
Concept explainers
Amide Lewis Structural Formulas
Lewis formulas are the major means by which structural information is communicated in
Two or more Lewis formulas, differing only in the placement of electrons, can often be written for a single compound. In such cases the separate structures represented by the Lewis formulas are said to be in resonance, and the true electron distribution is a hybrid of the electron distributions of the contributing structures.
The amide function is an important structural unit in peptides and proteins. Formamide, represented by the Lewis structure shown, is the simplest amide. It is a planar molecule with a dipole moment of
D. Lewis structures I–IV represent species that bear some relationship to the Lewis structure for formamide.
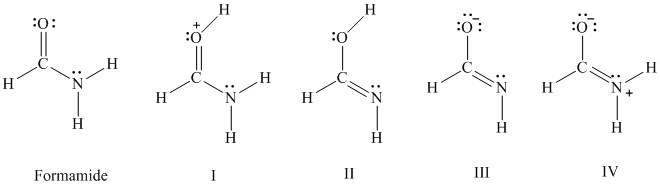
According to VSEPR, which Lewis formula has a pyramidal
arrangement of bonds to nitrogen?
I
II
III
IV
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PACKAGE >CUSTOM<
- Give correct detailed Solution with explanation needed...don't give Handwritten answer..give correct answerarrow_forwardDraw the Lewis dot structure of the conjugate base of cyclopentane by assuming all the atoms in the molecule obey the octet rule. Show all lone pairs and formal charges. Do no draw resonance structures.arrow_forward[Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Use the following Lewis diagram for propanoic acid to answer the questions: H H :0: Remember that geometry refers to the geometry defined by the atoms, not the electron pairs. The geometry about atom C, is trigonal planar The ideal value of the C-C-C angle at atom C2 is 180 degrees. The geometry about atom C3 is bent An error has been detected in your answer. Check for typos, miscalculations etc. before submitting your answer. Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 8 more group attempts remaining Previous Nextarrow_forward
- Four major contributing resonance structures are possible for the given cation, which is the intermediate o complex of an electrophilic aromatic substitution involving phenol and bromine. Two structures are given but are incomplete. Complete the given structures by adding nonbonding electrons and formal charges. Draw the remaining structures (in any order), including nonbonding electrons and formal charges. Complete structure A. Complete structure B. : 0 H :0- Br : Brarrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardEthanol, , is a compound in which the formal charge on all the atoms is zero. Under certain conditions the bond can be broken so that both electrons remain with the oxygen atom. The products are In this structure the oxygen owns one electron from shared pair and two electrons from each of unshared pairs. The total number of electrons belonging to oxygen is Oxygen is a Group element. The formal charge on the oxygen atom is . The correct Lewis structure for the ethoxide ion is Note that the other fragment, the proton, leaves with a formal charge of +1.arrow_forward
- Give the molecular formula, the line bond structural formula, the condensed structural formula, and the skeletal formula for octane. 4. Molecular formula: Line bond structural formula:arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structures for the following molecules. For each molecule, determine its (a) electronic geometry, (b) number of nonbonding domains on the central atom, and (c) polarity of the molecule. Remember, that molecules that have zero nonbonding domains on the central atom AND have all of the outer atoms the same are NONPOLAR. Generally, molecules with different outer atoms or with more than one nonbonding domain are POLAR. However, these may be NONPOLAR ONLY IF the dipoles cancel each other due to a symmetrical arrangement. CIF3 (a) electronic geometry: -Select-- (b) number of nonbonding domains on central atom: -Select-v (c) molecule polarity: -Select- SO2 .(a) electronic geometry: --Select- (b) number of nonbonding domains on central atom: -Select---V (c) molecule polarity: --Select--v SF5 (a) electronic geometry: [-Select- (b) number of nonbonding domains on central atom: --Select--- ♥ (c) molecule polarity: --Select-- v IFS (a) electronic geometry: -Select-- (b) number of…arrow_forwardWrite the net ionic chemical equilibrium that gets established triethylamine, is dissolved in water. Use full lewis structures and show all lone electron pairs for reactants and products. Above each reaction arrow, write whether the reaction represents a Ka or Kb reaction.arrow_forward

 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





