
Label the parts of the human
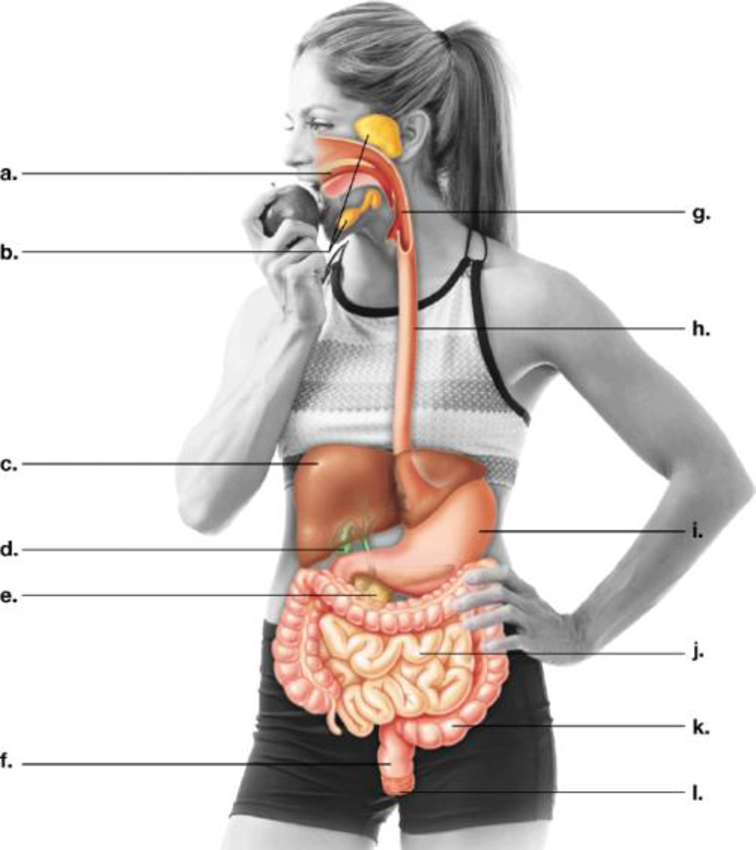
To label: The parts of human digestive system in the figure given and indicate their functions.
Introduction: Human digestive system consists of gastrointestinal (GI) tract and accessory organs. The gastrointestinal tract is made up of mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. The accessory organs for digestion are liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. Each part of the digestive system moves ingested food through gastrointestinal tract, breaks it into small parts, so that they can be absorbed if needed or expelled out.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Pictorial representation: A labeled diagram showing the various parts of a human digestive system.
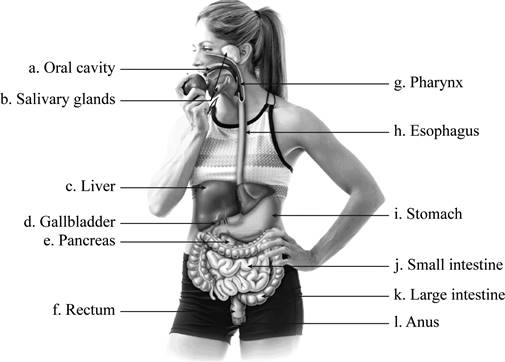
Fig.1 Human digestive system
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Correct answer: Oral cavity
Explanation: In a digestive system, the first section is ingestion and chewing of food. This is done by the oral cavity or mouth cavity. It consists of lips, cheek lining, teeth, front part of the tongue, gums, and roof of the mouth. Hence, the correct answer is oral cavity.
(b)
Correct answer: Salivary glands
Explanation: The ingested food moves through gastrointestinal tract by the process known as peristalsis. After chewing, the salivary glands form digestive juice called saliva, which moistens food to easily pass through the esophagus into the stomach. Hence, the correct answer is salivary glands.
(c)
Correct answer: Liver
Explanation: The liver’s function is to produce and secrete a digestive juice known as bile. Bile ducts carry bile from liver to gall bladder for storage, and it helps in digestion of fats. Also, the liver contributes in filtering and purifying the blood. Hence, the correct answer is liver.
(d)
Correct answer: Gall bladder
Explanation: Gall bladder is located below liver and stores bile juice. When fatty food enters the duodenum of the small intestine, the gall bladder squeezes into small intestine through bile ducts. Hence, the correct answer is gall bladder.
(e)
Correct answer: Pancreas
Explanation: Pancreas mainly forms digestive enzymes that are released into small intestine through ducts. These enzymes help in digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. Hence, the correct answer is pancreas.
(f)
Correct answer: Rectum
Explanation: Rectum is a part of the large intestine that connects the colon to the anus. It receives stool from the colon and accommodates it until it is expelled out through sphincters. Hence, the correct answer is rectum.
(g)
Correct answer: Pharynx
Explanation: Pharynx is also referred as throat in the digestive tract. It receives food from the mouth. It branches into the esophagus and the trachea. The esophagus further takes food to the stomach for digestion, and trachea carries air to the lungs. Hence, the correct answer is pharynx.
(h)
Correct answer: Esophagus
Explanation: After ingestion and chewing of food, the food is pushed to the stomach through peristaltic movement. It is carried through the esophagus. The esophagus is also known as food pipe. Hence, the correct answer is esophagus.
(i)
Correct answer: Stomach
Explanation: Stomach is a digestive organ in the abdominal cavity. It secretes digestive enzymes (breaking of large molecules), mucus (moisten), and hydrochloric acid (protection against microbes) for digestion of ingested food. Hence, the correct answer is stomach.
(j)
Correct answer: Small intestine
Explanation: Small intestine is a coiled structure and secretes digestive juices. It consists of folds that contribute in digestion and absorption of nutrients. Hence, the correct answer is small intestine.
(k)
Correct answer: Large intestine
Explanation: Large intestine consists of cecum, colon, and rectum. It helps in absorption of water from the gastrointestinal tract into the bloodstream. The unused particles are moved further into the rectum for elimination. Hence, the correct answer is large intestine.
(l)
Correct answer: Anus
Explanation: Anus is the last part of the digestive system. It is the external opening at the end of rectum for elimination of feces from the body. Defecation is controlled by two sphincters namely internal and external anal sphincters. Hence, the correct answer is anus.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
CAMPBEL BIOLOGY:CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS
- Molecular Biology Question A gene that codes for a protein was removed from a eukaryotic cell and inserted into a prokaryotic cell. Although the gene was successfully transcribed and translated, it produced a different protein than it produced in the eukaryotic cell. What is the most likely explanation?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology LIST three characteristics of origins of replicationarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you For E coli DNA polymerase III, give the structure and function of the b-clamp sub-complex. Describe how the structure of this sub-complex is important for it’s function.arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology LIST three characteristics of DNA Polymerasesarrow_forwardMolecular Biology RNA polymerase core enzyme structure contains what subunits? To form holo enzyme, sigma factor is added to core. What is the name of the structure formed? Give the detailed structure of sigma factor and the function of eachdomain. Please help. Thank youarrow_forwardMolecular Biology You have a single bacterial cell whose DNA is labelled with radioactiveC14. After 5 rounds of cell division, how may cells will contain radioactive DNA? Please help. Thank youarrow_forward
- 1. Explain the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins). Also add some pictures.arrow_forward1. In the Sentinel Cell DNA integrity is preserved through nanoscopic helicase-coordinated repair, while lipids in the membrane are fortified to resist environmental mutagens. also provide pictures for this question.arrow_forwardExplain the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins). Also add some pictures.arrow_forward
- In the Sentinel Cell DNA integrity is preserved through nanoscopic helicase-coordinated repair, while lipids in the membrane are fortified to resist environmental mutagens. also provide pictures for this question.arrow_forward1. Explain how genetic information is stored, copied, transferred, and expressed. Also add some pictures for this question.arrow_forward!. Describe biological macromolecules (DNA, RNA, proteins, lipids, etc.) and how they function in the cell. also provide some images for this question.arrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning





