
Do lizards play a role in spreading plant seeds? Some research carried out in South Africa would suggest so (“Dispersal of Namaqua Fig [Ficus cordata cordata] Seeds by the Augrabies Flat Lizard [Platysaurus broadleyi]” Journal of Herpetology [1999]: 328–330). The researchers collected 400 seeds of this particular type of fig, 100 of which were from each treatment: lizard dung, bird dung, rock hyrax dung, and uneaten figs. They planted these seeds in batches of 5, and for each group of 5 they recorded how many of the seeds germinated. This resulted in 20 observations for each treatment. The treatment means and standard deviations are given in the accompanying table.
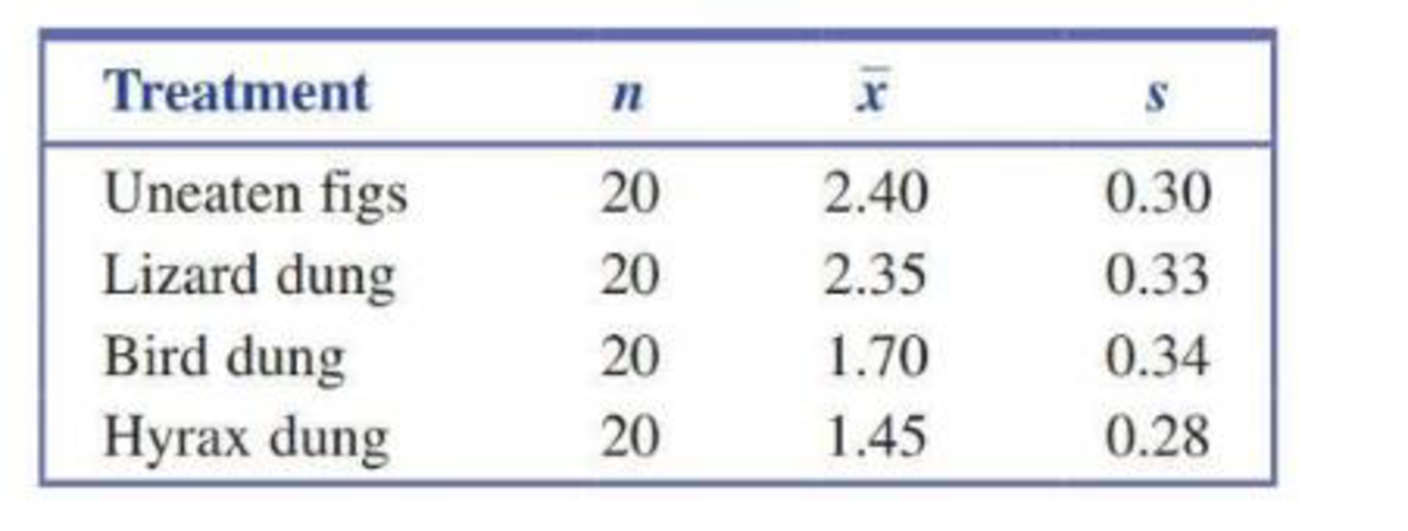
- a. Construct the appropriate ANOVA table, and test the hypothesis that there is no difference between the means for the number of seeds germinating for the four treatments.
- b. Is there evidence that seeds eaten and then excreted by lizards germinate at a higher rate, on average, than those eaten and then excreted by birds? Give statistical evidence to support your answer.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 15 Solutions
Bundle: Introduction to Statistics and Data Analysis, 5th + WebAssign Printed Access Card: Peck/Olsen/Devore. 5th Edition, Single-Term
- Using all 1991 birth records in the computerized national birth certificate registry compiled by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), statisticians Traci Clemons and Marcello Pagano found that the birth weights of babies in the United States are not symmetric ("Are babies normal?" The American Statistician, Nov 1999, 53:4). However, they also found that when infants born outside of the "typical" 37-43 weeks and infants born to mothers with a history of diabetes are excluded, the birth weights of the remaining infants do follow a Normal model with mean u = 3432 g and standard deviation o = 482 g. The following questions refer to infants born from 37 to 43 weeks whose mothers did not have a history of diabetes. Compute the z-score of an infant who weighs 4412 g. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Approximately what fraction of infants would you expect to have birth weights between 3130 g and 3820 g? (Express your answer as a decimal, not a percent, and round to three…arrow_forwardUsing all 1991 birth records in the computerized national birth certificate registry compiled by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), statisticians Traci Clemons and Marcello Pagano found that the birth weights of babies in the United States are not symmetric ("Are babies normal?" The American Statistician, Nov 1999, 53:4). However, they also found that when infants born outside of the "typical" 37-43 weeks and infants born to mothers with a history of diabetes are excluded, the birth weights of the remaining infants do follow a Normal model with mean p = 3432 g and standard deviation o = 482 g. The following questions refer to infants born from 37 to 43 weeks whose mothers did not have a history of diabetes. %3D Compute the z-score of an infant who weighs 2189 g. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Approximately what fraction of infants would you expect to have birth weights between 2760 g and 4230 g? (Express your answer as a decimal, not a percent, and round to…arrow_forwardUsing all 1991 birth records in the computerized national birth certificate registry compiled by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), statisticians Traci Clemons and Marcello Pagano found that the birth weights of babies in the United States are not symmetric ("Are babies normal?" The American Statistician, Nov 1999, 53:4). However, they also found that when infants born outside of the "typical" 37-43 weeks and infants born to mothers with a history of diabetes are excluded, the birth weights of the remaining infants do follow a Normal model with mean μ = 3432 g and standard deviation o = 482 g. The following questions refer to infants born from 37 to 43 weeks whose mothers did not have a history of diabetes. Compute the z-score of an infant who weighs 4465 g. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Approximately what fraction of infants would you expect to have birth weights between 2930 g and 3140 g? (Express your answer as a decimal, not a percent, and round to three…arrow_forward
- Using all 1991 birth records in the computerized national birth certificate registry compiled by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), statisticians Traci Clemons and Marcello Pagano found that the birth weights of babies in the United States are not symmetric ("Are babies normal?" The American Statistician, Nov 1999, 53:4). However, they also found that when infants born outside of the "typical" 37-43 weeks and infants born to mothers with a history of diabetes are excluded, the birth weights of the remaining infants do follow a Normal model with mean μ = 3432 g and standard deviation o = 482 g. The following questions refer to infants born from 37 to 43 weeks whose mothers did not have a history of diabetes. Compute the z-score of an infant who weighs 3374 g. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Approximately what fraction of infants would you expect to have birth weights between 3210 g and 4140 g? (Express your answer as a decimal, not a percent, and round to three…arrow_forwardUsing all 1991 birth records in the computerized national birth certificate registry compiled by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), statisticians Traci Clemons and Marcello Pagano found that the birth weights of babies in the United States are not symmetric ("Are babies normal?" The American Statistician, Nov 1999, 53:4). However, they also found that when infants born outside of the "typical" 37-43 weeks and infants born to mothers with a history of diabetes are excluded, the birth weights of the remaining infants do follow a Normal model with mean μ = 3432 g and standard deviation σ = 482 g. The following questions refer to infants born from 37 to 43 weeks whose mothers did not have a history of diabetes.Compute the z-score of an infant who weighs 2903 g. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)−1.10Correct Approximately what fraction of infants would you expect to have birth weights between 3060 g and 4410 g? (Express your answer as a decimal, not a percent, and…arrow_forwardUsing all 1991 birth records in the computerized national birth certificate registry compiled by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), statisticians Traci Clemons and Marcello Pagano found that the birth weights of babies in the United States are not symmetric ("Are babies normal?" The American Statistician, Nov 1999, 53:4). However, they also found that when infants born outside of the "typical" 37-43 weeks and infants born to mothers with a history of diabetes are excluded, the birth weights of the remaining infants do follow a Normal model with mean u = 3432 g and standard deviation o = 482 g. The following questions refer to infants born from 37 to 43 weeks whose mothers did not have a history of diabetes. Compute the z-score of an infant who weighs 4769 g. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Preview Approximately what fraction of infants would you expect to have birth weights between 3100 g and 4040 g? (Express your answer as a decimal, not a percent, and round…arrow_forward
