
Concept explainers
In this abbreviated diagram, identify the four major plant groups and the key terrestrial adaptation associated with each of the three major branch points.
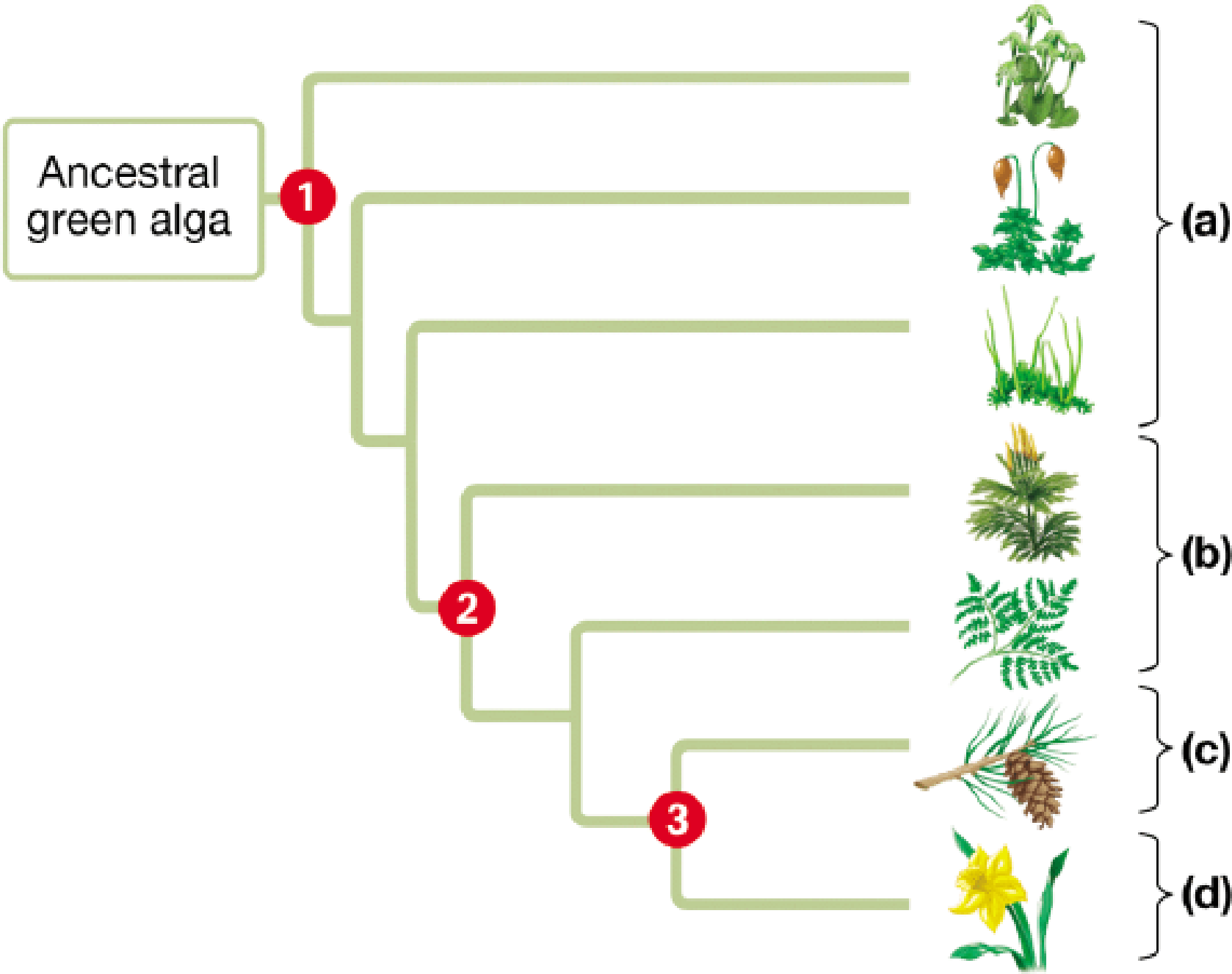
To determine: The four major plant group and their key terrestrial adaptation associated with each of the three major branch points.
Introduction:
The evolution of plants started with the origin of land plants that included the bryophytes. Land plants developed apical meristem and the embryos. After the land plants, the origin of vascular plants occurred. They involved the seedless fern and mosses. Lastly, the origin of seeded plants occurred. This includes the angiosperms and the gymnosperms.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Pictorial representation: The highlights of plant evolution are depicted in Fig.1.
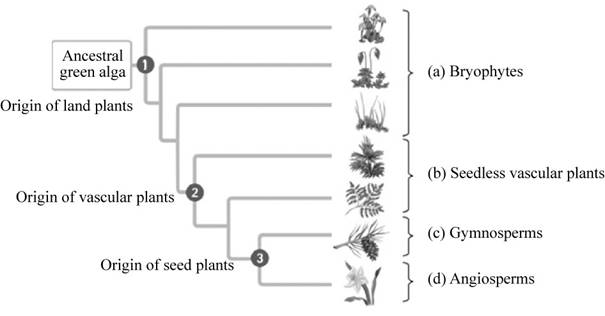
Fig.1: The major events in plant evolution.
Explanation of Solution
The three distinct adaptations which gave rise to the four major plant groups are:
(1)
Correct answer: The origin of land plants.
Explanation:
The first terrestrial adaptation includes the origin of land plants. Their development included presence of the meristem and the embryos within the parent.
They include the major plant group (a) the bryophytes. The bryophytes are the non vascular plants and they evolved from the green algae about 475 million years ago. It included the development of apical meristem and embryos. For example: Mosses, hornworts, and liverworts. Hence, the correct answer is origin of land plants.
(2)
Correct answer: The origin of vascular plants.
Explanation:
The second adaptation includes the origin of vascular plants. It included the development of vascular tissues that helped the plants to grow tall and move away from the moist environment. They were now able to transport water to the leaves from the roots.
They include plant group (b) the seedless vascular plants. They evolved about 425 million years ago and include the ferns, club mosses and the horsetails. Hence, the correct answer is origin of vascular plants.
(3)
Correct answer: The origin of seed plants.
Explanation:
The third adaptation includes the origin of seed plants. They included the vascular seed plants. The seeds provided protection and dispersion of the embryos.
They include two major groups of plants:
Group (c) Gymnosperms: They include the seeded plants which have their seeds within the cones. They evolved about 360 million years ago. For example: pines, fir and spruce.
Group (d) Angiosperms: They include the vascular seeded plants that bear flowers. They evolved about 360 million years ago along with the gymnosperms. For example: rose, maple trees and oak trees. Hence, the correct answer is origin of seed plants.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
CAMPBEL BIOLOGY:CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS
- students in a science class investiged the conditions under which corn seeds would germinate most successfully. BAsed on the results which of these factors appears most important for successful corn seed germination.arrow_forwardI want to write the given physician orders in the kardex formarrow_forwardAmino Acid Coclow TABle 3' Gly Phe Leu (G) (F) (L) 3- Val (V) Arg (R) Ser (S) Ala (A) Lys (K) CAG G Glu Asp (E) (D) Ser (S) CCCAGUCAGUCAGUCAG 0204 C U A G C Asn (N) G 4 A AGU C GU (5) AC C UGA A G5 C CUGACUGACUGACUGAC Thr (T) Met (M) lle £€ (1) U 4 G Tyr Σε (Y) U Cys (C) C A G Trp (W) 3' U C A Leu בוט His Pro (P) ££ (H) Gin (Q) Arg 흐름 (R) (L) Start Stop 8. Transcription and Translation Practice: (Video 10-1 and 10-2) A. Below is the sense strand of a DNA gene. Using the sense strand, create the antisense DNA strand and label the 5' and 3' ends. B. Use the antisense strand that you create in part A as a template to create the mRNA transcript of the gene and label the 5' and 3' ends. C. Translate the mRNA you produced in part B into the polypeptide sequence making sure to follow all the rules of translation. 5'-AGCATGACTAATAGTTGTTGAGCTGTC-3' (sense strand) 4arrow_forward
- What is the structure and function of Eukaryotic cells, including their organelles? How are Eukaryotic cells different than Prokaryotic cells, in terms of evolution which form of the cell might have came first? How do Eukaryotic cells become malignant (cancerous)?arrow_forwardWhat are the roles of DNA and proteins inside of the cell? What are the building blocks or molecular components of the DNA and proteins? How are proteins produced within the cell? What connection is there between DNA, proteins, and the cell cycle? What is the relationship between DNA, proteins, and Cancer?arrow_forwardWhy cells go through various types of cell division and how eukaryotic cells control cell growth through the cell cycle control system?arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





