16. Which of the following human activities contributes the MOST to carbon dioxide emission in the atmosphere? A. Transportation B. Domestic and personal activities C. Agricultural and livestock raising D. Electricity production and industrial manufacturing 17. Which of the following human activities help conserve the atmosphere? A. Children are planting trees B. People are burning waste products. C. People throw their garbage in rivers and canals. D. People are using oil gasoline-powered vehicles. 18. What is the WORST effect of too much emission of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere? A. Air pollution C. Global warming B. Climate change D. Greenhouse effect 19. What is the most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere? A. Argon C. Nitrogen B. Oxygen D. Carbon dioxide 20. In which layer of the atmosphere ozone can be found? A. Troposphere C. Mesosphere B. Stratosphere D. Thermosphere 21. Which statement is correct about the Greenhouse Effect? A. It makes the Earth cooler. B. It keeps all the heat within the Earth. C. It absorbs the radiation released by the Sun. D. It is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface. 22. Why is the presence of ozone above the troposphere important for the survival of living things on earth? A. It warms Earth's surface. B. It helps in cloud formation. C. It makes jet flying more comfortable. D. It offers protection from the Sun's harmful UV rays 23. What is the region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than the surrounding areas? A. Low-pressure area C. Southwest monsoon D. Northeast monsoon B. High-pressure area 24. What is a cool and dry wind from Siberia carrying cold weather conditions and could bring rains over the eastern section of the country? A. Low-pressure area C. Southwest monsoon D. Northeast monsoon B. High-pressure area 25. Which of the following statements is the effect of Southwest monsoon on the western part of the country? A. It brings heavy rains to most of the eastern part of the country from June to September. B. It brings heavy rains to most of the western part of the country from June to September. C. It brings cold weather to most of the eastern part of the country from June to September. D. It brings cold weather to most of the western part of the country from June to September. 26. What do you call a weather phenomenon where winds in the tropics meet, rise and form clouds, resulting in thunderstorms during certain times of the year? A. ITCZ B. Monsoons C. Sea breeze D. Land breeze 27. Which breeze describes when warm air over the sea rises and cool air from the land takes its place? A. Sea breeze C. Sealand breeze B. Land breeze D. Landsea breeze 28. Which breeze describes when warm air over the land rises and cool air from the sea takes its place? A. Sea breeze C. Sealand breeze B. Land breeze D. Landsea breeze 29. Which accounts for the occurrence of land and sea breezes? A. radiation C. conduction B. convection D. weather system 30. Which statement is CORRECT about the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)? A. It is also known as the Polar Convergence Zone. B. It is a zone of convergence where the trade winds meet. C. ITCZ shifts only between 50° to 75° of latitude north or south of the equator D. It is a zone between the eastern and southern hemispheres where winds meet.
16. Which of the following human activities contributes the MOST to carbon dioxide emission in the atmosphere? A. Transportation B. Domestic and personal activities C. Agricultural and livestock raising D. Electricity production and industrial manufacturing 17. Which of the following human activities help conserve the atmosphere? A. Children are planting trees B. People are burning waste products. C. People throw their garbage in rivers and canals. D. People are using oil gasoline-powered vehicles. 18. What is the WORST effect of too much emission of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere? A. Air pollution C. Global warming B. Climate change D. Greenhouse effect 19. What is the most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere? A. Argon C. Nitrogen B. Oxygen D. Carbon dioxide 20. In which layer of the atmosphere ozone can be found? A. Troposphere C. Mesosphere B. Stratosphere D. Thermosphere 21. Which statement is correct about the Greenhouse Effect? A. It makes the Earth cooler. B. It keeps all the heat within the Earth. C. It absorbs the radiation released by the Sun. D. It is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface. 22. Why is the presence of ozone above the troposphere important for the survival of living things on earth? A. It warms Earth's surface. B. It helps in cloud formation. C. It makes jet flying more comfortable. D. It offers protection from the Sun's harmful UV rays 23. What is the region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than the surrounding areas? A. Low-pressure area C. Southwest monsoon D. Northeast monsoon B. High-pressure area 24. What is a cool and dry wind from Siberia carrying cold weather conditions and could bring rains over the eastern section of the country? A. Low-pressure area C. Southwest monsoon D. Northeast monsoon B. High-pressure area 25. Which of the following statements is the effect of Southwest monsoon on the western part of the country? A. It brings heavy rains to most of the eastern part of the country from June to September. B. It brings heavy rains to most of the western part of the country from June to September. C. It brings cold weather to most of the eastern part of the country from June to September. D. It brings cold weather to most of the western part of the country from June to September. 26. What do you call a weather phenomenon where winds in the tropics meet, rise and form clouds, resulting in thunderstorms during certain times of the year? A. ITCZ B. Monsoons C. Sea breeze D. Land breeze 27. Which breeze describes when warm air over the sea rises and cool air from the land takes its place? A. Sea breeze C. Sealand breeze B. Land breeze D. Landsea breeze 28. Which breeze describes when warm air over the land rises and cool air from the sea takes its place? A. Sea breeze C. Sealand breeze B. Land breeze D. Landsea breeze 29. Which accounts for the occurrence of land and sea breezes? A. radiation C. conduction B. convection D. weather system 30. Which statement is CORRECT about the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)? A. It is also known as the Polar Convergence Zone. B. It is a zone of convergence where the trade winds meet. C. ITCZ shifts only between 50° to 75° of latitude north or south of the equator D. It is a zone between the eastern and southern hemispheres where winds meet.
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN:9780134746241
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Chapter1: The Study Of Minerals
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1LR
Related questions
Question
100%

Transcribed Image Text:16. Which of the following human activities contributes
the MOST to carbon dioxide emission in the atmosphere?
A. Transportation
B. Domestic and personal activities
C. Agricultural and livestock raising
D. Electricity production and industrial manufacturing
17. Which of the following human activities help conserve
the atmosphere?
A. Children are planting trees
B. People are burning waste products.
C. People throw their garbage in rivers and canals.
D. People are using oil gasoline-powered vehicles.
18. What is the WORST effect of too much emission of
carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
A. Air pollution
C. Global warming
D. Greenhouse effect
B. Climate change
19. What is the most abundant gas in the Earth's
atmosphere?
A. Argon
C.
Nitrogen
B. Oxygen
D. Carbon dioxide
20. In which layer of the atmosphere ozone can be found?
A. Troposphere
C. Mesosphere
B. Stratosphere
D. Thermosphere
21. Which statement is correct about the Greenhouse
Effect?
A. It makes the Earth cooler.
B. It keeps all the heat within the Earth.
C. It absorbs the radiation released by the Sun.
D. It is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface.
22. Why is the presence of ozone above the troposphere
important for the survival of living things on earth?
A. It warms Earth's surface.
B.
It helps in cloud formation.
C. It makes jet flying more comfortable.
D. It offers protection from the Sun's harmful UV rays
23. What is the region where the atmospheric pressure is
lower than the surrounding areas?
A. Low-pressure area
C. Southwest monsoon
D. Northeast monsoon
B. High-pressure area
24. What is a cool and dry wind from Siberia carrying cold
weather conditions and could bring rains over the eastern
section of the country?
A. Low-pressure area
C. Southwest monsoon
D. Northeast monsoon
B. High-pressure area
25. Which of the following statements is the effect of
Southwest monsoon on the western part of the country?
A. It brings heavy rains to most of the eastern part of the
country from June to September.
B. It brings heavy rains to most of the western part of the
country from June to September.
C. It brings cold weather to most of the eastern part of the
country from June to September.
D. It brings cold weather to most of the western part of the
country from June to September.
26. What do you call a weather phenomenon where winds
in the tropics meet, rise and form clouds, resulting in
thunderstorms during certain times of the year?
A. ITCZ
C. Sea breeze
B. Monsoons
D. Land breeze
27. Which breeze describes when warm air over the sea
rises and cool air from the land takes its place?
A. Sea breeze
C. Sealand breeze
B. Land breeze
D. Landsea breeze
28. Which breeze describes when warm air over the land
rises and cool air from the sea takes its place?
A. Sea breeze
C. Sealand breeze
B. Land breeze
D. Landsea breeze
29. Which accounts for the occurrence of land and sea
breezes?
C. conduction
A. radiation
B. convection
D. weather system
30. Which statement is CORRECT about the
Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)?
A. It is also known as the Polar Convergence Zone.
B. It is a zone of convergence where the trade winds meet.
C. ITCZ shifts only between 50° to 75° of latitude north or
south of the equator
D. It is a zone between the eastern and southern
hemispheres where winds meet.

Transcribed Image Text:31. What effect does the tilting of the earth have?
39. When it is summer in the southern hemisphere, which of the
A. When the earth is tilted away from the sun we have the following best describes the tilting of the earth in the northem
day.
B. When the earth is tilted away from the sun we have the hemisphere?
A. Towards the sun
night.
B. Away from the sun
C. It changes the angle that the sun strikes the earth in
different land areas.
C. Towards or away from the sun
D.
D. Neither toward or away from the moon
It causes the earth to be farther away from the sun at
different times of the year.
40. Which part of the earth experiences summer in December
and colder in June?
32. Earth's seasons are caused by which of the following?
A The varying amount of sunspot activity.
A. Northern Hemisphere since the sun is tilted towards itin
June and December.
B. The rotation of the earth during a 24-hour day.
The earth's orbit about the sun is an eclipse rather
than a circle.
C.
B. Northern Hemisphere because it receives direct rays
from the sun in December and less in June.
D. The tilt of the earth's axis of rotation relative to the
path as Earth revolves around the Sun.
C. Southern Hemisphere because it receives direct rays
from the Sun in December and lesser solar energy in
June.
33. Which motion do the arrows in the diagram represent?
D. Both southern and Northern Hemisphere because they
receive equal rays directed from the Sun in December
and June.
41. What causes day and night?
A. The sun goes around the earth.
B. The earth orbits the sun.
C. The earth rotates or spins every 24 hours.
D. The moon rises causing night time
A Sun's rotation
C. Sun's revolution
D. Earth's revolution
42. As you go to the top of the mountain, what happens to the
temperature?
B. Earth's rotation
A. The temperature goes up and down.
34. What do direct "rays mean"?
B. The temperature increases.
A. The rays of the sun hit the ground at 30°.
C. The temperature decreases.
B. The rays of the sun hit the ground at 60°.
D. Nothing happens to the temperature
C. The rays of the sun hit the ground at 90°.
D. The rays of the sun hit the ground at 1200°.
43. Which of the following statements is true?
35. How long does it take to make one revolution around the
sun?
A. Places located at high latitude receive less sunlight than
places at low latitude.
B.
Places located at low lastude receives less sunlight than
A 12 hours
C. 1 month
D. 365 days
places at high latitude
B. 24 hours
C.
Places located at high latitude receive more sunlight
than places at low latitude.
36. Which of the following shows how the earth is tilted as it
rotates on its axis?
D.
Places at high and low latitude receive the same amount
of sunlight.
A 20.5* B. 23.5*
C. 25.5 D. 30.5*
37. Why do seasons change in the Philippines?
44. How is the length of daytime related to the amount of
solar energy?
A. The sun is directed to the southern hemisphere only.
B. The sun is somehow tited to both the northern and
southern hemisphere.
A. The longer the daytime, the lower the amount of energy
received.
B.
C. Season changes because the earth is stationary, always
directing its ways to the Northem Hemisphere.
The shorter the length of daytime, the lesser the amount
of energy received.
C.
The shorter the length of daytime, the higher the amount
of energy is received.
D. Seasons change because direct rays of the sun shift
from one hemisphere to the other as the Earth goes
around the sun.
D. The longer the daytime, the higher the amount of energy
received.
38. In the month of June which hemisphere receives direct rays 45. Why do people in the Northern Hemisphere experience
from the sun?
longer days and shorter nights in June ?
1. Northern Hemisphere
A. The sun shines directly on the equator.
II Southern Hemisphere
B. The earth wobbles on its axis.
III. Northem and Southern Hemisphere
C. The earth's axis tilts towards the sun.
D. The earth rotates on its axis.
C. Ill only
D. I, II, and Ill
A. I only
B. II only
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Answer the following except 58, 59 & 51.
Transcribed Image Text:D. When the sun is on the opposite side of the
Earth and the moon.
56. If you were outside during a total solar eclipse,
what would it look like?
A. Like the Sun is setting in the west
B. Like the Moon had disappeared entirely
C. Like day had suddenly become night
D. Like the entire sky had turned orange
57. What factors limit the number of eclipses per
year?
A. Distance between the moon and the Earth.
B. Tilt of the moon's orbit around the Earth.
C. Distance between the Earth and the Sun.
D. Tilt of the Earth's axis of rotation
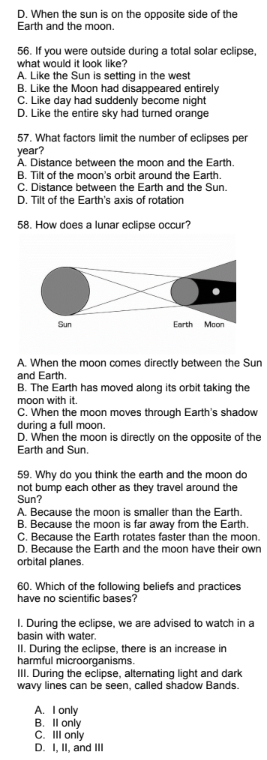
58. How does a lunar eclipse occur?
Sun
Earth Moon
A. When the moon comes directly between the Sun
and Earth.
B. The Earth has moved along its orbit taking the
moon with it.
C. When the moon moves through Earth's shadow
during a full moon.
D. When the moon is directly on the opposite of the
Earth and Sun.
59. Why do you think the earth and the moon do
not bump each other as they travel around the
Sun?
A. Because the moon is smaller than the Earth.
B. Because the moon is far away from the Earth.
C. Because the Earth rotates faster than the moon.
D. Because the Earth and the moon have their own
orbital planes.
60. Which of the following beliefs and practices
have no scientific bases?
1. During the eclipse, we are advised to watch in a
basin with water.
II. During the eclipse, there is an increase in
harmful microorganisms.
III. During the eclipse, alternating light and dark
wavy lines can be seen, called shadow Bands.
A. I only
B. II only
C. III only
D. I, II, and III
Transcribed Image Text:46. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes
through the Earth's shadow. A lunar eclipse can
only occur during a
A. full moon
B. new moon
first quarter moon
D. last quarter moon
47. During the solar eclipse, the Moon is positioned
between the Earth and the Sun. During which
phase of the moon does a solar eclipse occur?
A. full
C. crescent
D. gibbous
B. new
48. What kind of eclipse do we see when the moon
is entirely within the Earth's umbral shadow?
C. Total Lunar
Partial Lunar
B. Total Solar
D. Partial Solar
49. Which of the following pictures shows the
phase of the Moon when a solar eclipse occurs?
A.
B.
D.
50. A total lunar eclipse will occur when the moon
moves into the
A. umbra of the earth
B. umbra of the moon
C. penumbra of the earth
D. penumbra of the moon
51. A lunar eclipse will occur when the line-up is
A. Sun-Earth-Moon
C. Earth-Sun-Moon
D. Sun-Moon-Earth
B. Moon-Sun-Earth
52. Below is an image of a partial solar eclipse as
seen by an observer on Earth.
Which part of the shadow do you think is the
observer watching?
Key
Moon
Sun
A. Penumbra of the Moon
B. Penumbra of the Earth
C. Between the umbra and penumbra of the Moon
D. Between the umbra and penumbra of the Earth
53. The diagram below shows the Moon at four
positions in its orbit around Earth.
Sunlight
An observer on Earth could see a lunar eclipse
when the Moon is at position
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
54. The diagram below shows the relative positions
of the Sun, the Moon and Earth when an eclipse
was observed on Earth. Positions X and Y are
locations on Earth's surface. Which statement
correctly describes the type of eclipse that was
occurring and the position on Earth where this
eclipse was observed?
Earth
Moon
Sunlight
A. A total solar eclipse was observed in position X
B. A total solar eclipse was observed from position
Y
C. A total lunar eclipse was observed from position
X
D. A total lunar eclipse was observed from position
Y
55. How does a solar eclipse occur?
Earth
SUN
Moon
A. When the shadows of Earth and moon are cast
in space.
B. When the moon comes directly between the Sun
and the Earth.
C. When the shadows of the moon come and Earth
is neither too high nor too low.
Solution
Recommended textbooks for you

Applications and Investigations in Earth Science …
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134746241
Author:
Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:
PEARSON

Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134041360
Author:
Greg Carbone
Publisher:
PEARSON

Environmental Science
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781260153125
Author:
William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Applications and Investigations in Earth Science …
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134746241
Author:
Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:
PEARSON

Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134041360
Author:
Greg Carbone
Publisher:
PEARSON

Environmental Science
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781260153125
Author:
William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Earth Science (15th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134543536
Author:
Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:
PEARSON

Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781337569613
Author:
G. Tyler Miller, Scott Spoolman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Geology
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781259916823
Author:
Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, Lisa
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,