounds around corners but we cannot...Ch. 34 - Can the wavelength of light be determined from...Ch. 34 - Two rays of light from the same source...Ch. 34 - Monochromatic red light is incident on a double...Ch. 34 - If Youngs double-slit experiment were submerged in...
Ch. 34 - Compare a double-slit experiment for sound waves...Ch. 34 - Suppose white light falls on the two slits of Fig....Ch. 34 - Why doesnt the light from the two headlights of a...Ch. 34 - Why are interference fringes noticeable only for a...Ch. 34 - Prob. 13QCh. 34 - Some coated lenses appear greenish yellow when...Ch. 34 - A drop of oil on a pond appears bright at its...Ch. 34 - (II) Derive the law of reflectionnamely, that the...Ch. 34 - (I) Monochromatic light falling on two slits 0.018...Ch. 34 - (I) The third-order bright fringe of 610 nm light...Ch. 34 - (II) Monochromatic light falls on two very narrow...Ch. 34 - (II) If 720-nm and 660-nm light passes through two...Ch. 34 - (II) A red laser from the physics lab is marked as...Ch. 34 - (II) Light of wavelength passes through a pair of...Ch. 34 - (II) Light of wavelength 680 nm falls on two slits...Ch. 34 - (II) A parallel beam of light from a HeNe laser,...Ch. 34 - (II) A physics professor wants to perform a...Ch. 34 - (II) Suppose a thin piece of glass is placed in...Ch. 34 - (II) In a double-slit experiment it is found that...Ch. 34 - (II) Two narrow slits separated by 1.0 mm are...Ch. 34 - (II) In a double-slit experiment, the third-order...Ch. 34 - (II) Light of wavelength 470 nm in air falls on...Ch. 34 - (II) A very thin sheet of plastic (n = 1.60)...Ch. 34 - (I) If one slit in Fig. 3412 is covered, by what...Ch. 34 - (II) Derive an expression similar to Eq. 342 which...Ch. 34 - (II) Show that the angular full width at half...Ch. 34 - (II) In a two-slit interference experiment, the...Ch. 34 - (III) Suppose that one slit of a double-slit...Ch. 34 - (III) (a) Consider three equally spaced and...Ch. 34 - (I) If a soap bubble is 120 nm thick, what...Ch. 34 - (I) How far apart are the dark fringes in Example...Ch. 34 - (II) (a) What is the smallest thickness of a soap...Ch. 34 - (II) A lens appears greenish yellow ( = 570 nm is...Ch. 34 - (II) A thin film of oil (nO = 1.50) with varying...Ch. 34 - (II) A thin oil slick (no = 1.50) finals on water...Ch. 34 - (II) A total of 31 bright and 31 dark Newtons...Ch. 34 - (II) A line metal foil separates one end of two...Ch. 34 - (II) How thick (minimum) should the air layer be...Ch. 34 - (II) A uniform thin film of alcohol (n = 1.36)...Ch. 34 - (II) Show that the radius r of the mth dark...Ch. 34 - (II) Use the result of Problem 33 to show that the...Ch. 34 - (II) When a Newtons ring apparatus (Fig. 3418) is...Ch. 34 - (II) A planoconvex lucite lens 3.4 cm in diameter...Ch. 34 - (II) Lets explore why only thin layers exhibit...Ch. 34 - (II) How far must the mirror M1 in a Michelson...Ch. 34 - (II) What is the wavelength of the light entering...Ch. 34 - (II) A micrometer is connected to the movable...Ch. 34 - (III) One of the beams of an interferometer (Fig,...Ch. 34 - (III) The yellow sodium D lines have wavelengths...Ch. 34 - Prob. 44PCh. 34 - (II) The luminous efficiency of a lightbulb is the...Ch. 34 - Light of wavelength 5.0 107 m passes through two...Ch. 34 - Television and radio waves reflecting from...Ch. 34 - A radio station operating at 88.5 MHz broadcasts...Ch. 34 - Light of wavelength 690 nm passes through two...Ch. 34 - Monochromatic light of variable wavelength is...Ch. 34 - Suppose the mirrors in a Michelson interferometer...Ch. 34 - A highly reflective mirror can be made for a...Ch. 34 - Calculate the minimum thickness needed for an...Ch. 34 - Stealth aircraft are designed to not reflect...Ch. 34 - Light or wavelength strikes a screen containing...Ch. 34 - Consider two antennas radiating 6.0-MHz radio...Ch. 34 - What is the minimum (non-zero) thickness for the...Ch. 34 - Lloyds mirror provides one way of obtaining a...Ch. 34 - Consider the antenna army of Example 345, Fig....Ch. 34 - A thin film of soap (n = 1.34) coats a piece of...Ch. 34 - Two identical sources S1 and S2, separated by...Ch. 34 - A two-slit interference set-up with slit...Ch. 34 - A radio telescope, whose two antennas are...Ch. 34 - In a compact disc (CD), digital information is...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Fibrous connective tissue consists of ground substance and fibers that provide strength, support, and flexibili...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
1. Write a single sentence, using no more than 25 words, to summarize each of the following cellular processes...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Why is it necessary to be in a pressurized cabin when flying at 30,000 feet?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
A source of electromagnetic radiation produces infrared light. Which of the following could be the wavelength ...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
15. A woman with severe discoloration of her tooth enamel has four children with a man who has normal tooth ena...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
What is the difference between cellular respiration and external respiration?
