
(a)
Interpretation: MOs for the given conjugated systems has to be drawn and the HOMO has to be predicted as symmetric or antisymmetric.
Concept introduction:
Conjugated system: A system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons with alternating single and multiple bonds and the compound may be cyclic, linear or mixed.
Molecular orbital theory suggests that atomic orbitals of different atoms combines to create molecular orbitals.
Molecular orbitals can be constructed from linear combination of atomic orbitals.
Bonding orbotals are formed by the additive combination of atomic orbitals and the antibonding orbitals are formed by the substractive combination of atomic orbitals.
Antibonding orbital is a molecular orbital that results when two parallel atomic orbitals with opposite phases interact.
Antibonding orbitals have higher energy than the bonding molecular orbitals.
Ground state and and exited states are the positions with lower and higher energy respectively.
HOMO is a molecular orbital which is the abbrevation of Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital.
LUMO is also a molecular orbital which is the short form of Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital.
If the lobes at the ends of the MO are in phase, then the MO is symmetric.
If the two lobes are out phase then the MO is antisymmetric.
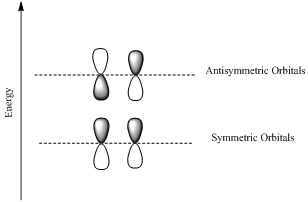
Woodward –Hoffmann rules are the set of rules used to vindicate or predict certain aspects of the stereo chemical outcome and activation energy of pericyclic reactions.
Woodward – Hoffmann rules for Electrocyclic reactions are listed below
(b)
Interpretation: The validity of Woodward – Hoffmann rule for an electrocyclic reaction has to be checked using the MOs of given systems.
Concept introduction:
Woodward –Hoffmann rules are the set of rules used to vindicate or predict certain aspects of the stereo chemical outcome and activation energy of pericyclic reactions.
Woodward – Hoffmann rules for Electrocyclic reactions are listed below
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- True or False Using the following equilibrium, if heat is added the equilibrium will shift toward the products. N2O4(g) + heat ⇔ 2NO2(g)arrow_forwardtrue or false Using the following equilibrium, if solid carbon is added the equilibrium will shift toward the products. C(s) + CO2(g) ⇔ 2CO(g)arrow_forwardProvide the complete mechanism for the reaction below. You must include appropriate arrows,intermediates, and formal charges. Please also provide a reason to explain why the 1,4-adduct is preferred over the 1,3-adduct.arrow_forward
- Which of the following pairs are resonance structures of one another? I. III. || III IV + II. :0: n P !༠ IV. EN: Narrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) and byproducts (either organic or inorganic) for thefollowing reactions.arrow_forwardA 8.25 g sample of aluminum at 55°C released 2500 J of heat. The specific heat of aluminum is 0.900 J/g°C. The density of aluminum is 2.70 g/mL. Calculate the final temperature of the aluminum sample in °C.arrow_forward
- Experiment 1 Data Table 1: Conservation of Mass - Initial Mass Data Table 1 Data Table 2 Data Table 3 Data Table 4 Panel 1 Photo 1 Data Table 5 Reaction Mass of test tube and 5.0% HC₂H₂O2 (g) # (A) (B) Mass of NaHCO, (g) Mass of balloon and NaHCO, (g) (C) 0.10 1 0829 14.38g 0.20 2 0.929 14.29g 0.35 1.00g 3 14.25g 0.50 1.14g 14.29 Experiment 1 Data Table 2: Moles of HC2H3O2 Reaction Volume of Mass of Moles of HC₂H₂O₂ 5.0% Vinegar (g) (ML) 5.0 0.25 0042 mol 2 5.0 0.25 0042 mol 3 5.0 0.25 0042 mol 5.0 0.25 0042 mol Experiment 1 Data Table 3: Moles of NaHCO3 Reaction Mass of NaHCO (g) 10g 20g 35g 50g Experiment 1 Data Table 4: Theoretical Yield of CO₂ Reaction # 1 2 3 Experiment 1 Total mass before reaction (g) (D=A+C) 15.29 15.21g 15.25g 15.349 Exercise 1 Data Table 1 Data Table 2 Data Table 3 Data Table 4 Panel 1 Photo 1 Data Table 5 Exercise 1- Data Table 1 Data Table 2 DataTable 3 Data Table 4 Panel 1 Photo 1 Data Table 5 Exercise 1- Moles of NaHCO 0012 mol 0025 mol 0044 mol 0062 mol…arrow_forwardThe chemical reaction you investigated is a two-step reaction. What type of reaction occurs in each step? How did you determine your answer?arrow_forwardWhat is the relationship between the limiting reactant and theoretical yield of CO2?arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
