
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780137514724
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 18, Problem 28P
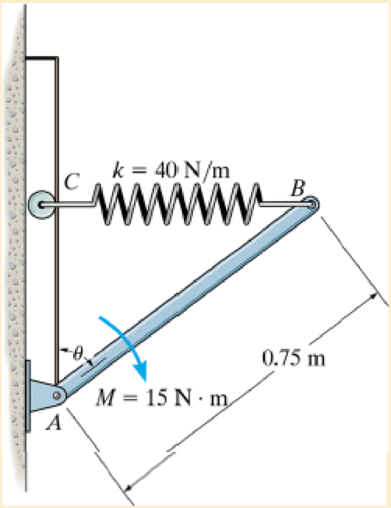
The 10-kg rod AB is pin connected at A and subjected to a couple moment of M = 15 N·m. If the rod is released from rest when the spring is unstretched at θ = 30°, determine the rod's angular velocity at the instant θ = 60°. As the rod rotates, the spring always remains horizontal, because of the roller support at C.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Each of the two links has a mass of 2 kg and a centroidal radius of gyration of 60mm. The slider at B has a mass of 3 kg and moves freely in the vertical guide. The springhas a stiffness of 6 kN/m. If a constant torque M = 20 N∙m is applied to link OA throughits shaft at O starting from the rest position at θ = 45°, determine the angular velocity ofOA when θ = 0.
The cylinder is at rest supported by the spring of stiffness 205 N/m when a torque of 78 Nm is applied as shown.
The mass of the cylinder is 2.5 kg and its radius is 205 mm.
If the wheel rolls without slipping, find the velocity of the centre of the wheel when it has moved a distance 352 mm up the slope with the angle ẞ= 25°.
4. The 10-kg rod AB is pin-connected at A and subjected to a couple
moment of M = 15 Nm. If the rod is released from rest when the spring is
unstretched at 8 = 30°, determine the angular velocity of the rod at the
instant 0 = 60°. Thanks to the roller support at C, the spring always
remains horizontal when the rod rotates.
A
O
k= 40 N/m
M=15 N·m
0.75 m
Chapter 18 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Ch. 18 - The 80-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its...Ch. 18 - The uniform 50-lb slender rod is subjected to a...Ch. 18 - The uniform 50-kg slender rod is at rest m the...Ch. 18 - The 50-kg wheel is subjected to a force of 50 N....Ch. 18 - If the uniform 30-kg slender rod starts from rest...Ch. 18 - The 20-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its...Ch. 18 - At a given instant the body of mass m has an...Ch. 18 - A force of P = 20 N is applied to the cable, which...Ch. 18 - A force of P = 20 N is applied to the cable, which...Ch. 18 - The double pulley consists of two parts that are...
Ch. 18 - The double pulley cons1sts of two parts that are...Ch. 18 - Prob. 9PCh. 18 - The 10-kg uniform slender rod is suspended at rest...Ch. 18 - Prob. 14PCh. 18 - The pendulum consists of a 10-kg uniform disk and...Ch. 18 - The center O of the thin ring of mass m is given...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18PCh. 18 - Prob. 19PCh. 18 - Prob. 22PCh. 18 - Prob. 23PCh. 18 - Prob. 27PCh. 18 - The 10-kg rod AB is pin connected at A and...Ch. 18 - Motor M exerts a constant force of P = 750 Non the...Ch. 18 - The two 2-kg gears A and B are attached to the...Ch. 18 - F187. If the 30-kg disk is released from rest when...Ch. 18 - The 50-kg reel has a radius of gyration about its...Ch. 18 - The 60-kg rod OA is released from rest when = 0....Ch. 18 - Prob. 10FPCh. 18 - The 30-kg rod is released from rest when = 45....Ch. 18 - Prob. 12FPCh. 18 - Prob. 36PCh. 18 - Prob. 37PCh. 18 - The 40-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its...Ch. 18 - The assembly consists of two 10-kg bars which are...Ch. 18 - The assembly consists of two 10-kg bars which are...Ch. 18 - Prob. 51PCh. 18 - Prob. 52PCh. 18 - If the 250-lb block is released from rest when the...Ch. 18 - The slender 15-kg bar is initially at rest and...Ch. 18 - The 50-lb wheel has a radius of gyration about its...Ch. 18 - The system consists of 60-lb and 20-lb blocks A...Ch. 18 - The pendulum of the Charpy impact machine has a...Ch. 18 - Prob. 2RPCh. 18 - The drum has a mass of 50 kg and a radius of...Ch. 18 - The spool has a mass of 60 Kg and a radius of...Ch. 18 - Prob. 5RPCh. 18 - At the Instant shown, the 50-lb bar rotates...Ch. 18 - Prob. 7RPCh. 18 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The 153-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its center of mass O of kO = 283 mm. If it rotates counterclockwise at an angular speed of 1431 rev/min and the tension force applied to the braking band at A is TA = 1771N,a) Determine the angular acceleration, in rad/s2, so that the wheel comes to rest in 67.6 revolutions after TA and TB are applied.arrow_forwardEach of the two links has a mass of 1.5 kg and a centroidal radius of gyration of 55 mm. The slider at B has a mass of 3.4 kg and moves freely in the vertical guide. The spring has a stiffness of 5.9 kN/m. If a constant torque M = 14.0 N-m is applied to link OA through its shaft at O starting from the rest position at = 45°, determine the angular velocity of OA when 0 = 0. 40 mm 330 mm O Answer: w= i 165 mm 165 mm rad/sarrow_forwardThe 50-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its center of gravity G of kG = 300mm. If it rolls without slipping, determine its angular velocity when it has rotated clockwise 90° from the position shown. The spring AB has a stiffness k = 200 N/m and an unstretched length of 400 mm. The wheel is released from rest.arrow_forward
- A constant couple moment M is acted on the drum O to pull the spool C up the incline. Both drum O and spool C can be treated as uniform disk. If spool C is rolling without slipping, determine the angular acceleration of the drum and the cord force. R R (0 Marrow_forwardAt the instant shown, the 200-lb bar rotates clockwise at 4 rad/s. The spring attached to its endalways remains vertical due to the roller guide at C. If the spring has an unstretched length of 2ft and a stiffness of k = 9 lb/ft, determine the angular velocity of the bar the instant it has rotated 39° clockwise.arrow_forwardThe 21-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its center O of ko =260 mm, and radius r = 0.5 m. When the wheel is subjected to the constant force F = 247 N, applied to the wheel's center axle at an angle = 6°, it starts rolling from rest. Determine the wheel's angular velocity W (in rad/s) after 4.0 seconds if the wheel has been rolling without slipping. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 1 place after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s². Your Answer: G Answer r 0 Farrow_forward
- The 27-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its center O of ko = 260 mm, and radius r = 0.5 m. When the wheel is subjected to the constant force F = 354 N, applied to the wheel's center axle at an angle = 6°, it starts rolling from rest. Determine the wheel's angular velocity W (in rad/s) after 3.2 seconds if the wheel has been rolling without slipping. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 1 place after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s². F 0 Your Answer: Answerarrow_forwardA force of P = 60 N is applied to the cable, which causes the 200-kg reel to turn since it is resting on the two rollers A and B of the dispenser. Determine the angular velocity of the reel after it has made two revolutions starting from rest. Neglect the mass of the rollers and the mass of the cable. Assume the radius of gyration of the reel about its center axis remains constant at k, = 0.6 m.arrow_forwardThe 30-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its center O of ko = 240 mm, and radius r = 0.5 m. When the wheel is subjected to the constant force F = 388 N, applied to the wheel's center axle at an angle = 6°, it starts rolling from rest. Determine the total angular impulse L (in N•m.s) about the wheel's IC after 3.7 seconds if the wheel has been rolling without slipping. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 1 place after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s². Your Answer: G Answer Ө Farrow_forward
- The 31-kg reel is mounted on the 16-kg cart. Part A: If the cable wrapped around the inner hub of the reel is subjected to a force of P=50N, determine the velocity of the cart when t = 4.2 s. The radius of gyration of the reel about its center of mass O is kO=250mm. Neglect the size of the small wheels. Part B: Determine the angular velocity of the reel when t = 4.2 s.arrow_forwardThe 28-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its center O of ko = 220 mm, and radius r = 0.4 m. When the wheel is subjected to the couple moment M = 63 N•m, it slips as it rolls. Determine the linear acceleration of the wheel's center O (in m/s²). The coefficient of kinetic friction between the wheel and the plane is μ = 0.47. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s². M Your Answer: Answer 1arrow_forward18–2. A force of P = 20 N is applied to the cable, which causes the 175-kg reel to turn since it is resting on the two rollers A and B of the dispenser. Determine the angular velocity of the reel after it has made two revolutions starting from rest. Neglect the mass of the rollers and the mass of the cable. The radius of gyration of the reel about its center axis is 30° 250 mm kG = 0.42 m. OG 500 mm -400 mm-arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Power Transmission; Author: Terry Brown Mechanical Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YVm4LNVp1vA;License: Standard Youtube License