
Concept explainers
Cloning can be done by somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) (see Figure 20-12). Some conservation biologists have proposed using SCNT technology to preserve highly endangered animal species. What might be some of the genetic disadvantages of this approach?
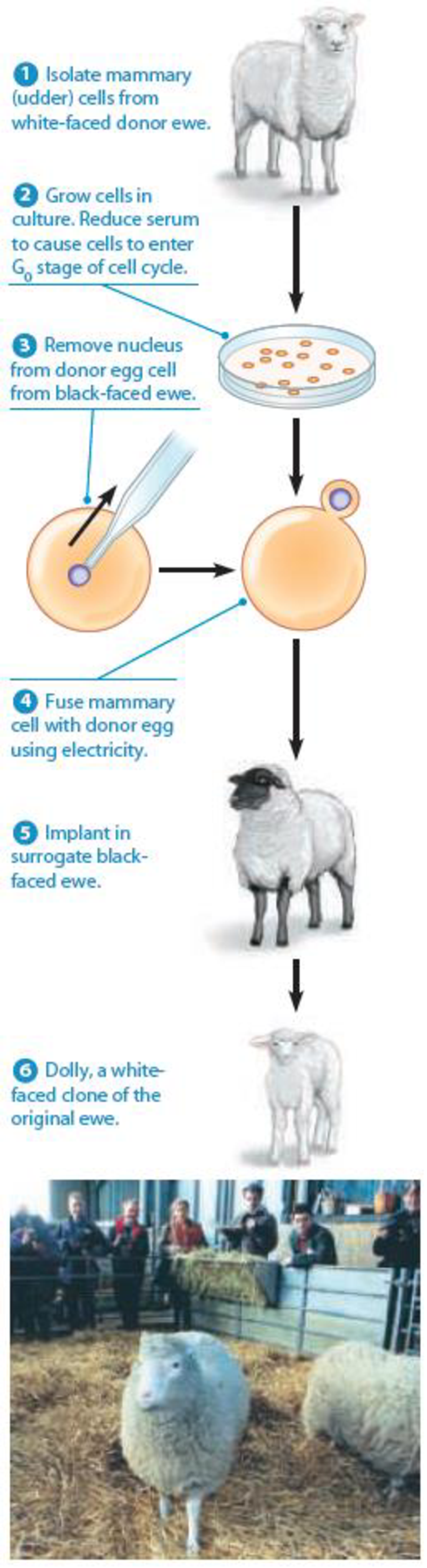
Figure 20-12 Dolly, the First Mammal Cloned from an Adult Cell. (a) Dolly was cloned from a serum-starved mammary (udder) cell that was fused with an egg cell from which the nucleus had been removed. (b) Dolly as an adult.
To explain: The genetic disadvantages of cloning done by Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT).
Introduction: In sexual reproduction, genetic information from both the parents is combined together to produce the offspring. A cell having two sets of chromosomes is known as diploid whereas, a cell having a single copy of chromosomes is known as haploid. Sperms are the gametes produced by males and eggs are the gamete produces by females, these gametes fuse together to form a zygote.
Explanation of Solution
An offspring which is the identical copy of the parent is known as its clone. Asexual reproduction is a method to produce clones naturally. Clones can also be produced artificially in the laboratories. Somatic cell nuclear transfer is a method of producing clones artificially. In the somatic cell, nuclear transfer nucleus from a somatic cell is implanted into an enucleated oocyte to produce an embryo. Therefore, SCNT can be used for cloning experiments. Dolly the sheep was the first clone produced by the technique.
Following are the genetic disadvantages of cloning done by SCNT to preserve highly endangered animals:
- As the clones are identically similar to the parents, genetic diversity will decrease in producing a clone through SCNT and as a resulting susceptibility to a particular genetic disease carried by the parent will increase in the next generation.
- Producing clones will also increase homozygosity and decrease the chances of evolution.
- Incomplete reprogramming of the cells can also produce abnormal phenotypes.
Thus, SCNT has certain genetic disadvantages such as production of abnormal phenotypes, an increase in homozygosity, an increase in susceptibility to genetic diseases.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Becker's World of the Cell (9th Edition)
- Molecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you Explain what is meant by the term “defective virus.” Explain how a defective virus is able to replicate.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain why changing the codon GGG to GGA should not be harmful. Please help . Thank youarrow_forwardStage Percent Time in Hours Interphase .60 14.4 Prophase .20 4.8 Metaphase .10 2.4 Anaphase .06 1.44 Telophase .03 .72 Cytukinesis .01 .24 Can you summarize the results in the chart and explain which phases are faster and why the slower ones are slow?arrow_forward
- Can you circle a cell in the different stages of mitosis? 1.prophase 2.metaphase 3.anaphase 4.telophase 5.cytokinesisarrow_forwardWhich microbe does not live part of its lifecycle outside humans? A. Toxoplasma gondii B. Cytomegalovirus C. Francisella tularensis D. Plasmodium falciparum explain your answer thoroughly.arrow_forwardSelect all of the following that the ablation (knockout) or ectopoic expression (gain of function) of Hox can contribute to. Another set of wings in the fruit fly, duplication of fingernails, ectopic ears in mice, excess feathers in duck/quail chimeras, and homeosis of segment 2 to jaw in Hox2a mutantsarrow_forward
- Select all of the following that changes in the MC1R gene can lead to: Changes in spots/stripes in lizards, changes in coat coloration in mice, ectopic ear formation in Siberian hamsters, and red hair in humansarrow_forwardPleiotropic genes are genes that (blank) Cause a swapping of organs/structures, are the result of duplicated sets of chromosomes, never produce protein products, and have more than one purpose/functionarrow_forwardA loss of function mutation in Pitx1 enhancers can cause (blank) Removal of Pitx1 exons and growth of ectopic hindlimbs, growth of extra ectopic forelimbs, loss of forelimb specification and development, and loss of hindlimb specification and developmentarrow_forward
- Hox1a most likely contributes to (blank) patterning in the developing embryo? Ventral, posterior, limb or anteriorarrow_forwardSelect all of the following that can help establish Hox gene expression boundaries (things that affect Hox and not things that Hox affects). Retinoic acid, anterior/posterior axis, fibroblast growth factors, vagal neural crest, and enhancersarrow_forwardEctopic expression of Hox often results in (blank) phenotypes. (Blank) transformations are characterized by the replacement of one body part/structure with another. Hoxeotic, homealoneotic, joexotic, or homeoticarrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





