
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
8th Edition
ISBN: 8220102744127
Author: Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 64P
For each compound, indicate the atom that is most apt to be protonated.
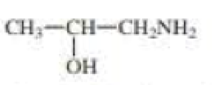
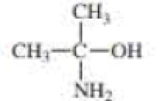
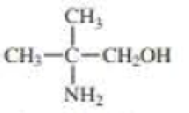
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In the box below, specify which of the given compounds are very soluble in polar aprotic solvents. You may select more than one compound. Choose one or more: NaCl NH4Cl CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CN CH3CH2OH hexan-2-one NaOH CH3SCH3
On the following structure, select all of the atoms that could ACCEPT a hydrogen bond. Ignore possible complications of aromaticity. When selecting be sure to click on the center of the atom.
Rank the compounds below from lowest to highest melting point.
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 2.1 - Which of the following are not acids? CH3COOH CO2...Ch. 2.1 - Consider the following reaction: a. What is the...Ch. 2.1 - Draw the products of the addbase renc1 ion when a....Ch. 2.1 - a. What is the conjugate acid of each or the...Ch. 2.2 - a. Which is a stronger acid: one with a pKa of 5.2...Ch. 2.2 - An acid has a Ka of 4.53 106 in water. What is...Ch. 2.2 - Prob. 7PCh. 2.2 - Antacids are compounds that neutralize stomach...Ch. 2.2 - Are the following body fluids acidic or basic? a....Ch. 2.3 - Draw the conjugate acid of each of the following:...
Ch. 2.3 - a. Write an equation showing CH3OH reacting as an...Ch. 2.3 - Estimate the pKa values of the following...Ch. 2.3 - a. Which is a stronger base: CH3COO or HCOO? (The...Ch. 2.3 - Using the pKa values in Section 2.3, rank the...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 15PCh. 2.5 - a. For each of the acid-base reactions in Section...Ch. 2.5 - Ethyne has a pKa value of 25, water has a pKa...Ch. 2.5 - Which of the following bases can remove a proton...Ch. 2.5 - Calculate the equilibrium constant for the...Ch. 2.6 - Rank the ions (CH3, NH2, HO, and F) from most...Ch. 2.6 - Rank the carbanions shown in the margin from most...Ch. 2.6 - Which is the stronger acid?Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 23PCh. 2.6 - What reaction in Problem 23 has the smallest...Ch. 2.6 - Rank the halide ions (F, Cl, Br, and l) from...Ch. 2.6 - a. Which is more electronegative, oxygen or...Ch. 2.6 - Which is a stronger acid? a. HCl or HBr b....Ch. 2.6 - a. Which of the halide ions (F, Cl, Br, and l) is...Ch. 2.6 - Which is a stronger base? (The potential maps in...Ch. 2.7 - What is a stronger acid? a. CH3OCH2CH2OH or...Ch. 2.7 - Rank the following compounds from strongest add to...Ch. 2.7 - What is a stronger base?Ch. 2.8 - For each of the following compounds, indicate the...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 35PCh. 2.8 - Which is a stronger acid? Why?Ch. 2.8 - Fosamax (shown on the previous page) has six...Ch. 2.9 - Using the table of pKa values given in Appendix I,...Ch. 2.10 - For each of the following compounds (here shown in...Ch. 2.10 - As long as the pH is not less than _______, at...Ch. 2.10 - a. Indicate whether a protonated amine (RN+H3)...Ch. 2.10 - A naturally occurring amino acid such as alanine...Ch. 2.10 - a. At what pH is the concentration of a compound,...Ch. 2.10 - For each of the following compounds, indicate the...Ch. 2.10 - Given the data in Problem 47: a. What pH would you...Ch. 2.11 - Write the equation that shows how a buffer made by...Ch. 2.12 - Draw the products of the following react ions. Use...Ch. 2.12 - What product are formed when each of the following...Ch. 2 - Which is a stronger base? a. HS or HO b. CH3O or...Ch. 2 - According to the explanations by Lewis, if a...Ch. 2 - a. Rank the following alcohols from strongest to...Ch. 2 - a. Rank the following carboxylic acids from...Ch. 2 - Prob. 57PCh. 2 - For the following compound. a. draw its conjugate...Ch. 2 - Rank the following compounds from strongest to...Ch. 2 - Prob. 60PCh. 2 - Prob. 61PCh. 2 - a. Rank the following alcohols from strongest to...Ch. 2 - A single bond between two carbons with different...Ch. 2 - For each compound, indicate the atom that is most...Ch. 2 - a. Given the Ka values, estimate the pKa value of...Ch. 2 - Tenormin, a member of the group of drugs known as...Ch. 2 - From which of the following compounds can HO...Ch. 2 - a. For each of the following pairs of reactions,...Ch. 2 - Prob. 69PCh. 2 - Which is a stronger acid? a. b. c. d.Ch. 2 - Prob. 71PCh. 2 - Prob. 72PCh. 2 - Given that pH+ pOH = 14 and that the concentration...Ch. 2 - How could you separate a mixture of the following...Ch. 2 - Prob. 75PCh. 2 - a. If an add with a pKa of 5.3 is in an aqueous...Ch. 2 - Calculate the pH values of the following...Ch. 2 - Prob. 1PCh. 2 - Prob. 2PCh. 2 - Prob. 3PCh. 2 - Which of the reactions in Problem 3 favor...Ch. 2 - Prob. 5PCh. 2 - Prob. 6PCh. 2 - Prob. 7PCh. 2 - Which is the stronger acid? a. ClCH2CH2OH or...Ch. 2 - Prob. 9PCh. 2 - Prob. 10PCh. 2 - Which is a more stable base? Remembering that the...Ch. 2 - Which is the Stronger acid?Ch. 2 - Prob. 13PCh. 2 - a. Draw the structure of (CH3COOH (pKa = 4.7) at...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 18 Question (1 point) Draw the line structure form of the given partially condensed structure in the box provided. :ÖH HC HC H2 ΙΩ Н2 CH2 CH3 CH3 partially condensed formarrow_forwardsomeone else has already submitted the same question on here and it was the incorrect answer.arrow_forwardThe reaction: 2NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4(g) is an exothermic reaction, ΔH=-58.0 kJ/molrxn at 0°C the KP is 58.If the initial partial pressures of both NO2(g) and N2O4(g) are 2.00 atm:A) Is the reaction at equilibrium? If not, what is the value of Q? B) Which direction will the reaction go to reach equilibrium? C) Use an ICE table to find the equilibrium pressures.arrow_forward
- The dissociation of the weak acid, nitrous acid, HNO2, takes place according to the reaction: HNO2 (aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + NO2–(aq) K=7.2 X 10-4 When 1.00 mole of HNO2 is added to 1.00 L of water, the H+ concentration at equilibrium is 0.0265 M.A) Calculate the value of Q if 1.00 L of water is added? B) How will reaction shift if 1.00 L of water is added?arrow_forwardSuppose a certain copolymer elastomeric material “styrene-butadiene rubber”) contains styrene ("S") monomers –(C8H8)– and butadiene ("B") monomers –(C4H6)– and that their numerical ratio S:B = 1:8. What is the mass ratio mS:mB of the two monomers in the material? What is the molecular mass M of a macromolecule of this copolymer with degree of polymerization n = 60,000? Data: AC = 12.01 u, AH = 1.008 u.arrow_forwardLab Questions from Lab: Gravimetric Determination of Calcium as CaC2O4•H2O What is the purpose of the methyl red indicator? Why does a color change to yellow tell you that the reaction is complete? Why is the precipitate rinsed with ice-cold water in step 4? Why not room temperature or hot water? Why is it important that the funnels be placed in a desiccator before weighing (steps 1 and 5)?arrow_forward
- What mass of ethylene glycol, HOCH2CH2OH, Mustbe added to 5.50 kg of water to antifreeze that would work for the car radiator to -10.0 degrees celcius? MM (g/mol): 62.07arrow_forwardWhat is the molarity of a 0.393 m glucose solution if its density is 1.16 g/mL? MM glucose 180.2 g/molarrow_forwardThe rate constant for the decay of a radioactive element is 2.28 × 10⁻³ day⁻¹. What is the half-life of this element in days?arrow_forward
- Handwritten pleasearrow_forwardChoose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. i H A B 1. CH3CH2Na 2. H3O+ 1. CH3CH2MgBr 2. H3O+ 1. CH3MgBr Q C 2. H3O+ 1. H3O+ D 2. CH3MgBr 00 OH Q E CH³MgBrarrow_forwardThe kinetics of a gas phase reaction of the form A → Products results in a rate constant of 0.00781 M/min. For this reaction, the initial concentration of A is 0.501 M. What is the half-life for this reaction?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning



Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry | Acids & Bases; Author: Ninja Nerd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AOr_5tbgfQ0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY