
Concept explainers
In this problem, we examine the basis of three different electronegativity scales and work through the same types of calculations as those performed by the people who initially suggested these scales. The scale developed by Robert Mulliken employs ionization energies (E) and electron amenities
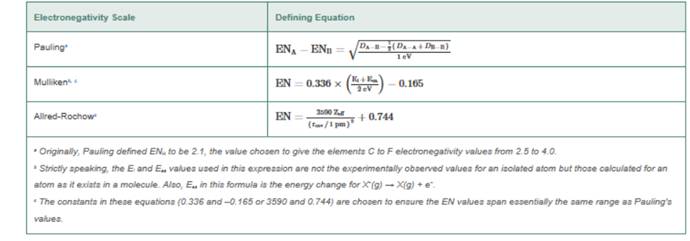
In devising his scale, Pauling observed that the bond energy,
Mulliken argued that the ionization energy
Alred and Rochow focused on the attractive Coulombic force between an electron near the surface of an atom and the nucleus of that atom.
They argued that the magnitude of this force is proportional to where
The values of
Atom, EN(Pauling), EN(MuIliken), (Hint: The Pauling values you calculate will not be exactly equal to those in Figure 10-6. The values in Figure 10-6 are based on bond dissociation energies from a wider range of molecules than we are considering in this problem. 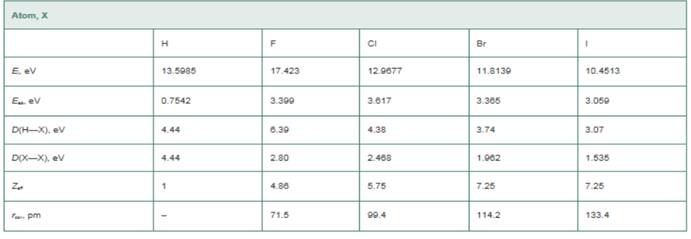
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications (11th Edition)
- In each of the following Lewis diagrams, Z represents a main-group element. Name the group to which Z belongs in each case and give an example of such a compound or ion that actually exists.arrow_forwardThe molecular ion S3N3 has the cyclic structure All SN bonds are equivalent. (a) Give six equivalent resonance hybrid Lewis diagrams for this molecular ion. (b) Compute the formal charges on all atoms in the molecular ion in each of the six Lewis diagrams. (c) Determine the charge on each atom in the polyatomic ion, assuming that the true distribution of electrons is the average of the six Lewis diagrams arrived at in parts (a) and (b). (d) An advanced calculation suggests that the actual charge resident on each N atom is 0.375 and on each S atom is +0.041 . Show that this result is consistent with the overall +1 charge on the molecular ion.arrow_forwardThe molecules BH3 and SF6 and the ion SO42 exist and are stable. Draw a Lewis structure of each,and comment on whether they are exceptions to Lewis’ octet rule.arrow_forward
- Although I3- is a known ion, F3- is not. (a) Draw the Lewis structure for I3- (it is linear, not a triangle). (b) One of your classmates says that F3 - does not exist because F is too electronegative to make bonds with another atom. Give an example that proves your classmate is wrong. (c) Another classmate says F3- does not exist because it would violate the octet rule.Is this classmate possibly correct? (d) Yet another classmatesays F3- does not exist because F is too small to make bonds tomore than one atom. Is this classmate possibly correct?arrow_forwardDescribe the difference between a full Lewis structure and bond-line notation. What changes? Why is it easier to write?Dontarrow_forwardPlease explain where I am going wrong. I can't seem to figure it out.arrow_forward
- Please help mearrow_forwardA resonance hybrid is a structure that can be depicted by more than one valid Lewis structure. part1: Draw the major resonance form of fulminic acid, HCNO, with the atoms connected as indicated in the formula. Your structure should have nonzero formal charges minimized, and it should include all nonzero formal charges and all nonbonding electrons. part2: Draw the second most important resonance form of fulminic acid, HCNO, with the atoms connected as indicated in the formula. Your structure should have nonzero formal charges minimized, and it should include all nonzero formal charges and all nonbonding electrons. part3: Draw the least important resonance contributor for fulminic acid, HCNO, with the atoms connected as indicated in the formula. Your structure should have nonzero formal charges minimized and should include all nonzero formal charges and all nonbonding electrons.arrow_forward= O ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE AND CHEMICAL BONDING Predicting the arrangement of electron groups around the centr... Answer the questions in the table below about the shape of the phosphorus trifluoride (PF3) How many electron groups are around the central phosphorus atom? Note: one "electron group" means one lone pair, one single bond, one double bond, or one triple bond. What phrase best describes the arrangement of these electron groups around the central phosphorus atom? (You may need to use the scrollbar to see all the choices.) (choose one) (choose one) linear bent T-shaped trigonal planar trigonal pyramidal square planar square pyramidal tetrahedral sawhorse trigonal bipyramidal octahedral molecule.arrow_forward
- ing and lea X G The element in period 5 that has X ent/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator-assignment-take 3 eq 2. The central nitrogen atom V A. Obeys the octet rule B. Has an incomplete octet. C. Has an expanded octet. Submit Answer [Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Lewis Structures Lewis Structures are used to describe the covalent bonding in molecules and ions. Draw a Lewis structure for NH4 and answer the following questions based on your drawing. 1. For the central nitrogen atom: The number of lone pairs The number of single bonds = The number of double bonds= 3 Retry Entire Group 4+ C Solved The following Lewis diagr X 00 144 6 9 more group attempts remaining + 0 44 ort sc A ENG deleta Previous back space 16 ☆ Next 11:55 AM 11/28/2022 end 1arrow_forwardPart A The Lewis structure for the chlorate ion is Calculate the formal charge on the chlorine (CI) atom. Express your answer as an integer. • View Available Hint(s) formal charge on Cl = Submit Part B Calculate the formal charge on each of the oxygen (O) atoms labeled a, b, and e in the following Lewis structure. :O: Express your answers as integers separated by commas. View Available Hint(s) formal charge on 0,, O, O, = Submitarrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning





