
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780132915540
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.6, Problem 13FP
Determine the coordinate direction angles of the force.
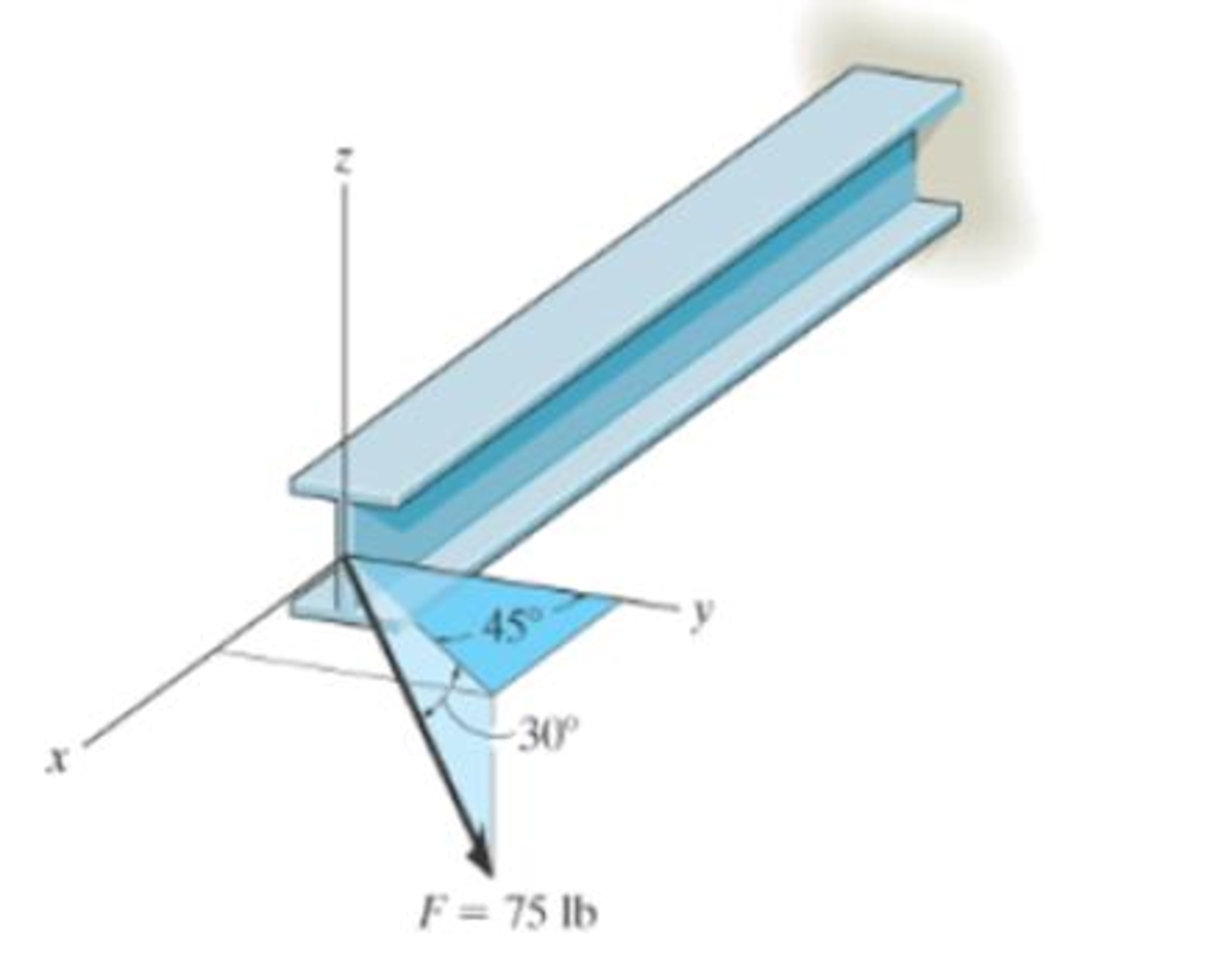
Prob. F2-13
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule07:24
Students have asked these similar questions
from this problem a want you to help to draw the shear moment and the bending moment
reaction at a is 1.6 wL (pos)
handwritten solutions only please. correct answers upvoted
1
8
4
Add numbers so that the sum of any
row or column equals .30 Use only
these numbers:
.1.2.3.4.5.6.10.11.12.12.13.14.14
Chapter 2 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force....Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the 30-lb force into components along the...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve this force into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - along the v axis. Prob. F2-6Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.3 - If = 60 and F = 450 N, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the magnitude of the resultant force is to be...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...
Ch. 2.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 2.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 2.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the two components of...Ch. 2.3 - Solve with F = 350 lb. Prob. 2-4/5Ch. 2.3 - Prob. 9PCh. 2.3 - Prob. 10PCh. 2.3 - Resolve this force into two components acting...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of F and its component...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of F and its direction ....Ch. 2.3 - Prob. 14PCh. 2.3 - If = 60, determine the magnitude of the resultant...Ch. 2.3 - Also, what is the magnitude of the resultant...Ch. 2.3 - What is the component of force acting along member...Ch. 2.3 - Take = 30. Probs. 2-19/20Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - If F1 = 400 N and F2 = 600 N, determine the angle...Ch. 2.3 - If their lines of action are at an angle apart...Ch. 2.3 - Prob. 23PCh. 2.3 - Prob. 24PCh. 2.3 - Prob. 25PCh. 2.3 - Prob. 26PCh. 2.3 - Prob. 27PCh. 2.3 - directed along the positive x axis, determine the...Ch. 2.3 - If FB = 3 kN and = 45, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force of the two tugboats is...Ch. 2.3 - Prob. 31PCh. 2.4 - Resolve each force acting on the post into its x...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.4 - determine the magnitude of F and its direction ....Ch. 2.4 - If the magnitude of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 32PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 33PCh. 2.4 - Resolve F1 and F2 into their x and y components.Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve each force acting on the gusset plate into...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 38PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 39PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 40PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 41PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and orientation of FB so...Ch. 2.4 - measured counterclockwise from the positive y...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 44PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 45PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 46PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 49PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 50PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 51PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 52PCh. 2.4 - What is the magnitude of the resultant force?...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 54PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 55PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 56PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 57PCh. 2.4 - If the magnitude of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.4 - Set = 30. Probs. 2-56/57Ch. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of the...Ch. 2.6 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.6 - Determine the resultant force acting on the hook....Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 60PCh. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Specify the coordinate direction angles of F1 and...Ch. 2.6 - If the magnitude of F is 80 N, and = 60 and =...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 64PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 65PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 66PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 67PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 68PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 69PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 70PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 71PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 72PCh. 2.6 - Express each force as a Cartesian vector.Ch. 2.6 - Determine the resultant of the two forces and...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 75PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 76PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 77PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 78PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 79PCh. 2.6 - If the coordinate direction angles for F1 are 3 =...Ch. 2.6 - If the coordinate direction angles for F1 are 3 =...Ch. 2.6 - If the direction of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.6 - Express each force in Cartesian vector form and...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 84PCh. 2.6 - If = 75, determine the magnitudes of F and Fy....Ch. 2.8 - Express the position vector rAB in Cartesian...Ch. 2.8 - What is the angle ? Prob. F2-20Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 21FPCh. 2.8 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force at...Ch. 2.8 - Determine the resultant force at A. Prob. F2-24Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 86PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 87PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 88PCh. 2.8 - If F = {350i 250j 450k} N and cable AB is 9 m...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 90PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 91PCh. 2.8 - If FB = 560 N and FC = 700 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - If FB = 700 N, and FC = 560 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 94PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 95PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 96PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 97PCh. 2.8 - Express this force as a Cartesian vector acting on...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 99PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 100PCh. 2.8 - Represent each force as a Cartesian vector and...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 102PCh. 2.8 - If the force in each cable tied to the bin is 70...Ch. 2.8 - Due to symmetry, the tension in the four cables is...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 105PCh. 2.8 - If the force in each chain has a magnitude of 60...Ch. 2.8 - If the resultant force at O has a magnitude of 130...