
Determine the required magnitude of force P to maintain equilibrium of the linkage at θ = 60°. Each link has a mass of 20 kg.
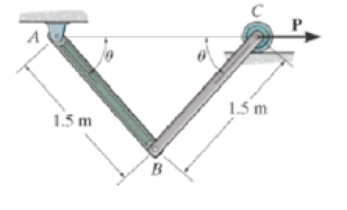
The required magnitude of force P to maintain equilibrium.
Answer to Problem 1FP
The required magnitude of force P to maintain equilibrium is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of each link
The given angle
Show the free body diagram of the forces acting on the link as in Figure (1).
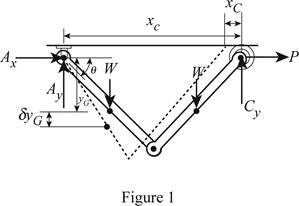
Observation:
The weight W and the horizontal component of P do positive work, when the position coordinates
Virtual displacement:
Write the position coordinate about x axis at point C.
Here, the length of the link AB is
Write the position coordinate about y axis about the center of the link.
Determine the weight of the link W.
Here, the acceleration due to gravity is g.
Virtual work equation:
Write the virtual work equation to determine the magnitude of force P.
Here, the angle of force
Conclusion:
Differentiate Equation (I) with respect to
Substitute 1.5 m for
Differentiate Equation (II) with respect to
Substitute 1.5 m for
Substitute 20 kg for m and
Substitute 196.2 N for W,
Here, the value of
Modify the Equation,
Thus, the required magnitude of force P to maintain equilibrium is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- PROBLEM 3.46 The solid cylindrical rod BC of length L = 600 mm is attached to the rigid lever AB of length a = 380 mm and to the support at C. When a 500 N force P is applied at A, design specifications require that the displacement of A not exceed 25 mm when a 500 N force P is applied at A For the material indicated determine the required diameter of the rod. Aluminium: Tall = 65 MPa, G = 27 GPa. Aarrow_forwardFind the equivalent mass of the rocker arm assembly with respect to the x coordinate. k₁ mi m2 k₁arrow_forward2. Figure below shows a U-tube manometer open at both ends and containing a column of liquid mercury of length l and specific weight y. Considering a small displacement x of the manometer meniscus from its equilibrium position (or datum), determine the equivalent spring constant associated with the restoring force. Datum Area, Aarrow_forward
- 1. The consequences of a head-on collision of two automobiles can be studied by considering the impact of the automobile on a barrier, as shown in figure below. Construct a mathematical model (i.e., draw the diagram) by considering the masses of the automobile body, engine, transmission, and suspension and the elasticity of the bumpers, radiator, sheet metal body, driveline, and engine mounts.arrow_forward3.) 15.40 – Collar B moves up at constant velocity vB = 1.5 m/s. Rod AB has length = 1.2 m. The incline is at angle = 25°. Compute an expression for the angular velocity of rod AB, ė and the velocity of end A of the rod (✓✓) as a function of v₂,1,0,0. Then compute numerical answers for ȧ & y_ with 0 = 50°.arrow_forward2.) 15.12 The assembly shown consists of the straight rod ABC which passes through and is welded to the grectangular plate DEFH. The assembly rotates about the axis AC with a constant angular velocity of 9 rad/s. Knowing that the motion when viewed from C is counterclockwise, determine the velocity and acceleration of corner F.arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
