
Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol 1. (Chs 1-21)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134110646
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 11EAP
A 1500 kg car traveling at 10 m/s suddenly runs out of gas while approaching the valley shown in FIGURE EX10.11. The alert driver immediately puts the car in neutral so that it will roll. What will be the car’s speed as it coasts into the gas station on the other side of the valley?
FIGURE EX10.11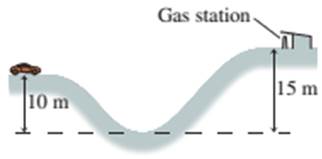
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule03:36
Students have asked these similar questions
Dr. Jekyll (m = 70kg) is riding a skateboard when he realizes the cranberry juice he’s drinking is sweetened with artificial sweetener and turns into Mr. Hyde (m = 155kg). If Dr. Jekyll was initially moving at 6.5m/s, what is Mr. Hyde’s speed? (assume no external forces act)
III A sled starts from rest at the top of the frictionless, hemi-
spherical, snow-covered hill shown in FIGURE CP10.74.
a. Find an expression for the sled's speed when it is at angle .
b. Use Newton's laws to find the maximum speed the sled can
have at angle without leaving the surface.
c. At what angle
max does the sled "fly off" the hill?
FIGURE CP10.74
$ R
40 identical balls are rolling a straight line. They all have speed equal to v, but some of them might move in opposite directions. When two of them collide they immediately switch their direction and keep the speed v. What is the maximal number of collisions that can happen.
Chapter 10 Solutions
Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol 1. (Chs 1-21)
Ch. 10 - Prob. 1CQCh. 10 - Can kinetic energy ever be negative? Can...Ch. 10 - Prob. 3CQCh. 10 - 4. The three balls in FIGURE Q1O.4, which have...Ch. 10 - Rank in order, from most to least, the elastic...Ch. 10 - 6. A spring is compressed 1.0 cm. How far must you...Ch. 10 - Prob. 7CQCh. 10 - A particle with the potential energy shown in...Ch. 10 - A compressed spring launches a block up an...Ch. 10 - 10. A process occurs in which a system’s potential...
Ch. 10 - A process occurs in which a system’s potential...Ch. 10 - FIGURE Q10.12 is the energy bar chart for a...Ch. 10 - Prob. 13CQCh. 10 - Object A is stationary while objects B and C are...Ch. 10 - Prob. 2EAPCh. 10 - 3. The lowest point in Death Valley is 85 m below...Ch. 10 - Prob. 4EAPCh. 10 - Prob. 5EAPCh. 10 - 6. What height does a frictionless playground...Ch. 10 - 7. A 55 kg skateboarder wants to just make it to...Ch. 10 - Prob. 8EAPCh. 10 - A pendulum is made by tying a 500 g ball to a...Ch. 10 - A 20 kg child is on a swing that hangs from...Ch. 10 - A 1500 kg car traveling at 10 m/s suddenly runs...Ch. 10 - Prob. 12EAPCh. 10 - A cannon tilted up at a 30° angle fires a cannon...Ch. 10 - In a hydroelectric dam, water falls 25 m and then...Ch. 10 - How far must you stretch a spring with k = 000 N/m...Ch. 10 - A stretched spring stores 2.0 J of energy. How...Ch. 10 - A student places her 500 g physics book on a...Ch. 10 - A block sliding along a horizontal frictionless...Ch. 10 - A 10 kg runaway grocery cart runs into a spring...Ch. 10 - As a 15,000 kg jet plane lands on an aircraft...Ch. 10 - The elastic energy stored in your tendons can...Ch. 10 - The spring in FIGURE EX10.22a is compressed by ?x....Ch. 10 - The spring in FIGURE EXIO.23a is compressed by ?x....Ch. 10 - FIGURE EX10.24 is the potential-energy diagram for...Ch. 10 - Prob. 25EAPCh. 10 - In FIGURE EX10.26, what is the maximum speed of a...Ch. 10 - Prob. 27EAPCh. 10 - FIGURE EX10.28 shows the potential energy of a 500...Ch. 10 - In FIGURE EX10.28, what is the maximum speed a 200...Ch. 10 - A system in which only one particle can move has...Ch. 10 - A system in which only one particle can move has...Ch. 10 - A particle moving along the y-axis is in a system...Ch. 10 - A particle moving along the x-axis is in a system...Ch. 10 - FIGURE EX10.34 shows the potential energy of a...Ch. 10 - A particle moves from A to D in FIGURE EX10.35...Ch. 10 - A force does work on a 50 g particle as the...Ch. 10 - A system loses 400 J of potential energy. In the...Ch. 10 - What is the final kinetic energy of the system for...Ch. 10 - How much work is done by the environment in the...Ch. 10 - A cable with 20.0 N tension pulls straight up on a...Ch. 10 - A very slippery ice cube slides in a vertical...Ch. 10 - A 50 g ice cube can slide up and down a...Ch. 10 - You have been hired to design a spring-launched...Ch. 10 - It’s been a great day of new, frictionless snow....Ch. 10 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 10 - A 1000 kg safe is 2.0 m above a heavy-duty spring...Ch. 10 - You have a ball of unknown mass, a spring with...Ch. 10 - Sam, whose mass is 75 kg, straps on his skis and...Ch. 10 - A horizontal spring with spring constant 100 N/m...Ch. 10 - Truck brakes can fail if they get too hot. In some...Ch. 10 - Prob. 51EAPCh. 10 - Use work and energy to find an expression for the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 53EAPCh. 10 - The spring shown in FIGURE 10.54 is compressed 50...Ch. 10 - Prob. 55EAPCh. 10 - Prob. 56EAPCh. 10 - A system has potential energy U(x) = x + sin ((2...Ch. 10 - Prob. 58EAPCh. 10 - Prob. 59EAPCh. 10 - Prob. 60EAPCh. 10 - The potential energy for a particle that can move...Ch. 10 - A particle that can move along the x-axis...Ch. 10 - An object moving in the xy-plane is subjected to...Ch. 10 - An object moving in the xy-plane is subjected to...Ch. 10 - Prob. 65EAPCh. 10 - In Problems 66 through 68 you are given the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 67EAPCh. 10 - Prob. 68EAPCh. 10 - A pendulum is formed from a small ball of mass m...Ch. 10 - Prob. 70EAPCh. 10 - Prob. 71EAPCh. 10 - Prob. 72EAPCh. 10 - The spring in FIGURE CP10.73 has a spring constant...Ch. 10 - A sled starts from rest at the top of the...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2 using a Born-Haber cycle and data from Appendices F and L and Table 7.5. ...
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Explain why 92% of 2,4-pemtanedione exists as the enol tautomer in hexane but only 15% of this compound exists ...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
5. In a type of parakeet known as a “budgie,” feather color is controlled by two genes. A yellow pigment is syn...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Why are BSL-4 suits pressurized? Why not just wear tough regular suits?
