
Concept explainers
Identify the
(a) Isomer A has the
(b) Isomer B has three peaks in its
(c) Isomer C has two peaks in its
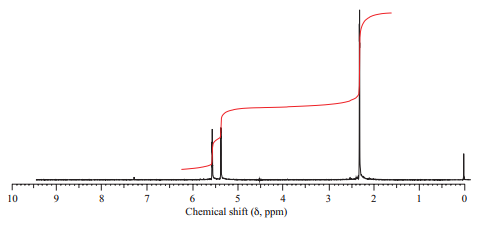
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PACKAGE >CUSTOM<
- A ¹H NMR spectrum is shown for a molecule with the molecular formula of C9H10O2. Draw the structure that best fits this data. 1H 11 10 9 8 SH 7 4 214 21 1 pom Qarrow_forwardCompound 1 has molecular formula C7H15Cl. It shows two signals in the 1H-NMR spectrum, one at 1.08 ppm and one at 1.59 ppm. The relative integrals of these two signals are 3 and 2, respectively. Propose structures for compound 1, explaining how you reach your conclusion.arrow_forward1Compound 1 has molecular formula C7H16. It shows three signals in the 1H-NMR spectrum, one at 0.85 ppm, one at 1.02 ppm, and one at 1.62 ppm. The relative integrals of these three signals are 6, 1, and 1, respectively. Compound 2 has molecular formula C7H14. It shows three signals in the 1H-NMR spectrum, one at 0.98 ppm, one at 1.36 ppm, and one at 1.55 ppm. The relative integrals of these three signals are 3, 2, and 2, respectively. Propose structures for compounds 1 and 2, explaining how you reach your conclusion.arrow_forward
- Draw the three isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12. Determine how many proton environments there are in each of the isomers.arrow_forwardCompound B has molecular formula C9H12. It shows five signals in the 1H-NMR spectrum - a doublet of integral 6 at 1.22 ppm, a septet of integral 1 at 2.86 ppm, a singlet of integral 1 at 5.34 ppm, a doublet of integral 2 at 6.70 ppm, and a doublet of integral 2 at 7.03 ppm. The 13C-NMR spectrum of B shows six unique signals (23.9, 34.0, 115.7, 128.7, 148.9, and 157.4). Identify B and explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardThe NMR spectrum of bromocyclohexane indicates a low field signal (1H) at δ 4.16. To room temperature, this signal is a singlet, but at -75 ° C it separates into two peaks of unequal area (but totaling one proton): δ 3.97 and δ 4.64, in ratio 4.6: 1.0. How do you explain the doubling in two peaks? According to the generalization of the previous problem, what conformation of the molecule predominates (at -75 ° C)? What percentage of the molecules does it correspond to? Solve all parts otherwise down vote and hand written solutionarrow_forward
- Propose a structural formula for the analgesic phenacetin, molecular formula C10H13NO2, based on its 1H-NMR spectrum.arrow_forwardDraw the H1 NMR spectra of ethylcyclopropane. Draw the chemical structure and predict the proton splitting and chemical shifts.arrow_forwardJ of Br G K OH Br H L OCH 3 of 1 M OH NH (i) Compound H is an example of what functional group? Select alternative (ii) Compound G is classified as a: Select alternative ✓. (iii) Which compound has all carbons sp2 hybridised? Select alternative ✓ (iv) Which two compounds in Table 1 are constitutional isomers? Select alternative (v) Which statement best describes the stereochemistry of compo G? Select alternative (vi) Which compound in Table 1 is the MOST polar? Select alternative (vii) What is the systematic (IUPAC) name of compound G? Select alternative (viii) Which compounds will have MORE than 4 signals in their 13C NMR spectra? Select alternative (ix) Which electrophile from Table 1 will react fastest in an SN1 reaction? Select alternative (x) How many constitutionally isomeric alkenes will be formed when compound L reacts with NaOH? Select alternative (xi) Which compound(s) from Table 1 can be used to form a Grignard reagent? Select alternative (xii) Which functional groups can be…arrow_forward
- Below are two molecules, cyclohexylamine (A) and aniline (B). When analyzed by Infrared Spectroscopy (IR) two different frequencies are observed for the C-N absorption band. Which molecule will have the lower wavenumber absorption band for the C-N bond. Explain why in 35 words or less. „NH2 NH2 А Barrow_forwardThere are four esters with molecular formula C4H8O2. How can they be distinguished by 1H NMR?arrow_forwardDraw the structural formulas of the following compounds and indicate the number of NMR signals that would be expected for each compound. (a) methyl iodide (b) 2,4-dimethylpentane (c) cyclopentane (d) propylene (propene)arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