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forwardThe spring in the figure has a spring constant of 1300 N/m. It is compressed 17.0 cm, then launches a 200 g block. The horizontal surface is frictionless, but the block’s coefficient of kinetic friction on the incline is 0.200. What distance d does the block sail through the air?arrow_forwardSolve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA 10-m-long glider with a mass of 680 kg (including the passengers) is gliding horizontally through the air at 28 m/s when a 60 kg skydiver drops out by releasing his grip on the glider. What is the glider's speed just after the skydiver lets go?arrow_forwardPROBLEM 2 A cube of mass m is placed in a rotating funnel. (The funnel is rotating around the vertical axis shown in the diagram.) There is no friction between the cube and the funnel but the funnel is rotating at just the right speed needed to keep the cube rotating with the funnel. The cube travels in a circular path of radius r, and the angle between the vertical and the wall of the funnel is 0. Express your answers to parts (b) and (c) in terms of m, r, g, and/or 0. (a) Sketch a free-body diagram for the cube. Show all the forces acting on it, and show the appropriate coordinate system to use for this problem. (b) What is the normal force acting on the cube? FN=mg58 (c) What is the speed v of the cube? (d) If the speed of the cube is different from what you determined in part (c), a force of friction is necessary to keep the cube from slipping in the funnel. If the funnel is rotating slower than it was above, draw a new free-body diagram for the cube to show which way friction…arrow_forward
- Circular turns of radius r in a race track are often banked at an angle θ to allow the cars to achieve higher speeds around the turns. Assume friction is not present. Write an expression for the tan(θ) of a car going around the banked turn in terms of the car's speed v, the radius of the turn r, and g so that the car will not move up or down the incline of the turn. tan(θ) =arrow_forwardThe character Min Min from Arms was a DLC character added to Super Smash Bros. Min Min’s arms are large springs, with a spring constant of 8.53 ⋅ 10^3 N/m, which she uses to punch and fling away her opponents. Min Min pushes her spring arm against Steve, who is not moving, compressing it 1.20 m as shown in figure A. Steve has a mass of 81.6 kg. Assuming she uses only the spring to launch Steve, how fast is Steve moving when the spring is no longer compressed? As Steve goes flying away he goes over the edge of the level, as shown in figure C. What is the magnitude of Steve’s velocity when he is 2.00 m below where he started?arrow_forwardSlinky dog whose middle section is a giant spring with a spring constant of 10.9 N/m. Woody, who has a mass of 0.412 kg, grabs onto the tail end of Slink and steps off the bed with no initial velocity and reaches the floor right as his velocity hits zero again. How high is the bed? What is Woody’s velocity halfway down? Enter just the magnitude of velocity.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA positive charge of 91 is located 5.11 m to the left of a negative charge 92. The charges have different magnitudes. On the line through the charges, the net electric field is zero at a spot 2.90 m to the right of the negative charge. On this line there are also two spots where the potential is zero. (a) How far to the left of the negative charge is one spot? (b) How far to the right of the negative charge is the other?arrow_forwardA charge of -3.99 μC is fixed in place. From a horizontal distance of 0.0423 m, a particle of mass 7.31 x 103 kg and charge -9.76 µC is fired with an initial speed of 84.1 m/s directly toward the fixed charge. How far does the particle travel before its speed is zero?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Polarization of Light: circularly polarized, linearly polarized, unpolarized light.; Author: Physics Videos by Eugene Khutoryansky;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8YkfEft4p-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY