Explain the followings. Organiztion of E. coli origin of replication and initiation of replication. b. Semiconservative mode of replication. c. Okaski fragments?
Please find the attachement

Replication is one of the unique properties of DNA. Through replication, DNA produces carbon copies which are essential for the transfer of genetic information from one cell to its daughters and from one generation to the next.
a.
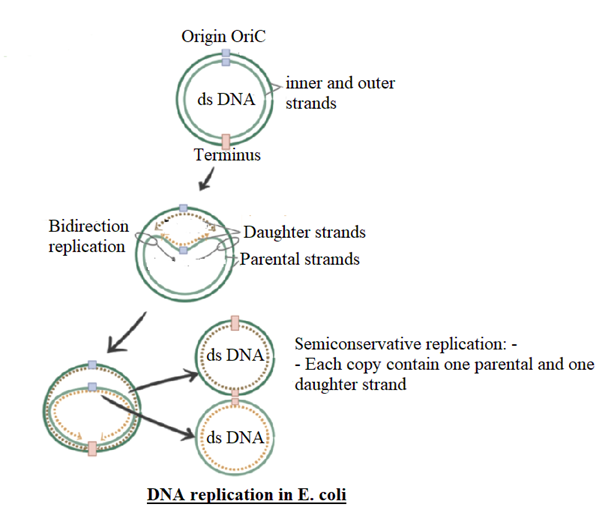
E. coli is a prokaryotic, gram-negative bacillus. In prokaryotes, the DNA replication is semiconservative bidirectional, and continuous. DNA replication occurs during the S-phase of the cell cycle. It is a multistep complex process that requires over a dozen enzymes and protein factors. It begins at a particular spot called the origin of replication or Ori. Bacterial DNA has a single origin of replication as a result whole prokaryotic DNA acts as a single replicating unit or replicon. In the absence of Ori, replication will not occur.
The Ori region is about 245 bp long and mostly consists of A/T base pairs. The replication is initiated when the DNA polymerase binds to the template DNA strand at the Ori site. RNA polymerase forms a replication bubble by hydrolyzing the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. As the Ori region has a high A and T count, it helps in easy unbinding of the DNA as A and T are bound to each other with two hydrogen bonds only rather than C and G which are bound to each other using three hydrogen bonds. The E.coli DNA contains two Y-shaped structures which are the two replication forks. The replication forks form a replication bubble. The replication is initiated and the replication forks proceed in opposite directions.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images