- Using all 1991 birth records in the computerized national birth certificate registry compiled by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), statisticians Traci Clemons and Marcello Pagano found that the birth weights of babies in the United States are not symmetric ("Are babies normal?" The American Statistician, Nov 1999, 53:4). However, they also found that when infants born outside of the "typical" 37-43 weeks and infants born to mothers with a history of diabetes are excluded, the birth weights of the remaining infants do follow a Normal model with mean u = 3432 g and standard deviation o = 482g. The following questions refer to infants born from 37 to 43 weeks whose mothers did not have a history of diabetes. %3D Compute the z-score of an infant who weighs 2536 g. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardUsing all 1991 birth records in the computerized national birth certificate registry compiled by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), statisticians Traci Clemons and Marcello Pagano found that the birth weights of babies in the United States are not symmetric ("Are babies normal?" The American Statistician, Nov 1999, 53:4). However, they also found that when infants born outside of the "typical" 37-43 weeks and infants born to mothers with a history of diabetes are excluded, the birth weights of the remaining infants do follow a Normal model with meanp = 3432 g and standard deviation o = 482 g. The following questions refer to infants born from 37 to 43 weeks whose mothers did not have a history of diabetes. Compute the z-score of an infant who weighs 3478 g. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Approximately what fraction of infants would you expect to have birth weights between 3160 g and 4590 g? (Express your answer as a decimal, not a percent, and round to three…arrow_forwardI. Write P if it is a primary source and S if it is a secondary source. An interview with the health officials concerning the effectiveness of the COVID 19 vaccine * Student's online evaluation of the performance of the faculty * A TV host was asked about the status of the entertainment industry. *arrow_forward
- Amorphophallus johnsonii is a plant called the "corpse flower" that grows in West Africa. Its flowers produce a pungent smell described as "a powerful aroma of rotting fish and faeces". It does so to attract its pollinator, the carrion beetle (Phaeochrous amplus) which live in rotting meat. Beath (1996) observed corpse flowers (hopefully wearing masks) and counted the number of beetles that arrived at each flower over the course of one night. The data is presented below: 51, 45, 61, 76, 11, 117, 7, 132, 52, 149 the mean of this sample is 70.1 beetles the standard deviation of this sample is 48.5 beetles Use the standard deviation of the sample to approximate the standard error of the mean. 1) What is the approximate SE that you calculated? Use the SE approximation method for normal sampling distributions to calculate Confidence Intervals 2) What are the 95% Confidence Intervals for this sample mean? 3) What are the 99% Confidence Intervals for this sample mean? 4) If an expanded…arrow_forwardthe wade tract in thomas county, georgia, is an old-growth forest of longleaf pine trees (pinus palustris) that has survived in a relatively undisturbed state since before the settlement of the area by europeans. foresters who study these trees are interested in how the trees are distributed in the forest. one way to formulate hypotheses about whether or not the trees are randomly distributed in the tract is to examine the average location in the north-side direction. the values range from 0 to 200, so if the trees are uniformly distributed in this direction, any difference from the middle value (100) should be due to chance variation. the sample mean for the 485 trees in the tract is 99.74. a theoretical calculation based on the assumption that the trees are uniformly distributed gives a standard deviation of 58. carefully state the null and alternative hypotheses in terms of this variable. note that this requires that you translate the research question about the random distribution…arrow_forwardResearchers studying the number of electric fish species living in various parts of the Amazon basin were interested in whether the presence of tributaries affected the local number of electric fish species in the main rivers (Fernandes et al. 2004) They counted the number of electric fish species above and below the entrance point of a major tributary at 12 different river locations. Here is what they found: Upstream number of Downstream number of species species Tributary Içá Jutaí Japurá Coari Purus 14 19 11 8. 18 5 10 16 Manacapuru 6 Negro 23 24 Madeira 29 Trombetas 19 16 Tapajós 16 25 20 Xingu Tocantins 21 10 12 What is the 95% confidence interval of the difference of means, ? Round your answers to two decimal places.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