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 108PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 109PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 110PCh. 2.8 - Determine the length of the chain, and express the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the projected component of the force...Ch. 2.9 - Find the magnitude of the projected component of...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the components of the force acting...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of the...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 112PCh. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the edges of the...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 114PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 115PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 116PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 117PCh. 2.9 - Determine the projection of the force F along the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the y axis of the...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of F =...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projection of force...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 122PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 123PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 124PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 125PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the two cables...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 128PCh. 2.9 - Express this component as a Cartesian vector....Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 130PCh. 2.9 - Determine the angles and made between the axes...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 132PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 133PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of the...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 135PCh. 2.9 - Express the force F in Cartesian vector form if it...Ch. 2.9 - Express force F in Cartesian vector form if point...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the projected...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 139PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 140RPCh. 2.9 - Determine the x and y components of F1 and F2....Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.9 - Express F1 and F2 as Cartesian vectors.Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.9 - The cable attach to the tractor at B exerts a...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 147RPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 148RPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 149RP
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What determines an objects appearance and other characteristics?
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Find the no-load value of υo in the circuit shown.
Find υo when RL is 150 Ω.
How much power is dissipated in th...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
What is the difference between the names defined in an ML let construct from the variables declared in a C bloc...
Concepts Of Programming Languages
The ________ object is assumed to exist and it is not necessary to include it as an object when referring to it...
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
is a graphical language that allows people who design software systems to use an industry-standard notation to ...
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Determine the maximum deflection of the simply supported beam. The beam is made of wood having a modulus of ela...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Uppgift 2 (9p) I77777 20 kN 10 kN/m 4 [m] 2 2 Bestäm tvärkrafts- och momentdiagram för balken i figuren ovan. Extrempunkter ska anges med både läge och värde i diagrammen.arrow_forward**Problem 8-45.** The man has a mass of 60 kg and the crate has a mass of 100 kg. If the coefficient of static friction between his shoes and the ground is \( \mu_s = 0.4 \) and between the crate and the ground is \( \mu_c = 0.3 \), determine if the man is able to move the crate using the rope-and-pulley system shown. **Diagram Explanation:** The diagram illustrates a scenario where a man is attempting to pull a crate using a rope-and-pulley system. The setup is as follows: - **Crate (C):** Positioned on the ground with a rope attached. - **Rope:** Connects the crate to a pulley system and extends to the man. - **Pulley on Tree:** The rope runs over a pulley mounted on a tree which redirects the rope. - **Angles:** - The rope between the crate and tree forms a \(30^\circ\) angle with the horizontal. - The rope between the tree and the man makes a \(45^\circ\) angle with the horizontal. - **Man (A):** Pulling on the rope with the intention of moving the crate. This arrangement tests the…arrow_forwardplease solve this problems follow what the question are asking to do please show me step by steparrow_forward
- please help me to solve this problem and determine the stress for each point i like to be explained step by step with the correct answerarrow_forwardplease solve this problem for me the best way that you can explained to solve please show me the step how to solvearrow_forwardplese solbe this problem and give the correct answer solve step by step find the forces and line actionarrow_forward
- please help me to solve this problems first write the line of action and them find the forces {fx=0: fy=0: mz=0: and them draw the shear and bending moment diagram. please explain step by steparrow_forwardplease solve this problem step by step like human and give correct answer step by steparrow_forwardPROBLEM 11: Determine the force, P, that must be exerted on the handles of the bolt cutter. (A) 7.5 N (B) 30.0 N (C) 52.5 N (D) 300 N (E) 325 N .B X 3 cm E 40 cm cm F = 1000 N 10 cm 3 cm boltarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Introduction To Engg Mechanics - Newton's Laws of motion - Kinetics - Kinematics; Author: EzEd Channel;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ksmsp9OzAsI;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY