
EBK MACHINE ELEMENTS IN MECHANICAL DESI
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134451947
Author: Wang
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 36P
Figure P3−36 shows a beam made from 4 in schedule 40 steel pipe. Compute the deflection at points A and B for two cases: (a) the simple cantilever and (b) the supported cantilever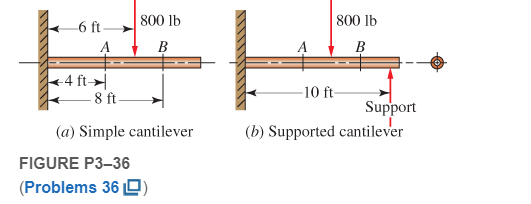
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Using P3-31. A beam is simply supported and carries the load shown in Figure P3–31. Specify an appropriate steel hollow tubing for the loaded beam shown. Also, determine its maximum deflection using the superposition method.
Compute the reaction forces at support A and B in terms of w0, with the aid of free body diagram.
pls do box your answer :) thumbs up will be given
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK MACHINE ELEMENTS IN MECHANICAL DESI
Ch. 3 - A tensile member in a machine structure is...Ch. 3 - Compute the stress in a round bar having a...Ch. 3 - Compute the stress in a rectangular bar having...Ch. 3 - A link in a packaging machine mechanism has a...Ch. 3 - Two circular rods support the 3800 lb weight of a...Ch. 3 - A tensile load of 5.00 kN is applied to a square...Ch. 3 - An aluminum rod is made in the form of a hollow...Ch. 3 - Compute the stress in the middle portion of rod AC...Ch. 3 - Compute the forces in the two angled rods in...Ch. 3 - If the rods from Problem 9 are circular, determine...
Ch. 3 - Repeat Problems 9 and 10 if the angle is 15 .Ch. 3 - Figure P312 shows a small truss spanning between...Ch. 3 - The truss shown in Figure P313 spans a total space...Ch. 3 - Figure P314 shows a short leg for a machine that...Ch. 3 - Consider the short compression member shown in...Ch. 3 - Refer Figure P38 . Each of the pins at A, B, and C...Ch. 3 - Compute the shear stress in the pins connecting...Ch. 3 - Prob. 18PCh. 3 - Prob. 19PCh. 3 - Prob. 20PCh. 3 - Prob. 21PCh. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress in a circular...Ch. 3 - If the shaft of Problem 22 is 850 mm long and is...Ch. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress due to a torque...Ch. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress in a solid...Ch. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress in a hollow...Ch. 3 - Compute the angle of twist for the hollow shaft of...Ch. 3 - A square steel bar, 25 mm on a side and 650 mm...Ch. 3 - A 3.00 in-diameter steel bar has a flat milled on...Ch. 3 - A commercial steel supplier lists rectangular...Ch. 3 - A beam is simply supported and carries the load...Ch. 3 - For each beam of Problem 31, compute its weight if...Ch. 3 - For each beam of Problem 31, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For the beam loading of Figure P334, draw the...Ch. 3 - For the beam loading of Figure P334, design the...Ch. 3 - Figure P336 shows a beam made from 4 in schedule...Ch. 3 - Select an aluminum I-beam shape to carry the load...Ch. 3 - Figure P338 represents a wood joist for a...Ch. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - Prob. 40PCh. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - Prob. 42PCh. 3 - Prob. 43PCh. 3 - Prob. 44PCh. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - For Problems 4850, draw the free-body diagram of...Ch. 3 - For Problems 4850, draw the free-body diagram of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 50PCh. 3 - Compute the maximum tensile stress in the bracket...Ch. 3 - Compute the maximum tensile and compressive...Ch. 3 - For the lever shown in Figure P353 (a), compute...Ch. 3 - Compute the maximum tensile stress at sections A...Ch. 3 - Prob. 55PCh. 3 - Refer to Figure P38. Compute the maximum tensile...Ch. 3 - Prob. 57PCh. 3 - Refer to P342. Compute the maximum stress in the...Ch. 3 - Refer to P343. Compute the maximum stress in the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 60PCh. 3 - Figure P361 shows a valve stem from an engine...Ch. 3 - The conveyor fixture shown in Figure P362 carries...Ch. 3 - For the flat plate in tension in Figure P363,...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - Prob. 68PCh. 3 - Figure P369 shows a horizontal beam supported by a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 70PCh. 3 - Prob. 71PCh. 3 - The beam shown in Figure P372 is a stepped, flat...Ch. 3 - Figure P373 shows a stepped, flat bar having a...Ch. 3 - Figure P374 shows a bracket carrying opposing...Ch. 3 - Prob. 75PCh. 3 - Figure P376 shows a lever made from a rectangular...Ch. 3 - For the lever in P376, determine the maximum...Ch. 3 - Figure P378 shows a shaft that is loaded only in...Ch. 3 - Prob. 79PCh. 3 - Prob. 80PCh. 3 - A hanger is made from ASTM A36 structural steel...Ch. 3 - A coping saw frame shown in Figure P382 is made...Ch. 3 - Prob. 83PCh. 3 - Figure P384 shows a hand garden tool used to break...Ch. 3 - Figure P385 shows a basketball backboard and goal...Ch. 3 - Prob. 86P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- All I want to know is how to get the deflection equation. Please explain in as much detail as possible! DON'T SOLVE THE PROBLEM, this picture was taken from the answer key; solving this problem does me no good. All I want is to know where the 17qL4/24EI is coming fromarrow_forward2. The figure shows a spring chair. The chair weight is 100 N. The spring free-length is 500 mm, mean diameter is 200 mm, wire diameter is 10 mm and number of turns is 12. The spring wire material is Music wire A228 with modulus of rigidity of 82700 MPa. Calculate the initial deflection of the spring under the chair weight. If a child seats on the chair, calculate his weight to bush the spring to the shut height. Calculate the stresses in the spring at that condition. BFD'N y = d*G 8FD T = K, 4C +2 K = 4C – 3 D C = --- o00000000odarrow_forwardpls box ur answerarrow_forward
- Figure 2 (b) Compute the stiffness matrix D-1 for D in (a) by using Cramer's rule. List the forces needed to produce a deflection of 0.04 inch at point 3, with zero deflections at the other points.arrow_forwardFor the beam shown, find the reactions at the supports and plot the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams. Label the diagrams properly and provide values at all key points.arrow_forwardSolve fastarrow_forward
- 52. Compute the maximum tensile and compressive stresses in the horizontal beam shown in Figure P3-52. 6 ft -W 8x10 beam -4 ft 8 ft - 1800 lbarrow_forwardAnswer letter Darrow_forward31. A beam is simply supported and carries the load shown in Figure P3–31. Specify suitable dimensions for the beam if it is steel and the stress is limited to 18 000 psi, for the following shapes: (a) Square (b) Rectangle with height three times the width (c) Rectangle with height one-third the width (d) Solid circular section (e) American Standard beam section (f) American Standard channel with the legs down (g) Standard steel pipe F | 1200 lb 1200 lb 3 ft 4 ft 3 ft R1 R2 IGURE P3–31 (Problems 31, 32, and 33)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanical SPRING DESIGN Strategy and Restrictions in Under 15 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsWQrzfQt3s;License: Standard Youtube License