
Concept explainers
You have seen that Earth’s terrestrial biomes reflect regional variations in climate. But what determines these climatic variations? Interpret the following diagrams in reference to how each represents effects on global patterns of temperature, rainfall, and winds.
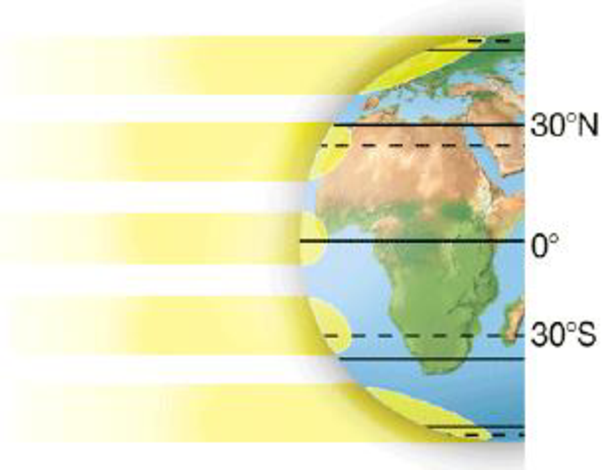
a. Solar radiation and latitude:
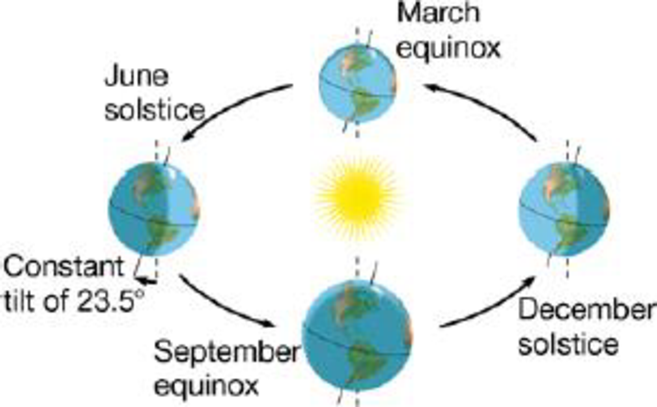
b. Earth’s orbit around the sun:
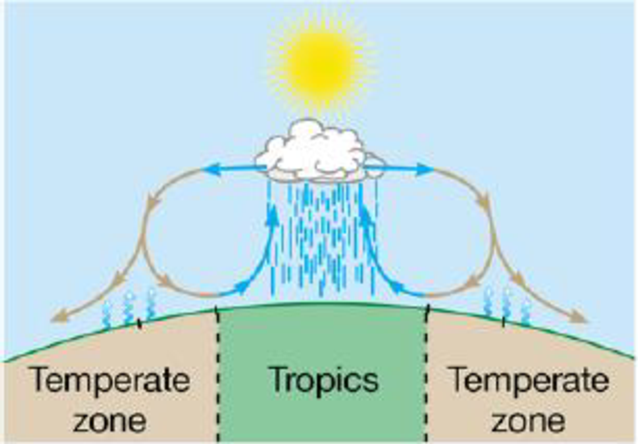
c. Global patterns of air circulation and rainfall:
(a)
To determine: Solar radiation and latitude representing the effects on global pattern of temperature, rainfall and wind and also the climatic variations.
Introduction:
Biomes are the regions with similar climate and terrestrial biome distribution is decided by rainfall and temperature. The terrestrial biomes are tundra, rainforest, desert, taiga, temperate forest, alpine and savanna.
Explanation of Solution
The solar radiation amount received by earth is depends upon the location of the biome. The amount of received sunlight will be high if the biome is located at equator, resulting in hot conditions in biome. At the poles, biomes are cold due to the availability of less sunlight.
(b)
To determine: Earth’s orbit around the sun representing the effects on global pattern of temperature, rainfall and wind and also the climatic variations.
Introduction:
Biomes are the regions with similar climate and terrestrial biome distribution is decided by rainfall and temperature. The terrestrial biomes are tundra, rainforest, desert, taiga, temperate forest, alpine and savanna.
Explanation of Solution
Different seasons are the result of earth rotation, because both hemisphere experience opposite season due to tilt of earth on its own axis.
The tilt of the northern hemisphere of earth towards the sun results in summer as the tilt allows entry of more sunlight and summer in the northern hemisphere means winter in the southern hemisphere because it is away from the sun so receives less sunlight.
(c)
To determine: Global pattern of air circulation and rainfall representing the effects on global pattern of temperature, rainfall and wind and also the climatic variations.
Introduction:
Biomes are the regions with similar climate and terrestrial biome distribution is decided by rainfall and temperature. The terrestrial biomes are tundra, rainforest, desert, taiga, temperate forest, alpine and savanna.
Explanation of Solution
Extreme sunlight at equators results in evaporation of water from the land and oceans, which cools and condenses, converting into rain. For example: tropical rainforests.
At 30 degree latitude of south and north, the circulating air warms as it fals causing evaporation of moisture present in the soil, leading to dryness (arid regions in the temperate zones). For example: deserts.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 34 Solutions
CAMPBEL BIOLOGY:CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS
- Molecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question A gene that codes for a protein was removed from a eukaryotic cell and inserted into a prokaryotic cell. Although the gene was successfully transcribed and translated, it produced a different protein than it produced in the eukaryotic cell. What is the most likely explanation?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology LIST three characteristics of origins of replicationarrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you For E coli DNA polymerase III, give the structure and function of the b-clamp sub-complex. Describe how the structure of this sub-complex is important for it’s function.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology LIST three characteristics of DNA Polymerasesarrow_forwardMolecular Biology RNA polymerase core enzyme structure contains what subunits? To form holo enzyme, sigma factor is added to core. What is the name of the structure formed? Give the detailed structure of sigma factor and the function of eachdomain. Please help. Thank youarrow_forward
- Molecular Biology You have a single bacterial cell whose DNA is labelled with radioactiveC14. After 5 rounds of cell division, how may cells will contain radioactive DNA? Please help. Thank youarrow_forward1. Explain the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins). Also add some pictures.arrow_forward1. In the Sentinel Cell DNA integrity is preserved through nanoscopic helicase-coordinated repair, while lipids in the membrane are fortified to resist environmental mutagens. also provide pictures for this question.arrow_forward
- Explain the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins). Also add some pictures.arrow_forwardIn the Sentinel Cell DNA integrity is preserved through nanoscopic helicase-coordinated repair, while lipids in the membrane are fortified to resist environmental mutagens. also provide pictures for this question.arrow_forward1. Explain how genetic information is stored, copied, transferred, and expressed. Also add some pictures for this question.arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





