PL.1 Another consequence of the Equivalence Principle is that light will be bent in a gravitational field. This has never been measured on the surface of the earth, but was verified qualitatively by observing starlight pass- ing near the sun's edge during a total eclipse in 1919. Let's explore how much bending we would prediet in a laboratory at rest on the surface of the earth. What one would observe in such a laboratory should be the same as what one would observe in a laboratory ac- celerating in deep space with a uniform acceleration of a =-, where g is the local acceleration of gravity on the earth's surface. Imagine that a laser at one end of the laboratory emits a beam of light that originally travels parallel to the laboratory floor. This light shines on the opposite wall of the laboratory a distance d= 3.0 m away from the laser. a. Find the magnitude of this deflection in a laboratory on the surface of the earth. b. Find the magnitude of this deflection if the labora- tory is on the surface of a neutron star of mass M= 3.0x 10" kg( 15 the mass of the sun) and a radius R=12 km. [Hint: First estimate the magnitude of g, using Newton's law of universal gravitation. G= 6.67 x 10 "N- m'/kg. h of light is emitted by a laser on he floor a

a.
consider the following figure which represents the motion of the laser in the laboratory frame.
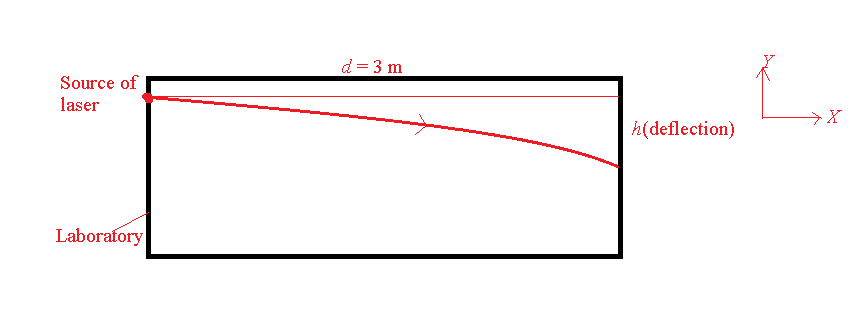
Let the horizontal distance traveled by the laser in a laboratory on the surface of the Earth be d, the initial speed (horizontal) of laser be v, the time taken by the laser to cover this horizontal distance d be t, and vertical deflection suffered by the laser due to the acceleration due to gravity be h.
The time taken by the laser to cover this horizontal distance is given by the following Newton’s equation of motion.
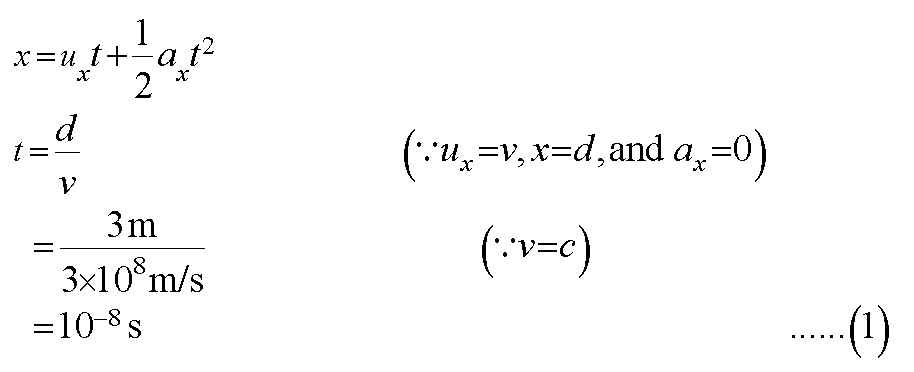
Let the vertical component of the initial velocity of the laser be uy and the vertical component of the acceleration of the laser beam be ay.
In this case,
uy = 0
According to Newton’s equation of motion, the vertical deflection of laser is given by the following equation.
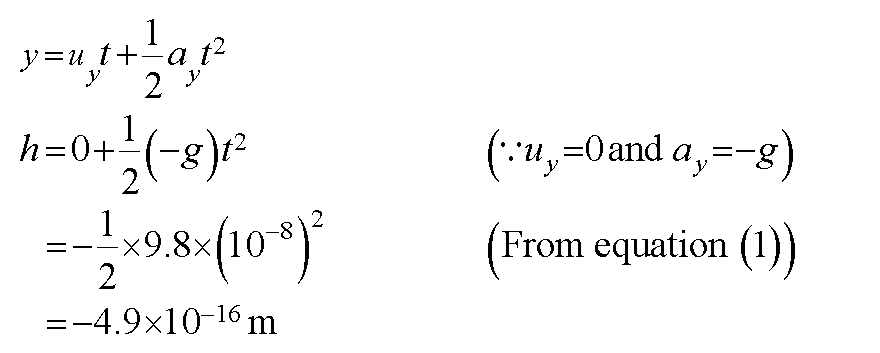
Here, the negative sign indicates that the laser has been deflected towards the floor (or along the negative y-axis).
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 7 images
