You wish to test the following claim (HaHa) at a significance level of α=0.001α=0.001. Ho:p1=p2Ho:p1=p2 Ha:p1≠p2Ha:p1≠p2 You obtain 186 successes in a sample of size n1=286n1=286 from the first population. You obtain 264 successes in a sample of size n2=486n2=486 from the second population. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the normal distribution as an approximation for the binomial distribution. What is the critical value for this test? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.) critical value = ±± What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.) test statistic = The test statistic is... in the critical region not in the critical region This test statistic leads to a decision to... reject the null accept the null fail to reject the null As such, the final conclusion is that... There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the first population proportion is not equal to the second population proprtion. There is not sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the first population proportion is not equal to the second population proprtion. The sample data support the claim that the first population proportion is not equal to the second population proprtion. There is not sufficient sample evidence to support the claim that the first population proportion is not equal to the second population proprtion.
Compound Probability
Compound probability can be defined as the probability of the two events which are independent. It can be defined as the multiplication of the probability of two events that are not dependent.
Tree diagram
Probability theory is a branch of mathematics that deals with the subject of probability. Although there are many different concepts of probability, probability theory expresses the definition mathematically through a series of axioms. Usually, these axioms express probability in terms of a probability space, which assigns a measure with values ranging from 0 to 1 to a set of outcomes known as the sample space. An event is a subset of these outcomes that is described.
Conditional Probability
By definition, the term probability is expressed as a part of mathematics where the chance of an event that may either occur or not is evaluated and expressed in numerical terms. The range of the value within which probability can be expressed is between 0 and 1. The higher the chance of an event occurring, the closer is its value to be 1. If the probability of an event is 1, it means that the event will happen under all considered circumstances. Similarly, if the probability is exactly 0, then no matter the situation, the event will never occur.
You wish to test the following claim (HaHa) at a significance level of α=0.001α=0.001.
Ho:p1=p2Ho:p1=p2
Ha:p1≠p2Ha:p1≠p2
You obtain 186 successes in a sample of size n1=286n1=286 from the first population. You obtain 264 successes in a sample of size n2=486n2=486 from the second population. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the
What is the critical value for this test? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.)
critical value = ±±
What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.)
test statistic =
The test statistic is...
- in the critical region
- not in the critical region
This test statistic leads to a decision to...
- reject the null
- accept the null
- fail to reject the null
As such, the final conclusion is that...
- There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the first population proportion is not equal to the second population proprtion.
- There is not sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the first population proportion is not equal to the second population proprtion.
- The sample data support the claim that the first population proportion is not equal to the second population proprtion.
- There is not sufficient sample evidence to support the claim that the first population proportion is not equal to the second population proprtion.
Hey, since there are multiple subparts posted, we will answer first three subparts. If you want any specific subpart to be answered then please submit that subpart only or specify the subpart in your message.
The critical value for this test is calculated as below:
The critical value is obtained from Excel using function "=NORMSINV(probability)
Output obtained from Excel is given below:
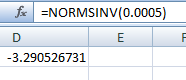
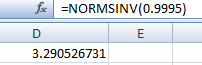
From the outputs, the critical value is
Thus, the critical value=
The value of is obtained below:
The value of is obtained below:
The pooled value is obtained below:
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images









