
Concept explainers
A graph of the x component of the electric field as a function of x in a region of space is shown in Fig. 24-35. The scale of the vertical axis is set by Exs = 20.0 N/C. The y and z components of the electric field are zero in this region. If the electric potential at the origin is 10 V, (a) what is the electric potential at x = 2.0 m, (b) what is the greatest positive value of the electric potential for points on the x axis for which 0 ≤ x ≤ 6.0 m, and (c) for what value of x is the electric potential zero?
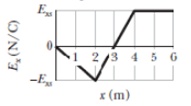
Figure 24-35 Problem 8.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 24 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Physics 11th Edition Loose-leaf Print Companion Volume 2 With Wileyplus Card Set
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
- An electric potential exists in a region of space such that V = 8x4 2y2 + 9z3 and V is in units of volts, when x, y, and z are in meters. a. Find an expression for the electric field as a function of position. b. What is the electric field at (2.0 m, 4.5 m, 2.0 m)?arrow_forwardFor the arrangement described in Problem 26, calculate the electric potential at point B, which lies on the perpendicular bisector of the rod a distance b above the x axis. Figure P20.26arrow_forwardA filament running along the x axis from the origin to x = 80.0 cm carries electric charge with uniform density. At the point P with coordinates (x = 80.0 cm, y = 80.0 cm), this filament creates electric potential 100 V. Now we add another filament along the y axis, running from the origin to y = 80.0 cm. carrying the same amount of charge with the same uniform density. At the same point P, is the electric potential created by the pair of filaments (a) greater than 200 V, (b) 200 V, (c) 100 V, (d) between 0 and 200 V, or (e) 0?arrow_forward
- The charge density on a disk of radius R = 12.0 cm is given by = ar, with a = 1.40 C/m3 and r measured radially outward from the origin (Fig. P26.45). What is the electric potential at point A, a distance of 40.0 cm above the disk? Hint: You will need to integrate the nonuniform charge density to find the electric potential. You will find a table of integrals helpful for performing the integration.arrow_forwardFour particles are positioned on the rim of a circle. The charges on the particles are +0.500 C, +1.50 C, 1.00 C, and 0.500 C. If the electric potential at the center of the circle due to the +0.500 C charge alone is 4.50 104 V, what is the total electric potential at the center due to the four charges? (a) 18.0 104 V (b) 4.50 104 V (c) 0 (d) 4.50 104 V (e) 9.00 104 Varrow_forwardAt a certain distance from a charged particle, the magnitude of the electric field is 500 V/m and the electric potential is 3.00 kV. (a) What is the distance to the particle? (b) What is the magnitude of the charge?arrow_forward
- A source consists of three charged particles located at the vertices of a square (Fig. P26.32), where the square has sides of length 0.243 m. The charges are q1 = 35.0 nC, q2 = 65.0 nC, and q3 = 56.5 nC. Find the electric potential at point A located at the fourth vertex. FIGURE P26.32 Problems 32 and 33.arrow_forwardAn infinite number of charges with q = 2.0 C are placed along the x axis at x = 1.0 m, x = 2.0 m, x = 4.0 m, x = 8.0 m, and so on, as shown in Figure P26.78. Determine the electric potential at the point x = 0 due to this set of charges. Hint: Use the mathematical formula for a geometric series, 1+r+r2+r3+r4+=11r FIGURE P26.78arrow_forwardThe electric potential inside a charged spherical conductor of radius R is given by V = keQ/R, and the potential outside is given by V = keQ/R, Using Er = dV/dr, derive the electric field (a) inside and (b) outside this charge distribution.arrow_forward
- A uniformly charged filament lies along the x axis between x = a = 1.00 m and x = a + = 3.00 m as shown in Figure P25.66. The total charge on the filament is 1.60 nC. Calculate successive approximations for the electric potential at the origin by modeling the filament as (a) a single charged particle at x = 2.00 m, (b) two 0.800-nC charged particles at x = 1.5 m and x = 2.5 m, and (c) four 0.400-nC charged particles at x = 1.25 m, x = 1.75 m, x = 2.25 m, and x = 2.75 m. (d) Explain how the results compare with the potential given by the exact expression v=klQlln(l+aa)arrow_forwardA particle with charge -40.0 nC is on the x axis at the point with coordinate x = 0. A second panicle, with charge -20.0 nC, is on the x axis at x = 0.500 in. (i) Is the point at a finite distance where the electric field is zero (a) to the left of .v = 0, (b) between x = 0 and x = 0.500 in, or (c) to the right of x m 0.500 in? (ii) Is the electric potential zero at this point? (a) No; it is positive, (b) Yes. (c) No; it is negative. (iii) Is there a point at a finite distance where the electric potential is zero? (a) Yes; it is to the left of x = 0. (b) Yes; it is between x = 0 and x = 0.500 in. (c) Yes; it is to the right of x = 0.500 in. (d) No.arrow_forwardAt a certain distance from a charged particle, the magnitude of the electric field is 500 V/m and the electric potential is 3.00 kV. (a) What is the distance to the particle? (b) What is the magnitude of the charge?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