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
The bioremediation process shown in the photograph is used to remove benzene and other hydrocarbons from soil c...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Sam, whose mass is 75 kg, takes off across level snow on his jet-powered skis. The skis have a thrust of 200 N and a coefficient of kinetic friction on snow of 0.10. Unfortunately, the skis run out of fuel after only 10 s. A. What is Sam’s top speed? B. How far has Sam traveled when he finally coasts to a stop?arrow_forward6. Your friend (mass 65.0 kg) is standing on the ice in the middle of a frozen pond. There is very little friction between her feet and the ice, so she is unable to walk. Fortunately, a light rope is tied around her waist and you stand on the bank holding the other end. You pull the rope for 3.00 s and accelerate your friend from rest to a speed of 6.00 m/s while you remain at rest. What is the average power supplied by the force you applied?arrow_forwardYou just turned 16 and thanks to some long hours at your job and some amazing parents you were able to purchase a tesla. This 3000 kg car can go from 0 to 27m/s (about 60 miles per hour) in 2.5 seconds. You peel away from a stoplight and do just that. a. How far from the light are you when you hit 27 m/s? m Since you live in the great city of Chicago and it is December and you encounter an icy patch. Your car experiences NO friction on the ice patch but you also cannot apply any force. Another small (m-2300 kg) van coming towards you at 25m/s in the other direction loses control and comes straight for you. They hit you and the two vehicles get tangled together and continue to slide across the ice. b. How fast are the cars going after the collision? m/s C. After you slide off the ice you hit the shoulder of the road with a coefficient of friction of 0.4 compared to the road. What is your acceleration as they start to slide to a stop? m/s/s d. How much momentum do you have after you have…arrow_forward
- On planet #2, you launch a projectile straight up from the ground at a speed of 77.4 m/s. The projectile reaches a maximum height of 23.2 m before falling back to the ground. What is the value of g for planet #2? A 6.95 m/s^2 B 129.11 m/s^2 C 258.22 m/s^2 D 3.48 m/s^2arrow_forwardA cart filled with sand rolls at a speed of 1.0 m/s along a horizontal path without friction. A ball of mass m = 2.0 kg is thrown with a horizontal velocity of 8.0 m/s toward the cart as shown in Figure P11.79. The ball gets stuck in the sand. What is the velocity of the cart after the ball strikes it? The mass of the cart is 15 kg. FIGURE P11.79 Problems 79 and 80.arrow_forwardSam, whose mass is 77 kg , takes off across level snow on his jet-powered skis. The skis have a thrust of 150 N and a coefficient of kinetic friction on snow of 0.1. Unfortunately, the skis run out of fuel after only 9.0 s . What is Sam's top speed? How far has Sam traveled when he finally coasts to a stop?arrow_forward
- Open Response 2: This is a multi-part problem. Please answer all parts here. A hollow sphere (m 0.5 kg, R = 0.8 m) is moving at 3 m/s down an incline. a. How fast is it moving after it has moved downward an additional 2 m in height? b. At what height would the sphere be moving at 5 m/s?arrow_forwardAs we noted, a desert locust is an excellent jumper. Suppose a 2.0 g locust leaps straight up, leaving the ground at 3.1 m/s, a speed that a desert locust can easily reach.a. If we ignore the drag force, how high will the locust jump?b. If 20% of the initial kinetic energy is lost to drag, how high will the locust jump?arrow_forwardPower vs airspeed curve for a jet airplane is shown in the Figure. The velocity that corresponds to the minimum velocity is PA PR PA Vs V6 V7 a. V5 b. V7 C. V6 d. Cannot be determined V8 V9arrow_forward
- The weight of an object by the sea is 2800 N. What is the weight of this object at a height with gravitational acceleration of 7.2 m/s? in terms of Newton, dyn, kgf and Ibf? If the velocity of this object at this height equals 22 m/s, what is the Kinetic Energy in terms of N.m, dyn.cm, kgf.m and Ibf.ft?arrow_forwardAn Atwood's machine consists of two masses m₁ and m₂ joined by a light cord which passes over a pulley. Initially, the heavier mass is positioned a distance h above the floor. The masses are released from rest. At what speed are the masses moving when the heavier mass strikes the floor? Here m₁ = 4kg, m₂ = 6kg, and h = 3m. The cord is long enough so that the lighter mass does not reach the pulley. Devices like this are used in the construction of elevators. (3.4 m/s)arrow_forwardA 5kg object is hanging by a 1.5m wire when it is suddenly hit by a 3kg missile traveling horizontally at 12m/s. The missile embeds itself in the object during the collision. What is the tension in the rod immediately after the collision? (Answer in whole number, no unit) UNIT: N Add your answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning