
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780137514724
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 20, Problem 11P
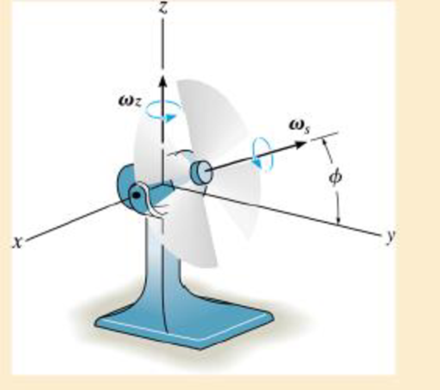
The electric fan is mounted on a swivel support such that the fan rotates about the z axis at a constant rate of ωz = 1 rad/s and the fan blade is spinning at a constant rate ωs, = 60 rad/s. If at the instant ϕ = 45°, ϕ = 2 rad/s for the motion, determine the angular velocity and the angular acceleration of the blade.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The small collar A is sliding on the bent bar with speed u = 1.5 m/s relative to the bar as shown. The distances are L= 2.60 m and d =
0.77 m. Simultaneously, the bar is rotating with angular velocity w = 2.33 rad/s about the fixed pivot B. Take the x-y axes to be fixed to
the bar and determine the Coriolis acceleration acor of the slider for the instant represented. Interpret your result.
В
Answer: acor = ( i
i+ i
j) m/s?
B.
What is the angular rate θ˙ measured in rad/s?
A disk oscillates about its axis of rotation given by its angular acceleration of ∝ = -kθ. First determine the value of k for which, ω = 19.3 rad/s when θ = 0 and θ = 6 radians when ω = 0. Then determine the angular velocity when θ = 3 radians.
Chapter 20 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Ch. 20 - The propeller of an airplane is rotating at a...Ch. 20 - The disk rotates about the z axis at a constant...Ch. 20 - The ladder of the fire truck rotates around the z...Ch. 20 - The ladder of the fire truck rotates around the z...Ch. 20 - At a given instant, the antenna has an angular...Ch. 20 - The disk rotates about the shaft S, while the...Ch. 20 - The electric fan is mounted on a swivel support...Ch. 20 - The electric fan is mounted on a swivel support...Ch. 20 - The truncated double cone rotates about the z axis...Ch. 20 - Prob. 20P
Ch. 20 - Gear B is driven by a motor mounted on turntable...Ch. 20 - Prob. 22PCh. 20 - Prob. 23PCh. 20 - Prob. 26PCh. 20 - Prob. 27PCh. 20 - Prob. 30PCh. 20 - So1ve Example 20.5 such that the x, y, z axes move...Ch. 20 - Prob. 38PCh. 20 - At the instant = 60, the telescopic boom AB of...Ch. 20 - Prob. 40PCh. 20 - Prob. 42PCh. 20 - Prob. 43PCh. 20 - Prob. 44PCh. 20 - Prob. 46PCh. 20 - Prob. 47PCh. 20 - Prob. 48PCh. 20 - Prob. 49PCh. 20 - Prob. 50PCh. 20 - Prob. 51P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If the wheel in each case rolls on the circular surface without slipping, determine the acceleration of point C on the wheel momentarily in contact with the circular surface. The wheel has an angular velocity ω = 3.6 rad/s and an angular acceleration α = 5.0 rad/s2. The distances R = 1.5 m and r = 0.6 m.arrow_forwardThe disk rotates about the shaft S, while the shaft is turning about the z axis at a rate of ωz = 5.5 rad/s , which is increasing at α = 2.5 rad/s2 . No slipping occurs. Determine the x, y, and z components of the velocity of point B on the disk at the instant shown using scalar notation. Determine the x, y, and z components of the acceleration of point B on the disk at the instant shown using scalar notation.arrow_forwardIf the compact disc is spinning at a constant angular rate θ˙ = 445 rev/min, determine the magnitudes of the accelerations of points A and B at the instant shown. Determine the magnitudes of the velocities of points A and B.arrow_forward
- The body is formed of slender rod and rotates about a fixed axis through point O. At time t = 0, the body is in the orientation 0 = 0 and has an angular velocity wo = 0.3 rad/s and a constant angular acceleration a = 0.8 rad/s². Determine the vectors of velocity and acceleration of point A at t = 1 s. Use d = 2r = 0.8 m. (√₁ = 0.106î + 1.240ŷ m/s, da -1.289 + 1.019ĵ m/s²) ω, α y = d x Aarrow_forwardThe disk has an angular velocity of 8 rad/s and is increasing at the rate of 5 rad/s' about its Z- axis and the yoke AB has a constant angular velocity w = 3 rad/s about its shaft as shown. Simultaneously the entire assembly revolves about the fixed X-axis with constant velocity o, = 5 rad/s. Determine the velocity and acceleration of point F on the disc for an instant shown in the figure. Also find angular velocity and angular acceleration of the disc. 20 cm 15. 30 cm 30 cm 30 cm N 20 cmarrow_forward4. As shown in the image below, the bucket of the backhoe traces the path of the cardioid r = C · (1 – cos 0) ft, where constant C= 28. At this instant angle 0 - = 121°, and the boom is rotating with an angular velocity of 0 = 2.3 rad/s and an angular acceleration of 0 = 0.19 rad/s?. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the bucket in rad/s². Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 1 place after the decimal point. Your Answer: Answerarrow_forward
- The wheel of radius r = - 4 ft rolls without slipping on the horizontal surface. At the instant shown, 3.7 rad/sec, ao : 8.8 ft/sec², and 0 = 60°. Determine the vectors of the accelerations of points A, B, and C on the wheel. (σ = 63.6i +8.8 ft/sec², dB = 43.8i - 43.0j ft/sec², ac = 54.8 ft/sec²) W= = y ω B r απ Ꮎ × A Carrow_forwardIn the mechanism illustrated below, the disk rolls without slip at constant angular velocity w = 10 rad/s in the indicated direction. R = 0.5ft. use the VECTOR method to determine the angular velocity of link AB and velocity of slider Aarrow_forwardA 3 in radius disk spins at the constant ω1 - 5 radian/s and a constant rate ω2= 4 radians/s. If the angle is 45 degrees, find the absolute acceleration at point P.arrow_forward
- The rotor B spins about its inclined axis OA at the angular speed N₁ = 215 rev/min, where 3 = 28°. Simultaneously, the assembly rotates about the vertical z-axis at the rate N₂. If the total angular velocity of the rotor has a magnitude of 41 rad/s, determine N2₂. N₁ Answer: N₂ = rev/min B N₂arrow_forwardThe rotor of an electric motor rotates at the constant rate ω1 = 1800 rpm. Determine the angular acceleration of the rotor as the motor is rotated about the y axis with a constant angular velocity ω2 of 6 rpm counterclockwise when viewed from the positive y axis.arrow_forwardb) Find the angular velocity and angular acceleration of disc B shown below, which is spinningatthe constant rate of ω2 = 90/πrpm. The disc is attached to collar A, which is rotating at the angular speed of ω1 = 5/π rpm, with the angular speed increasing at 0.5/π rpm/sec. Rod AB which connects the disc to the collar ispinned to the collar at A. The rod makes an angle of θ = 300 with the vertical, which is increasing at a constant rate of20/π0/sec.Express theAngularvelocityAcceleration of the disc in terms of a reference frame attached to thecollar.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY