
Prescott's Microbiology
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260211887
Author: WILLEY, Sandman, Wood
Publisher: McGraw Hill
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.4, Problem 1MI
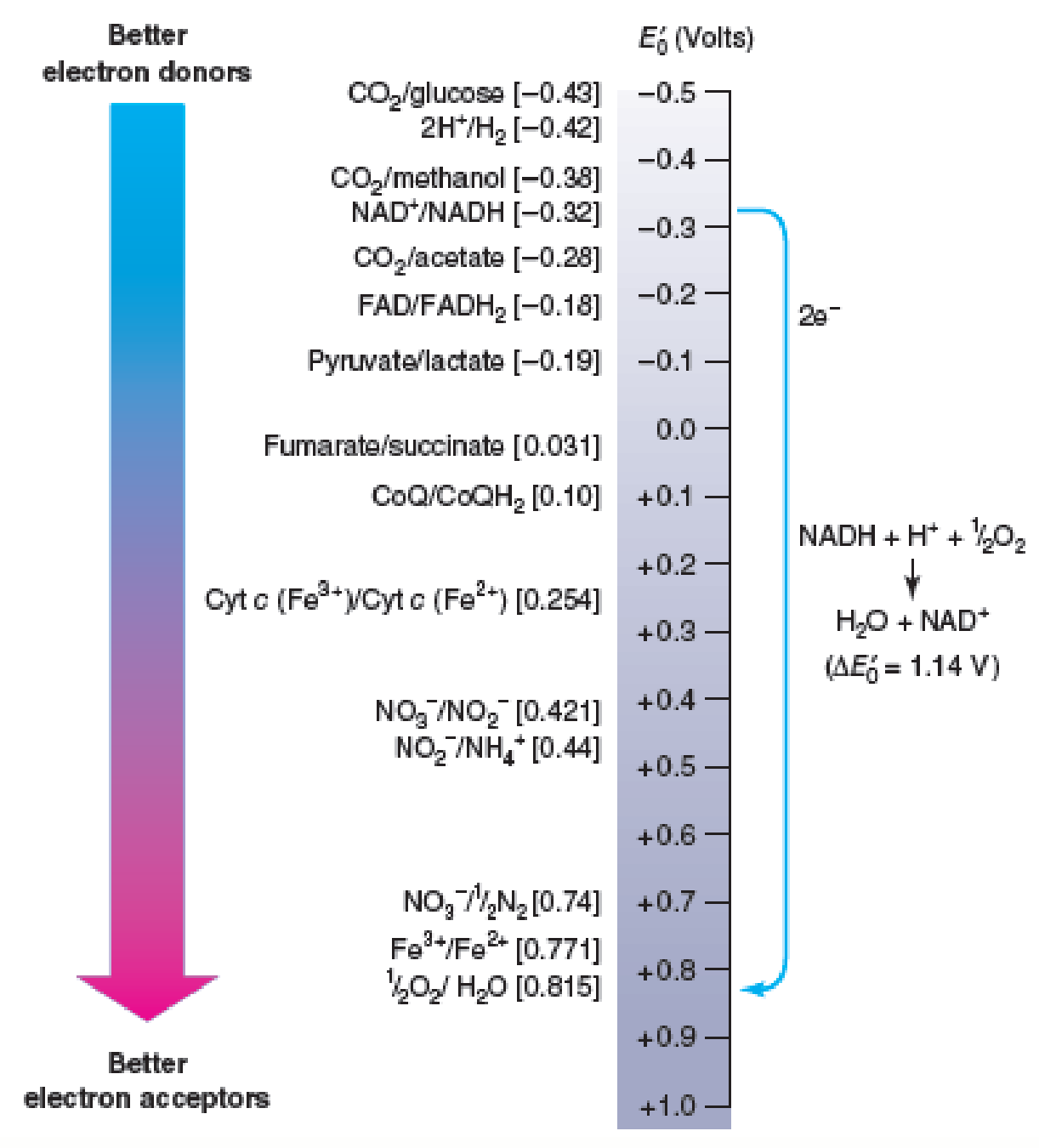
Figure 10.6 Electron Movement and Reduction Potentials. Electrons spontaneously move from donors higher on the tower (more negative potentials) to acceptors lower on the tower (more positive potentials). That is, the donor is always higher on the tower than the acceptor. For example, NADH will donate electrons to oxygen and form water in the process. Some typical conjugate redox pairs are shown on the left, and their reduction potentials are given in brackets.
Refer to figure 10.6 and determine the E′0 for NAD+/NADH and coenzyme Q/CoQH2. Suggest a plausible E′0 value for FMN.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Normal dive (for diving humans)
normal
breathing
dive
normal
breathing
Oz level
CO2 level
urgent need
to breathe
Oz blackout zone
high CO2 triggers breathing
6. This diagram shows rates of oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide accumulation in the blood in
relation to the levels needed to maintain consciousness and trigger the urgent need to breathe in
diving humans.
How might the location and slope of the O₂ line differ for diving marine mammals such as
whales and dolphins?
•
How might the location and slope of the CO₂ line differ for diving marine mammals such as
whales and dolphins?
•
•
Draw in predicted lines for O2 and CO2, based on your reasoning above.
How might the location of the Urgent Need to Breathe line and the O2 Blackout Zone line
differ for diving marine mammals?
What physiological mechanisms account for each of these differences, resulting in the ability
of marine mammals to stay submerged for long periods of time?
foraging/diet type
teeth
tongue
stomach
intestines
cecum
Insectivory
numerous, spiky, incisors procumbentExample: moleExample: shrew
--
simple
short
mostly lacking
Myrmecophagy
absent or reduced in numbers, peg-likeExample: tamandua anteater
extremely long
simple, often roughened
short
small or lacking
Terrestrial carnivory
sharp incisors; long, conical canines; often carnassial cheek teeth; may have crushing molarsExample: dog
--
simple
short
small
Aquatic carnivory
homodont, spiky, numerousExample: common dolphin
--
simple or multichambered (cetaceans only)
variable
small or absent
Sanguinivory
very sharp upper incisors; reduced cheek teethExample: vampire bat
grooved
tubular, highly extensible
long
small or lacking
Herbivory (except nectivores)
incisors robust or absent; canines reduced or absent; diastema; cheek teeth enlarged with complex occlusal surfacesExample: beaver
--
simple (hindgut fermenters) or multichambered (ruminants)
long
large
Filter feeding
none…
3. Shown below is the dental formula and digestive tract anatomy of three mammalian species
(A, B, and C). What kind of diet would you expect each species to have? Support your
answers with what you can infer from the dental formula and what you can see in the
diagram. Broadly speaking, what accounts for the differences?
Species A
3/3, 1/1, 4/4, 3/3
པར『ན་
cm 30
Species B
4/3, 1/1, 2/2, 4/4
cm 10
Species C
0/4, 0/0,3/3, 3/3
020
Chapter 10 Solutions
Prescott's Microbiology
Ch. 10.1 - Figure 10.2 The Relationship of G to the...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 1CCCh. 10.1 - Prob. 2CCCh. 10.1 - Prob. 3CCCh. 10.1 - Prob. 4CCCh. 10.2 - Why is ATP called a high-energy molecule? How is...Ch. 10.2 - Describe the energy cycle and ATPs role in it....Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 1MICh. 10.3 - Prob. 2MICh. 10.4 - Figure 10.6 Electron Movement and Reduction...
Ch. 10.4 - How is the direction of electron flow between...Ch. 10.4 - When electrons flow from the NAD+/NADH conjugate...Ch. 10.4 - Which among the following would be the best...Ch. 10.4 - In general terms, how is G related to E0? What is...Ch. 10.4 - Name and briefly describe the major electron...Ch. 10.6 - Will an enzyme with a relatively high Km have a...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 2MICh. 10.6 - Prob. 1CCCh. 10.6 - Prob. 2CCCh. 10.6 - How does enzyme activity change with substrate...Ch. 10.6 - What special properties might an enzyme isolated...Ch. 10.6 - What are competitive and noncompetitive...Ch. 10.6 - How are enzymes and ribozymes similar? How do they...Ch. 10.7 - Figure 10.19 Allosteric Regulation. The structure...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 2MICh. 10.7 - Define the terms metabolic channeling and...Ch. 10.7 - Define allosteric enzyme and allosteric effector.Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 3CCCh. 10.7 - Prob. 4CCCh. 10.7 - Prob. 5CCCh. 10 - Prob. 1RCCh. 10 - Prob. 2RCCh. 10 - Prob. 3RCCh. 10 - Examine the structures of macromolecules in...Ch. 10 - Examine the branched pathway shown here for the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 3AL
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3. Shown below is the dental formula and digestive tract anatomy of three mammalian species (A, B, and C). What kind of diet would you expect each species to have? Support your answers with what you can infer from the dental formula and what you can see in the diagram. Broadly speaking, what accounts for the differences? Species A 3/3, 1/1, 4/4, 3/3 cm 30 Species B 0/4, 0/0, 3/3, 3/3 cm 10 Species C 4/3, 1/1, 2/2, 4/4 E 0 cm 20 AILarrow_forwardNormal dive (for diving humans) normal breathing dive normal breathing Oz level CO₂ level urgent need to breathe Oz blackout zone high CO₂ triggers breathing 6. This diagram shows rates of oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide accumulation in the blood in relation to the levels needed to maintain consciousness and trigger the urgent need to breathe in diving humans. • How might the location and slope of the O2 line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • How might the location and slope of the CO2 line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • • Draw in predicted lines for O2 and CO2, based on your reasoning above. How might the location of the Urgent Need to Breathe line and the O2 Blackout Zone line differ for diving marine mammals? What physiological mechanisms account for each of these differences, resulting in the ability of marine mammals to stay submerged for long periods of time?arrow_forwardHow much ATP will be produced during the following metabolic scenario: Aerobic respiration of a 5mM lipid solution that is made up of one glycerol and an 8-carbon fatty acid and 12-carbon fatty acid. Recall that when glycerol breaks down to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate it costs one ATP but your get an extra FADH2. Every two carbons of a fatty acid break down to one acetyl-CoA. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forward
- If a bacterium using aerobic respiration was to degrade one small protein molecule into 8 molecules of pyruvic acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Assume there is no other carbon source. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in molecules of ATP.arrow_forwardIf a bacterium using aerobic respiration was to degrade a 30 mM solution of citric acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Assume no other carbon source is available. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forwardHow much ATP will be produced during the following metabolic scenario: Aerobic respiration of a 5mM lipid solution that is made up of one glycerol and an 8-carbon fatty acid and 12-carbon fatty acid. Recall that when glycerol breaks down to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate it costs one ATP but your get an extra FADH2. Every two carbons of a fatty acid break down to one acetyl-CoA. (pathways will be provided on the exam) Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forward
- When beta-lactamase was isolated from Staphylcoccus aureus and treated with a phosphorylating agent, only the active site, serine was phosphorylated. Additionally, the serine was found to constitute 0.35% (by weight) of this beta-lactamase enzyme. Using this, calculate the molecular weight of this enzyme and estimate the number of amino acids present in the polypeptide.arrow_forwardBased on your results from the Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) media, which of your bacteria were mannitol fermenters and which were not mannitol fermenters?arrow_forwardhelp tutor pleasearrow_forward
- Q8. A researcher wants to study the effectiveness of a pill intended to reduce stomach heartburn in pregnant women. The researcher chooses randomly 400 women to participate in this experiment for 9 months of their pregnancy period. They all need to have the same diet. The researcher designs two groups of 200 participants: One group take the real medication intended to reduce heartburn, while the other group take placebo medication. In this study what are: Independent variable: Dependent variable: Control variable: Experimental group: " Control group: If the participants do not know who is consuming the real pills and who is consuming the sugar pills. This study is It happens that 40% of the participants do not find the treatment helpful and drop out after 6 months. The researcher throws out the data from subjects that drop out. What type of bias is there in this study? If the company who makes the medication funds this research, what type of bias might exist in this research work?arrow_forwardHow do I determine the inhertiance pattern from the pedigree diagram?arrow_forwardits an open book assignemntarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to the NIOSH Manual of Analytical Methods Fifth edition; Author: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC);https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B5rUrKLMoas;License: Standard Youtube License