
Concept explainers
Ranger Industries has provided the following information at June 30:
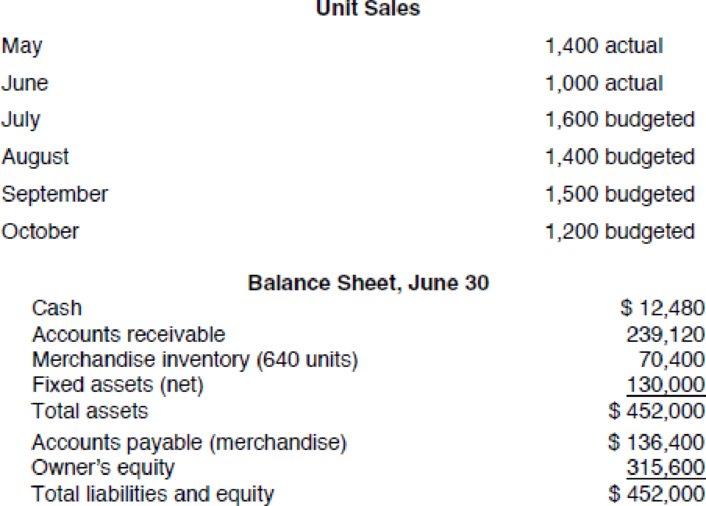
Other information:
Average selling price, $196
Average purchase price per unit, $110
Desired ending inventory, 40% of next month’s unit sales
Collections from customers:
In month of sale 20%
In month after sale 50%
Two months after sale 30%
Projected cash payments:
Inventory purchases are paid for in the month following acquisition.
Variable cash expenses, other than inventory, are equal to 25% of each month’s sales and are paid in the month of sale.
Fixed cash expenses are $40,000 per month and are paid in the month incurred.
REQUIREMENT
You have been asked to prepare a
Ranger Industries desires to maintain a minimum cash balance of $8,000 at the end of each month. If this goal cannot be met, the company borrows the exact amount needed to reach its goal. If the company has a cash balance greater than $8,000 and also has loans payable outstanding, the amount in excess of $8,000 is paid to the bank. Annual interest of 18% is paid on a monthly basis on the outstanding balance.
Prepare the master budget for July, August and September.
Explanation of Solution
Master budget: Master budget is an interrelated budget that collectively summarizes all the planned activities of the business. Master budget is not a single document and it consist the number of interrelated budgets like sales budget, production budget, and cash budget. Master budget helps the management to review the upcoming quarter budget with the monthly amount of budget figures.
Prepare a sales budget:
| Sales budget | |||
| Particulars | July | August | September |
| Units | 1,600 | 1,400 | 1,500 |
| Average selling price | $ 196 | 196 | 196 |
| Total | $313,600 | 274,400 | 294,000 |
Table (1)
Prepare a purchase budget:
| Purchase budget | |||
| Particulars | July | August | September |
| Desired ending inventory | 560 | 600 | 480 |
| Current month's unit sales | 1,600 | 1,400 | 1,500 |
| Total units needed | 2,160 | 2,000 | 1,980 |
| Less: Beginning inventory | 640 | 560 | 600 |
| Purchases (units) | 1,520 | 1,440 | 1,380 |
| Average purchase cost per unit | $110 | 110 | 110 |
| Purchases (dollars) | $167,200 | $158,400 | $151,800 |
Table (2)
Prepare a cash budget:
| Cash Budget | |||
| Particulars | July | August | September |
| Cash balance, beginning | $12,480 | $8,000 | $8,000 |
| Cash receipts: | |||
| Collections from customers: | |||
| From May sales | 82,320 | ||
| From June sales | 98,000 | 58,800 | |
| From July sales | 62,720 | 156,800 | 94,080 |
| From August sales | 54,880 | 137,200 | |
| From September sales | 58,800 | ||
| Total cash available | $255,520 | $278,480 | $298,080 |
| Cash disbursements: | |||
| Merchandise | $136,400 | $167,200 | $158,400 |
| Variable expenses | 78,400 | 68,600 | 73,500 |
| Fixed expenses | 40,000 | 40,000 | 40,000 |
| Interest paid | 0 | 109 | 191 |
| Total disbursements | $254,800 | $275,909 | $272,091 |
| Cash balance before financing | $720 | $2,571 | $25,989 |
| Less: Desired ending balance | 8,000 | 8,000 | 8,000 |
| Excess (deficit) of cash over needs | ($7,280) | ($5,429) | $17,989 |
| Financing | |||
| Borrowing | $7,280 | $5,429 | $0 |
| Repayment | 0 | 0 | (12,709) |
| Total effects of financing | $7,280 | $5,429 | ($12,709) |
| Cash balance, ending | $8,000 | $8,000 | $13,280 |
Table (3)
Prepare a forecasted income statement:
| Forecasted Income Statement | |
| For Quarter Ended September 30 | |
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| Sales | $882,000 |
| Cost of goods sold | 495,000 |
| Gross profit | $387,000 |
| Expenses: | |
| Variable expenses | $220,500 |
| Fixed expenses | 120,000 |
| Depreciation expense | 6,000 |
| Interest expense | 300 |
| Total expenses | $346,800 |
| Net income | $40,200 |
Table (4)
Prepare a forecasted balance sheet:
| Forecasted Balance Sheet | |
| as of September 30 | |
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Assets: | |
| Cash | $13,280 |
| Accounts receivable | 317,520 |
| Merchandise inventory | 52,800 |
| Fixed assets (net) | 124,000 |
| Total assets | $507,600 |
| Liabilities & equity: | |
| Accounts payable | $151,800 |
| Loans payable | 0 |
| Owner's equity | 355,800 |
| Total liabilities & equity | $507,600 |
Table (5)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Excel Applications for Accounting Principles
- Which of the following is an intangible asset? A) InventoryB) CopyrightC) EquipmentD) Accounts Receivableno aiarrow_forwardWhich of the following is an intangible asset? A) InventoryB) CopyrightC) EquipmentD) Accounts Receivablearrow_forwardWhat does a ledger account represent? A) A detailed record of all business transactionsB) A summary of trial balancesC) An individual record for each accountD) The final balance of a financial statement Need help!arrow_forward
- What is the primary purpose of accounting? A) To generate tax revenueB) To record, summarize, and report financial transactionsC) To determine the market value of assetsD) To manage payrollarrow_forwardWhat are the three main financial statements in accounting?arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forward
 Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT




